Purpose and principle of operation of the exhaust system
During the operation of the car engine, combustion products are formed that have a high temperature and are quite toxic. An exhaust system is provided in the design of the car to cool them and remove them from the cylinders, as well as to reduce the level of environmental pollution. Another function of this system is to reduce engine noise. The exhaust system is made up of a number of components, each with a specific function.
Exhaust system device
The main function of the exhaust system is to effectively remove exhaust gases from the engine cylinders, reduce their toxicity and noise level. Knowing what a car exhaust system is made of can help you better understand how it works and what causes potential problems. The design of a standard exhaust system depends on the type of fuel used, as well as on the applicable environmental standards. The exhaust system may consist of the following components:
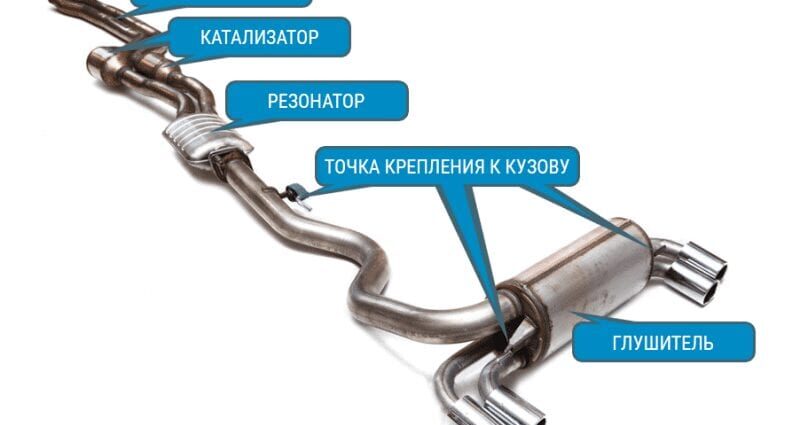
- Exhaust manifold - performs the function of gas removal and cooling (purging) of the engine cylinders. It is made of heat resistant materials as the average exhaust gas temperature is between 700°C and 1000°C.
- The front pipe is a complex-shaped pipe with flanges for mounting to a manifold or turbocharger.
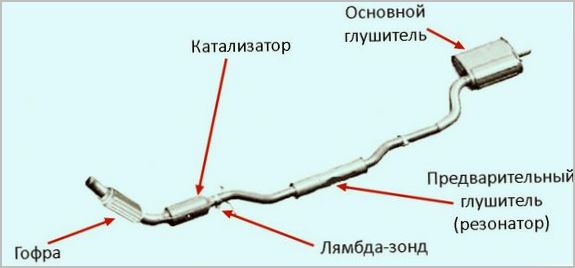
- The catalytic converter (installed in gasoline engines of the Euro-2 and higher environmental standard) removes the most harmful components CH, NOx, CO from the exhaust gases, turning them into water vapor, carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
- Flame arrester - installed in the exhaust systems of cars instead of a catalyst or a particulate filter (as a budget replacement). It is designed to reduce the energy and temperature of the gas stream exiting the exhaust manifold. Unlike a catalyst, it does not reduce the amount of toxic components in the exhaust gases, but only reduces the load on the mufflers.
- Lambda probe - used to monitor the level of oxygen in the exhaust gases. There may be one or two oxygen sensors in the system. On modern (in-line) engines with a catalyst, 2 sensors are installed.
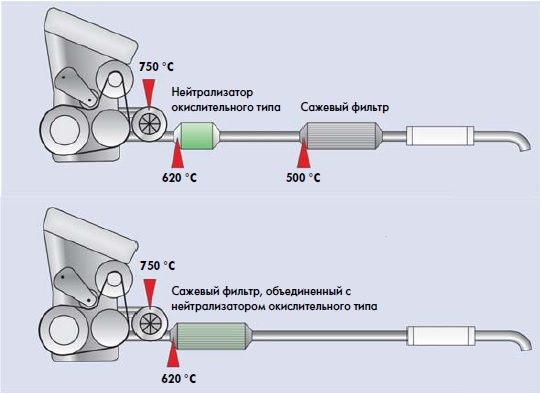
- Particulate filter (mandatory part of the exhaust system of a diesel engine) - removes soot from the exhaust gases. It can combine the functions of a catalyst.
- Resonator (pre-silencer) and main silencer - reduce exhaust noise.
- Piping - connects different parts of the car's exhaust system into one system.
How the exhaust system works
In the classic version for gasoline engines, the exhaust system of a car works as follows:
- The exhaust valves of the engine open and the exhaust gases with the remains of unburned fuel are removed from the cylinders.
- The gases from each cylinder enter the exhaust manifold, where they are combined into a single stream.
- Through the exhaust pipe, exhaust gases from the exhaust manifold pass through the first lambda probe (oxygen sensor), which registers the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. Based on this data, the electronic control unit regulates the fuel consumption and the air-fuel ratio.
- Then the gases enter the catalyst, where they react chemically with oxidizing metals (platinum, palladium) and reducing metal (rhodium). In this case, the working temperature of the gases must be at least 300 ° C.
- At the outlet of the catalyst, the gases pass through a second lambda probe, which makes it possible to assess the condition of the catalytic converter.
- The cleaned exhaust gases then enter the resonator and then the muffler, where the exhaust flows are converted (narrowed, expanded, redirected, absorbed), which reduces the noise level.
- The exhaust gases from the main muffler are already vented to the atmosphere.
The exhaust system of a diesel engine has some features:
- Exhaust gases leaving the cylinders enter the exhaust manifold. The exhaust temperature of a diesel engine ranges from 500 to 700°C.
- Then they enter the turbocharger, which produces boost.
- Exhaust gases pass through the oxygen sensor and enter the particulate filter, where harmful components are removed.
- Finally, the exhaust passes through the car's muffler and out into the atmosphere.
The development of the exhaust system is inextricably linked with the tightening of environmental standards for car operation. For example, from the Euro-3 category, the installation of a catalyst and a particulate filter for gasoline and diesel engines is mandatory, and their replacement with a flame arrester is considered a violation of the law.