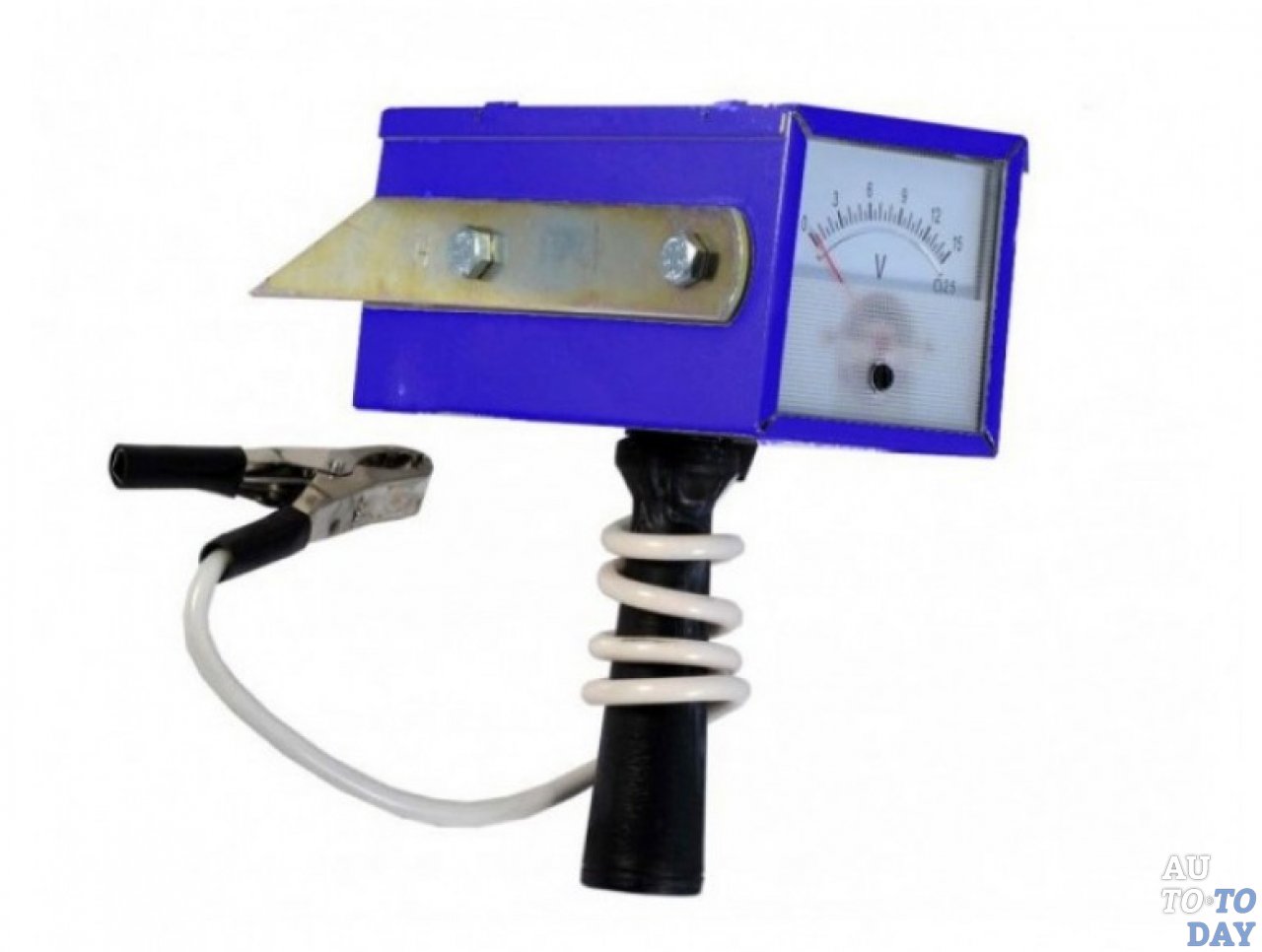
Load fork for checking the battery
Content
The car battery is an important element of the car's electrical equipment. Knowing its real state is absolutely necessary, especially in winter. A hidden battery malfunction can cause your battery to fail at the most inopportune moment. One of the devices by which you can diagnose the battery is the charging plug.
What is a load fork, what is it for?
Testing a car battery at idle will not give a complete picture of the condition of the battery, the battery must provide a large enough current, and for certain types of faults, the no-load test will work fine. When consumers are connected, the voltage of such a battery will drop below the permissible value.
Load modeling is not easy. It is necessary to have a sufficient number of resistors of the required resistance or incandescent lamps.
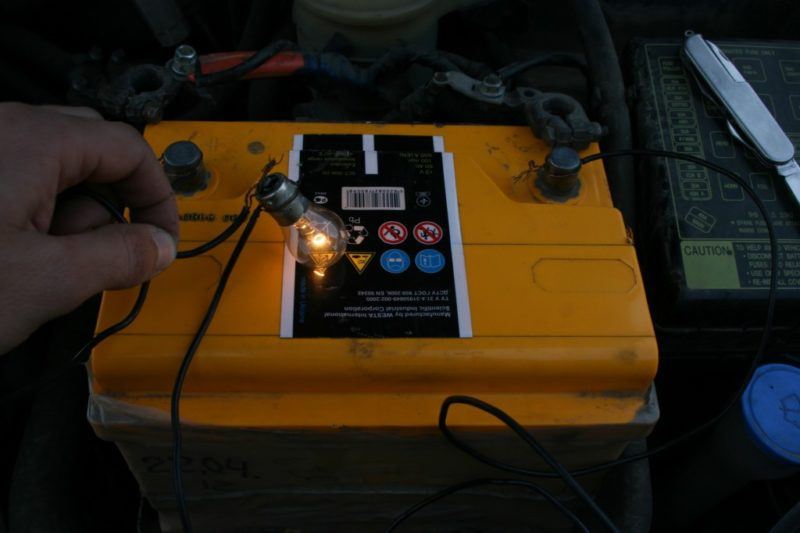

