Car battery voltage
Important indicators of the battery are its capacity, voltage and electrolyte density. The quality of work and functionality of the device depends on them. In a car, the battery supplies cranking current to the starter to start the engine and powers the electrical system when needed. Therefore, knowing the operating parameters of your battery and maintaining its performance is essential to keep your vehicle in good condition as a whole.
Battery voltage
First, let's look at the meaning of the term "voltage". In fact, this is the "pressure" of charged electrons, created by a current source, through a circuit (wire). Electrons do useful work (power light bulbs, aggregates, etc.). Measure the voltage in volts.
You can use a multimeter to measure battery voltage. Contact probes of the device are applied to the battery terminals. Formally, the voltage is 12V. The actual battery voltage should be between 12,6V and 12,7V. These figures refer to a fully charged battery.
These figures may vary depending on environmental conditions and testing time. Immediately after charging, the device can display 13 V - 13,2 V. Although such values \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbare considered acceptable. To get the correct data, you need to wait one to two hours after downloading.
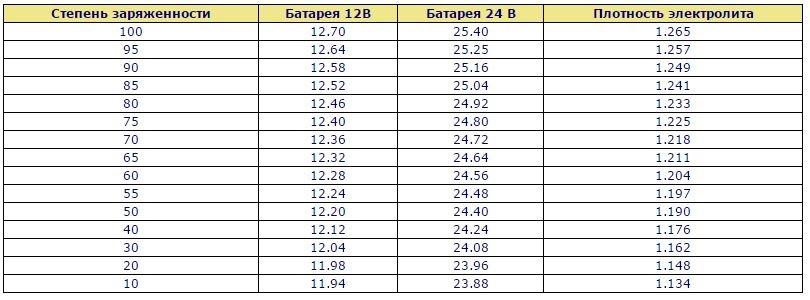
If the voltage drops below 12 volts, this indicates a dead battery. The voltage value and charge level can be compared according to the following table.
| Voltage, volt | Load degree, % |
| 12,6+ | one hundred |
| 12,5 | 90 |
| 12.42 | 80 |
| 12.32 | 70 |
| 12.20 | 60 |
| 12.06 | fifty |
| 11,9 | 40 |
| 11,75 | thirty |
| 11.58 | twenty |
| 11.31 | 10 |
| 10,5 | 0 |
As can be seen from the table, a voltage below 12V indicates a 50% discharge of the battery. The battery needs to be charged urgently. It must be taken into account that during the discharge process, the process of sulfation of the plates occurs. The density of the electrolyte drops. Sulfuric acid decomposes by participating in a chemical reaction. Lead sulfate forms on the plates. Timely charging starts this process in the opposite direction. If you allow deep discharge, it will be difficult to revive the battery. It will fail completely or lose its ability significantly.
The minimum voltage at which the battery can operate is 11,9 volts.
Loaded and unloaded
Even at low voltage, the battery is quite capable of starting the engine. The main thing is that after that the generator provides battery charging. When starting the engine, the battery supplies a lot of current to the starter and suddenly loses charge. If the battery is in order, the charge is gradually restored to normal values in 5 seconds.
The voltage of a new battery should be between 12,6 and 12,9 volts, but these values do not always reflect the actual condition of the battery. For example, at idle, in the absence of connected consumers, the voltage is within normal limits, and under load it drops sharply and the load is quickly consumed. It should be.
Therefore, the measurements are carried out under load. To do this, use a device such as a cargo fork. This test shows if the battery is charged or not.
The socket consists of a voltmeter, contact probes and a charging coil in a housing. The device creates a current resistance that is twice the capacity of the battery, simulating the starting current. For example, if the battery capacity is 50Ah, then the device charges the battery up to 100A. The main thing is to choose the right resistor. Above 100A you will need to connect two resistance coils to get accurate readings.
Load measurements are performed with a fully charged battery. The device is held for 5 seconds, then the results are recorded. Under load, the voltage drops. If the battery is good, it will drop to 10 volts and gradually recover to 12,4 volts or more. If the voltage drops to 9V or less, then the battery is not charging and is faulty. Although after charging it can show normal values \u12,4b\uXNUMXbof XNUMXV and higher.
Density of electrolyte
The voltage level also indicates the density of the electrolyte. The electrolyte itself is a mixture of 35% sulfuric acid and 65% distilled water. We have already said that during the discharge, the concentration of sulfuric acid decreases. The higher the discharge, the lower the density. These indicators are interrelated.
A hydrometer is used to measure the density of electrolytes and other liquids. In the normal state, when fully charged 12,6V - 12,7V and an air temperature of 20-25 ° C, the density of the electrolyte should be within 1,27g / cm3 - 1,28g / cm3.
The following table shows density versus charge level.
| Electrolyte density, g / cm3 | Charge level,% |
| 1,27 - 1,28 | one hundred |
| 1,25 | 95 |
| 1,24 | 90 |
| 1,23 | 80 |
| 1,21 | 70 |
| 1,20 | 60 |
| 1.19 | fifty |
| 1,17 | 40 |
| 1,16 | thirty |
| 1.14 | twenty |
| 1.13 | 10 |
The higher the density, the more resistant the battery to freezing. In regions with a particularly harsh climate, where the temperature drops to -30°C and below, the density of the electrolyte is increased to 1,30 g/cm3 by adding sulfuric acid. Density can be increased up to a maximum of 1,35 g/cm3. If it is higher, the acid will begin to corrode the plates and other components.
The graph below shows the hydrometer readings at different temperatures:
Hydrometer readings at different temperatures
In winter time
In winter, many drivers notice that as the temperature drops, it becomes more difficult to start the engine. The battery stops working at full capacity. Some motorists remove the battery overnight and leave it warm. In fact, when fully charged, the voltage does not drop, but even rises.
Negative temperature affects the density of the electrolyte and its physical state. When fully charged, the battery easily tolerates frost, but as the density decreases, the water becomes larger and the electrolyte may freeze. Electrochemical processes proceed more slowly.
At -10°C -15°C, a charged battery may show a charge of 12,9 V. This is normal.
At -30°C, the battery capacity is reduced to half of the nominal value. The voltage drops to 12,4 V at a density of 1,28 g/cm3. In addition, the battery stops charging from the generator already at -25°C.
As you can see, negative temperatures can significantly affect battery performance.
With proper care, a liquid battery can last 5-7 years. In the hot season, the charge level and electrolyte density should be checked at least once every two to three months. In winter, at an average temperature of -10°C, the load should be checked at least once every two to three weeks. In severe frost -25°C-35°C, it is recommended to recharge the battery once every five days, even on regular trips.