New fighters for the US Air Force
In 1991, the US Air Force had 4 people. tactical combat aircraft with an average age of 8 years, at the moment there are 2 of them,
an average of 26 years. This is not a very good situation.
The world is changing again, as is the security environment. After many years of relative peace, when fanatical terrorists posed the greatest threat, statesmen have again entered the scene. A new cold war begins, this time a multipolar one - the USA, the Republic of Korea, Japan, Australia against the PRC and the USA, NATO against the Russian Federation, and there is such a stormy male friendship between Russia and China. .. 1991 tactical combat aircraft with an average age of 4000 years, and currently has 8 such aircraft with an average age of 2000 years. Today, the earlier decision not to place further orders for 26th generation fighters is considered a mistake.
The inter-cold war period, well known and accelerating today, did not promote the development of the United States Air Force (USAF). Throughout this period, systematic reductions were made, which led to the fact that the Americans today are armed with 1981 tactical combat aircraft, the PRC - 1810, the Russian Federation - 1420. True, among the Chinese aircraft there are 728 outdated J-7 fighters and 96 almost the same old J-8 fighters, but the rest, such as J-10, Su-27, J-11, Su-30 and J-16, are comparable to fourth-generation American machines.
F-16C Block 42 of 310 Squadron and F-35A of 61 Squadron, 56th Fighter Wing from Luke AFB, Arizona. The wing is operated by the Air Education and Training Command.
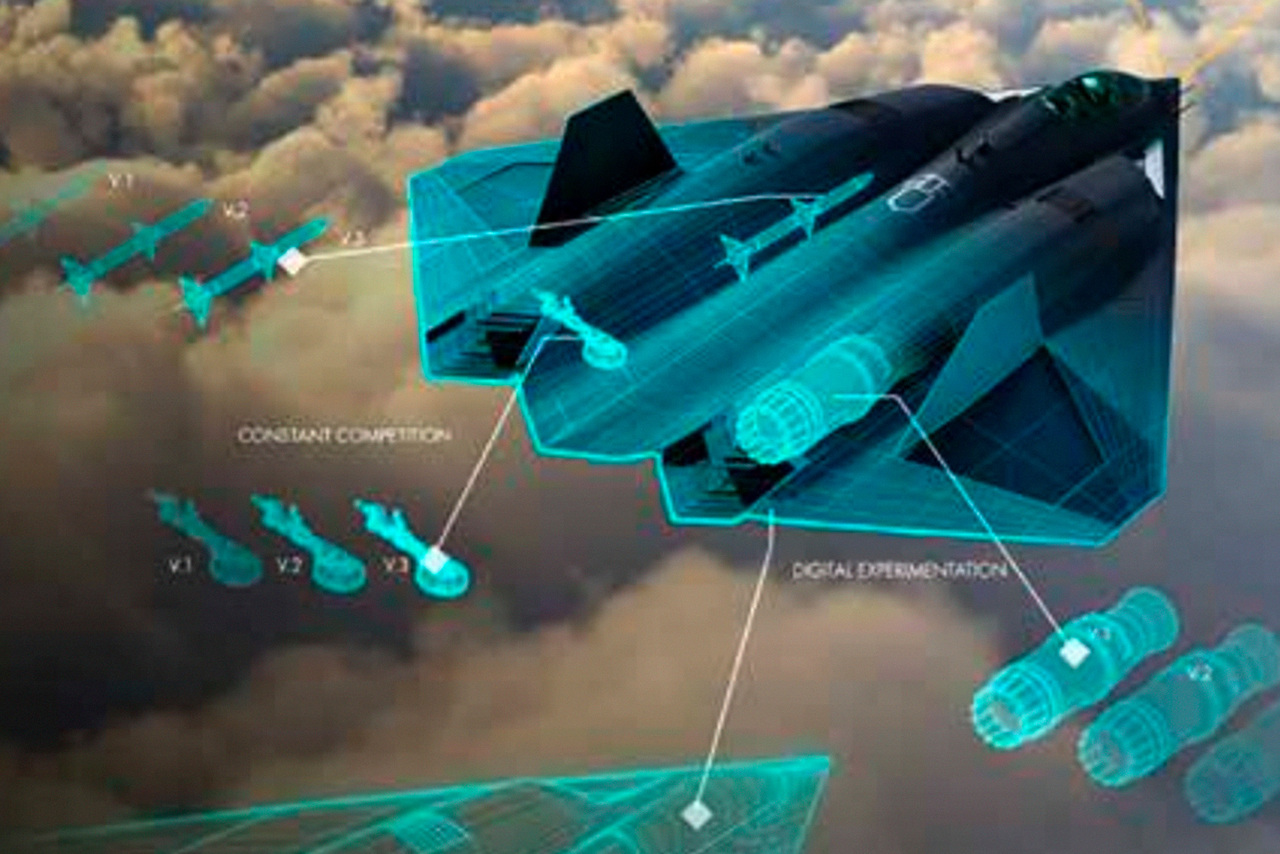
Therefore, the situation becomes quite alarming, because the Americans only have a qualitative advantage. But as it turns out, this is not always and not always provided by 5th generation fighters, mainly due to their subtle features, which, although theoretically a great advantage on the battlefield, at the same time introduce many form-related limitations. aircraft, and consequently, its aerodynamics, maneuverability, tactical range and the use of external suspension points, which reduces the carrying capacity and range of aviation weapons. Meanwhile, more and more advanced methods of detecting stealth aircraft are emerging.