Charging the battery with a car incandescent lamp.
Imitation "in combat conditions" is also inconvenient and ineffective. For example, to turn on the starter and measure the current at the same time, you will need an assistant, and the current may be too large. And if you need to take multiple measurements in this mode, there is a risk of discharging the battery to a minimum. There is also the problem of setting the ammeter to break the power circuit, and DC current clamps are relatively rare and more expensive than conventional ones.

Multimeter with DC clamps.
Therefore, a convenient device for a more complete diagnosis of batteries is a charging plug. This device is a calibrated load (or several), a voltmeter and terminals for connecting to battery terminals.
The device and the principle of operation
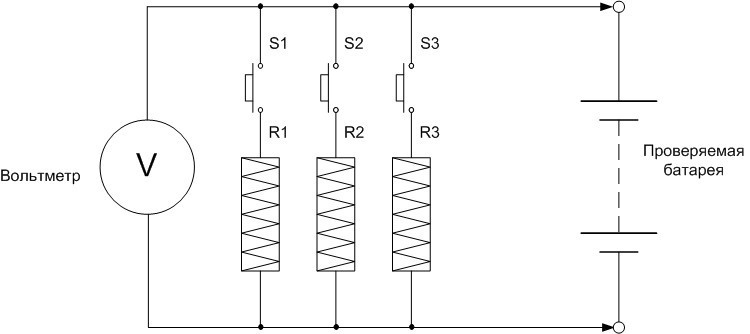
General scheme of the cargo fork.
In general, the socket contains one or more load resistors R1-R3, which can be connected in parallel with the tested battery using the appropriate switch S1-S3. If neither key is closed, the open circuit voltage of the battery is measured. The power dissipated by resistors during measurements is quite large, so they are made in the form of wire spirals with high resistivity. The plug can contain one resistor or two or three, for different voltage levels:
- 12 volts (for most starter batteries);
- 24 volts (for traction batteries);
- 2 volts for element testing.
Each voltage generates a different level of charging current. There may also be plugs with different levels of current per voltage (for example, the HB-01 device can set 100 or 200 amperes for a voltage of 12 volts).
There is a myth that checking with a plug is tantamount to a short circuit mode that disables the battery. In fact, the charging current with this type of diagnosis usually ranges from 100 to 200 amperes, and when starting the internal combustion engine - up to 600 to 800 amperes, therefore, subject to the maximum test time, there are no more modes that go beyond the battery.
One end of the plug (negative) in most cases is an alligator clip, the other - positive - is a pressure contact. For the test, it is important to make sure that the indicated contact is firmly attached to the battery terminal in order to avoid high contact resistance. There are also plugs, where for each measurement mode (XX or under load) there is a clamping contact.
Instructions for use
Each device has its own instructions for use. It depends on the design of the device. This document should be read carefully before using the plug. But there are also common points that are characteristic of all situations.
Battery preparation
It is recommended to fully charge the battery before starting measurements. If this is difficult, it is necessary that the power reserve level be at least 50%; so the measurements will be more accurate. Such a charge (or higher) is easily achieved during normal driving without connecting powerful consumers. After that, you should withstand the battery for several hours without charging by pulling the wire from one or both terminals (recommended 24 hours, but less is possible). You can test the battery without removing it from the vehicle.
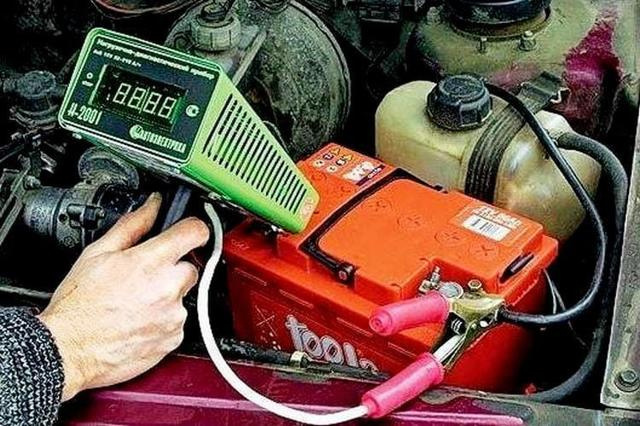

