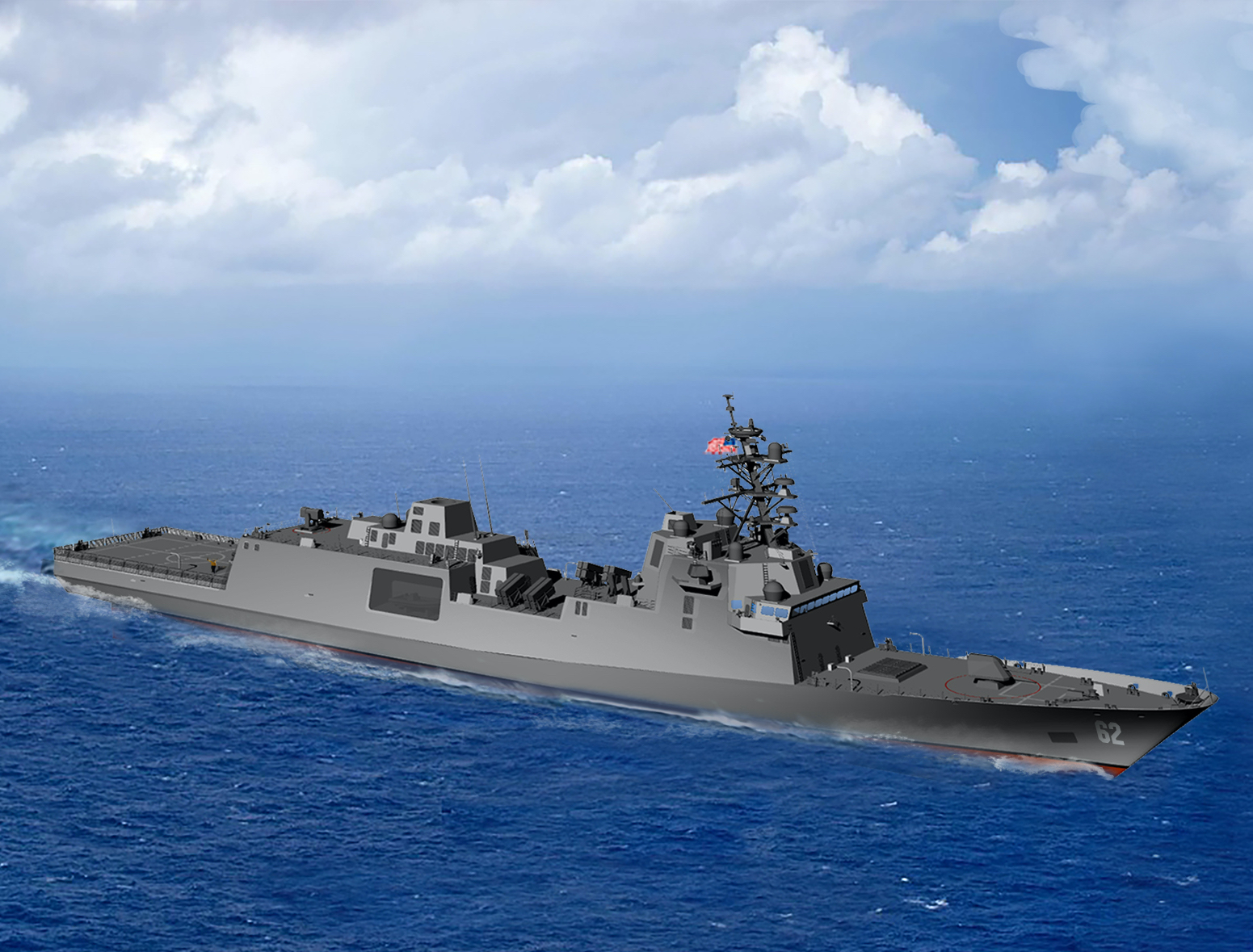
McFREMM - Americans will settle the FFG(X) program
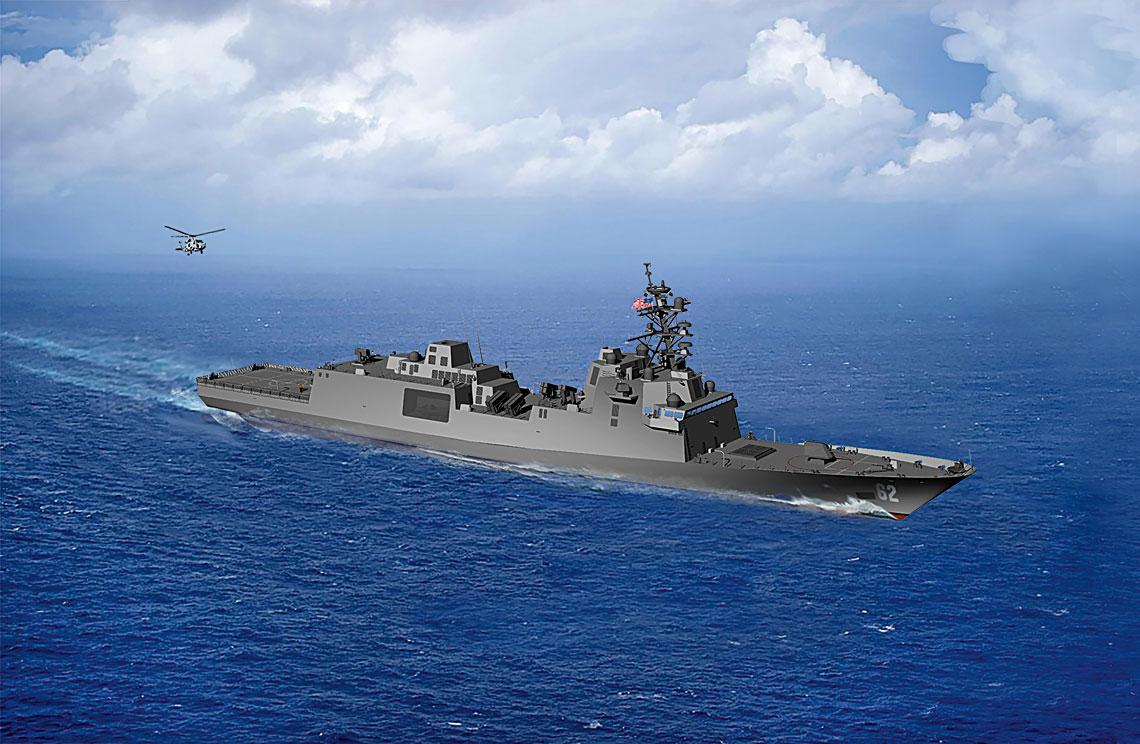

Visualization of FFG(X) based on the design of the Italian frigate FREMM. The differences are clearly visible and mainly relate to the shape of the upper tiers of superstructures, on which three antennas of the AN / SPY-6 (V) 3 station are installed, a new mast, similar to the design known from the Arleigh Burke destroyers, rocket and artillery weapons, were placed.
On April 30, the US Department of Defense completed an international tender for the selection of an industrial enterprise that will design and build a new generation of missile frigates, known as FFG (X), for the US Navy. This program, so far eclipsed by the mass production of subsequent versions of the Arleigh Burke missile destroyers, is being carried out in a truly un-American style. The decision itself is surprising, since the basis for the design of the future FFG (X) platform will be the Italian version of the European multi-purpose frigate FREMM.
The FFG(X) decision, expected in the first half of this year, is the result of an express program - for today's realities. The tender for the design work on a new generation missile frigate was announced by the Ministry of Defense on November 7, 2017, and on February 16, 2018, contracts were signed with five applicants. Each of them received a maximum of $ 21,4 million to prepare the necessary documentation until the customer makes the final choice of platform. Due to operational needs, as well as costs, the Americans abandoned the development of a completely new installation. Participants had to base their concepts on existing structures.