Checking the battery without disassembly from the car.
Checking with a load plug with a pointer voltmeter
The first measurement is taken at idle. The negative terminal of the alligator plug is connected to the negative terminal of the battery. The positive terminal is firmly pressed against the positive terminal of the battery. The voltmeter reads and stores (or records) the quiescent voltage value. Then the positive contact is opened (removed from the terminal). The charging coil is turned on (if there are several, the necessary one is selected). The positive contact is again firmly pressed against the positive terminal (possible sparks!). After 5 seconds, the second voltage is read and stored. Longer measurements are not recommended to avoid overheating of the load resistor.

Work with swept loading forks.
Table of indications
The battery status is determined by the table. Based on the results of measuring idling, the level of charge is determined. The voltage under load should correspond to this level. If lower, then the battery is defective.
As an example, you can disassemble measurements and tables for a battery with a voltage of 12 volts. Usually two tables are used: for measurements at idle and measurements under load, although they can be combined into one.
| Voltage, V | 12.6 and above | 12,3-12,6 | 12.1-12.3 | 11.8-12.1 | 11,8 or below |
| Charge level,% | one hundred | 75 | fifty | 25 | 0 |
This table checks the battery level. Let's say the voltmeter showed 12,4 volts at idle. This corresponds to a charge level of 75% (highlighted in yellow).
The results of the second measurement should be found in the second table. Let's say the voltmeter under load showed 9,8 volts. This corresponds to the same 75% charge level, and it can be concluded that the battery is good. If the measurement gave a lower value, for example, 8,7 volts, this means that the battery is defective and does not hold voltage under load.
| Voltage, V | 10.2 and above | 9,6 - 10,2 | 9,0-9,6 | 8,4-9,0 | 7,8 or below |
| Charge level,% | one hundred | 75 | fifty | 25 | 0 |
Next, you need to measure the open circuit voltage again. If it does not return to its original value, this also indicates problems with the battery.
If each battery bank can be charged, the failed cell can be calculated. But in modern car batteries of a non-separable design, this is not enough, which will give. It should also be understood that the voltage drop under load depends on the capacity of the battery. If the measurement values are "on the edge", this point must also be taken into account.
Differences in using a digital plug
There are sockets equipped with a microcontroller and a digital indicator (they are called "digital" sockets). Its power part is arranged in the same way as that of a conventional device. The measured voltage is displayed on the indicator (similar to a multimeter). But the functions of the microcontroller are usually reduced not only to the indication in the form of numbers. In fact, such a plug allows you to do without tables - the comparison of voltages at rest and under load is carried out and processed automatically. Based on the measurement results, the controller will display the diagnostic result on the screen. In addition, other service functions are assigned to the digital part: storing readings in memory, etc. Such a plug is much more convenient to use, but its cost is higher.
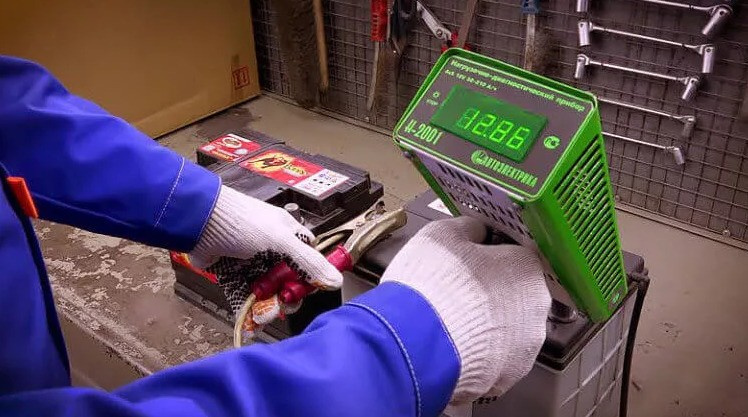

"Digital" charging plug.
Recommendations for selection
When choosing an outlet for checking the battery, first of all, pay attention to the operating voltage correctly. If you have to work from a battery with a voltage of 24 volts, a device with a range of 0..15 volts will not work, if only because the range of the voltmeter is not enough.
The operating current should be selected depending on the capacity of the tested batteries:
- for low-power batteries, this parameter can be selected within 12A;
- for car batteries with a capacity of up to 105 Ah, you must use a plug rated for current up to 100 A;
- devices used to diagnose powerful traction batteries (105+ Ah) allow a current of 200 A at a voltage of 24 volts (maybe 12).
You should also pay attention to the design of the contacts - they should be as convenient as possible for testing specific types of batteries.

How to restore an old car battery
As a result, you can choose between "digital" and conventional (pointer) voltage indicators. Digital readings are easier to read, but don't be fooled by the high accuracy of such displays; in any case, the accuracy cannot exceed plus or minus one digit from the last digit (in fact, the measurement error is always higher). And the dynamics and direction of voltage change, especially with a limited measurement time, are best read using dial indicators. Also they are cheaper.
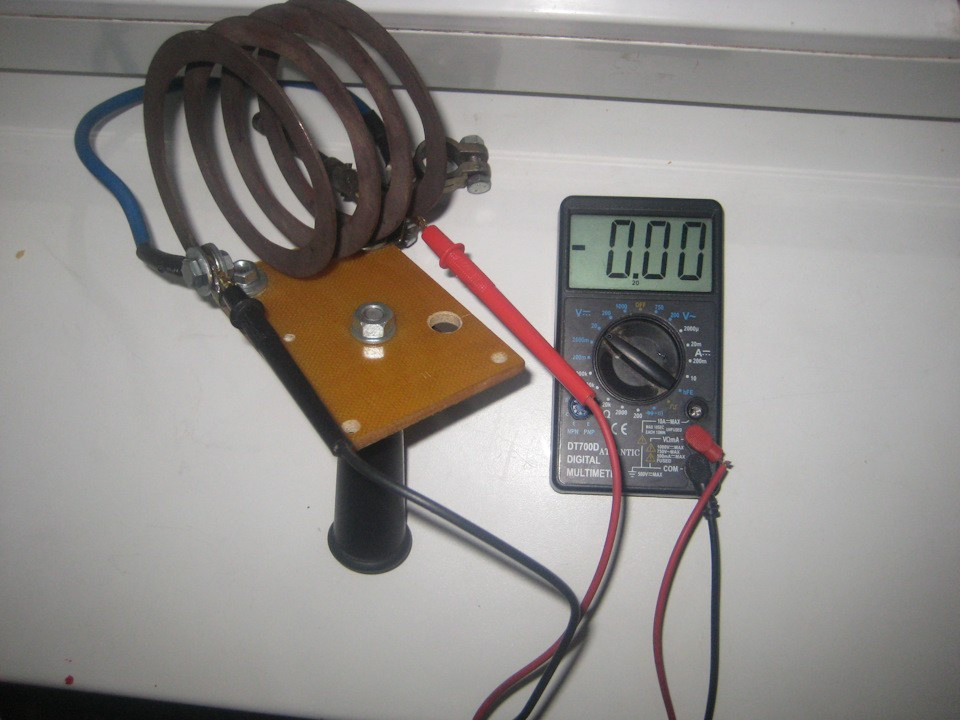

Homemade battery tester based on a multimeter.
In extreme cases, the plug can be made independently - this is not a very complicated device. It will not be difficult for a medium-skilled master to calculate and manufacture a device “for himself” (possibly, in addition to the service functions performed by the microcontroller, this will require a higher level or specialist assistance).