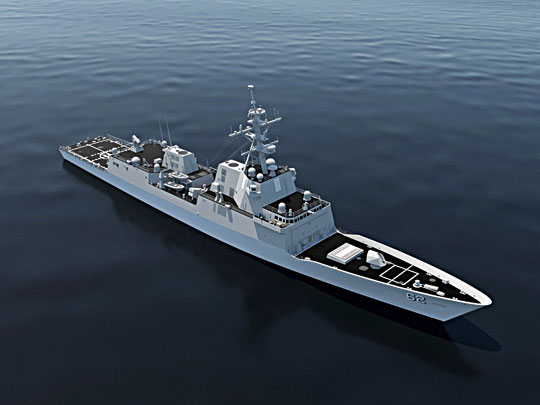

Another design of the Old Continent in the competition for the FFG (X) platform was the Spanish frigate Álvaro de Bazán, presented by General Dynamics Bath Iron Works. In this case, similar devices were used, which were the result of a combat system imposed by the customer.
The list of contenders includes the following teams:
- Austal USA (leader, shipyard), General Dynamics (combat systems integrator, design agent), platform - a modified project of a multi-purpose ship of the LCS Indenpedence type;
- Fincantieri Marinette Marine (leader, shipyard), Gibbs & Cox (design agent), Lockheed Martin (combat systems integrator), platform - FREMM-type frigate adapted to American requirements;
- General Dynamics Bath Iron Works (leader, shipyard), Raytheon (combat systems integrator), Navantia (project supplier), platform - Álvaro de Bazán-class frigate adapted to American requirements;
- Huntington Ingalls Industries (leader, shipyard), platform - modified large patrol ship Legend;
- Lockheed Martin (leader), Gibbs & Cox (design agent), Marinette Marine (shipyard), platform - modified Freedom-class LCS multi-purpose ship.
Interestingly, in 2018, the option of using German thyssenkrupp Marine Systems as a platform for the MEKO A200 project, as well as the British BAE Systems Type 26 (which in the meantime received orders in the UK, Canada and Australia) and Iver Huitfield Odense Maritime Technology with the support of the Danish government was considered. .
Competition in the FFG(X) program created an interesting situation. LCS program partners (Lockheed Martin and Fincantieri Marinette Marine) building the Freedom and its export variant of the Multi-Mission Surface Combatant for Saudi Arabia (now known as the Saud class) partly stood on opposite sides of the barricades. It is possible that this situation - not necessarily beneficial for the customer - was one of the factors that led to the removal of the Lockheed Martin team from the competition, which was announced on May 28, 2019. Officially, the reason for this step was to analyze the requirements of the Department of Defense, which could be met by a larger version of the Freedom-class ships. Despite this, Lockheed Martin did not lose its status as a sub-supplier in the FFG(X) program, as it was designated by the US Navy as a supplier of components or systems that were to be provided by new units.
Ultimately, by decision of the Ministry of Defense on April 30, 2020, the victory was awarded to Fincantieri Marinette Marine. The shipyard in Marinette, Wisconsin, a subsidiary of the Manitowoc Marine Group, was bought from it by the Italian shipbuilder Fincantieri in 2009. It signed a $795,1 million basic contract in April for the design and construction of a prototype frigate, the FFG(X). In addition, it includes options for another nine units, the use of which will increase the value of the contract to $5,5 billion. All work, including options, should be completed by May 2035. The construction of the first ship should begin in April 2022, and its commissioning is scheduled for April 2026.
Although one of them will benefit from the moment foreign companies are allowed to participate, the verdict of the Department of Defense turned out to be rather unexpected. In the history of the US Navy, there are few cases of exploitation of ships designed in other countries, but it is worth recalling that this is another example of US-Italian maritime cooperation in the near future. In 1991-1995, at the factories of Litton Avondale Industries in New Orleans and Intermarine USA in Savannah, 12 Osprey composite mine destroyers were built according to the project of Italian units of the Lerici type, developed by the Intermarine shipyard in Sarzana near La Spezia. They served until 2007, then half of them were disposed of, and sold in pairs to Greece, Egypt and the Republic of China.
Interestingly, none of the losing organizations chose to file a complaint with the US Government Accountability Office (GAO). This means that there is a high probability that the prototype construction schedule will be met. According to information from people associated with Secretary of the Navy (SECNAV) Richard W. Spencer canceled on November 24, 2019, the prototype unit should be called USS Agility and have tactical number FFG 80. However, we will have to wait. for official information on this subject.
New frigates for the US Navy
The order for a new type of escort ships from the US Navy is the result of analyzes that showed that the experiment with multi-purpose reconfigurable ships LCS (Littoral Combat Ships) was not particularly successful. Ultimately, according to the decision of the Ministry of Defense, their construction will be completed on 32 units (16 of both types), of which only 28 will be in service. The Americans are increasingly considering the premature withdrawal of the first four (Freedom, Independence, Fort Worth and Coronado , "relegated" to the role of units engaged in research and development) and offer them to allies, for example, through the procedure for excess defense articles (EDA).
The reason for this was the operational findings, which clearly stated that the LCS would not be able to independently carry out combat missions in the event of a full-scale conflict (expected, for example, in the Far East), and the growing number of Arleigh-Burke-class destroyers still needed to be supplemented. As part of the FFG (X) program, the US Navy plans to acquire 20 new-type missile frigates. The first two will be procured through FY2020-2021 budgets, and from 2022, the funding process should allow for the construction of a couple of units per year. According to the original plan, drawn up on the occasion of the publication of the draft budget for 2019, at the initial stage they are supposed to be delivered (alternately) to bases on the east and west coasts of the United States. In addition, at least two of them must be hosted in Japan.
The main task of the FFG(X) is to conduct independent operations in oceanic and coastal waters, as well as actions in national and allied teams. For this reason, their tasks include: protecting convoys, combating surface and underwater targets, and finally, the ability to eliminate asymmetric threats.
Frigates must bridge the gap between smaller and more limited LCSs and destroyers. They will take their place in the fleet structure after the last units of this class - the Oliver Hazard Perry class, which ended their service in the US Navy in 2015. It should be emphasized that the target plan involves an order of 20 units, but this year it is divided into two tranches of 10 each. Maybe this means that in the coming years the Ministry of Defense will announce a second tender to select another supplier of the remaining frigates of the new project or another contractor for ships to the base Fincantieri/Gibbs & Cox project.
FREMM more American
The April decision raised a fundamental question - what will the FFG(X) frigates look like? Thanks to the open policy of the American authorities, systematically publishing reports on the modernization programs of the armed forces, some information is already known to the public. In the case of the divisions described, the important document is the report of the US Congress dated May 4, 2020.
The FFG(X) frigates will be based on the solutions used in the Italian version of the FREMM type. They will have a length of 151,18 m, a width of 20 m and a draft of 7,31 m. The total displacement was determined at 7400 tons (in the case of the OH Perry type - 4100 tons). This means that they will be larger than the protoplasts, which measure 144,6 m and displace 6700 tons. Visualizations also show the absence of a bulb covering the hull sonar antenna. Probably because the main sonar systems will be towed. The architecture of the add-ons will also be different, which in turn is associated with the use of different electronic devices and systems, in particular the main radar station.
The drive system of the units will be configured with the CODLAG internal combustion system (combined diesel-electric and gas), which will allow a maximum speed of more than 26 knots when the gas turbine and both electric motors are turned on. In the case of using the economy mode only on electric motors, it should be over 16 knots. The tactical advantage of the CODLAG system is the low level of noise generated when driving on electric motors, which will be important when searching for and combating submarines. The cruising range at an economic speed of 16 knots was determined at 6000 nautical miles without refueling at sea.