Passive systems are being developed, as well as radar stations with a distributed antenna network (a network is created of transmitting and receiving radar antennas, which are fastened together into one device, while the pulse sent by one antenna can be received by another), because. as well as sufficiently accurate radars operating at lower frequencies, whose radiation-absorbing materials do not scatter as efficiently as the high frequencies characteristic of fire control systems of anti-aircraft missile systems and fighter radar sights. There are also alternative systems to stealth, such as swarms of drones designed to force anti-aircraft systems to wear out their missiles earlier so that the main strike groups can fly safely, and then attack radar stations for preliminary detection and fire control, as well as launchers of anti-aircraft guided missiles.
Another problem influencing changes in the fleet of tactical combat aircraft is the gradual transfer of many auxiliary functions (recognition and target designation, electronic warfare), as well as strike functions to unmanned aerial vehicles. The question still remains open, what part of the tasks will be performed by unmanned aerial vehicles in the coming years? What is a team in the form of a manned leader aircraft and one or more unmanned aerial vehicles to support or perform some basic tasks for aircraft? How can artificial intelligence help? And we also have independent combat operations of unmanned aerial vehicles, without “leadership” from manned aircraft. There is even talk of the cameras of unmanned fighter jets fighting aerial targets.
These are not easy dilemmas, because today it is extremely difficult to predict the long-term development of military aircraft in an era of crazy development of information technology, cyber-combat (attacks on aircraft systems and unmanned aerial vehicles using computer viruses; this is something completely new that ships need to be immunized, at the same time equipping them the same capabilities in relation to anti-aircraft missile systems or enemy fighters), artificial intelligence, automation and robotization of the battlefield ...
Lockheed Martin F-16 Viper
The F-16 is still the main type of US Air Force fighter, although its share in the overall equipment of tactical combat aircraft is clearly declining. In operational formations, i.e. as part of three commands: Air Combat Command (ACC; 152 F-16C and 19 F-16D) in the USA, USAF in Europe (USAFE; 75 F-16C and 4 F-16D) and Pacific Air Force (PACAF; 121 F- 16C and 12 F-16D) only four air wings are fully equipped with F-16s: 35th Fighter Wing at Misawa Base in Japan (5th PACAF Air Force; 13th and 14th Fighter Squadrons, F-16 Block 50) , 8th Fighter Wing in Kunsan, Republic of Korea (7th PACAF Air Force, 35th and 80th Fighter Squadrons, F-16 Block 40), 20th Fighter Wing in Shaw, South Carolina (15th Aviation Army ACC, 55th, 77th and 79th Fighter Squadrons, F-16 Block 50) and the 31st Fighter Wing at Aviano, Italy (USAF 3rd Aviation Army, 510th and 555th Fighter Squadrons , F-16 Block 40)). The following single F-16 squadrons in the wing: 36th Fighter Squadron as part of the 51st Fighter Wing at Osan Base in the Republic of Korea (7th Air Force, F-16 Block 40), 18th Aggressor Squadron as part of 354th Airlift Wing at Eielson, Alaska (11th Air Force, F-16 Block 30), 64th Fighter Squadron with 57th Airlift Wing at Nellis, Nevada (15th Air Force, F-16 Block 32 ), 480th Fighter Squadron as part of the 52nd Fighter Wing at Spangdalem in Germany (3rd Air Army, F-16 Block 50). In total, there are 13 squadrons of F-16s in American combat aviation, equipped with “sixteen” single-seat F-16Cs and two-seat F-16Ds.
Two more units (wing and group) of F-16s are present in the Air Education and Training Command (83 F-16Cs and 51 F-16Ds). This is the 54th Fighter Group in Holloman, New Mexico with the 8th Fighter Squadron (F-16 Block 40), the 311th and 314th Fighter Squadrons (both F-16 Block 42) and the 56th Fighter air regiment at Luke Air Force Base in Arizona. - 309th Fighter Squadron (F-16 Block 25) and 310th Fighter Squadron (F-16 Block 42). In addition to the two squadrons not mentioned here, whose aircraft belong to Taiwan and Singapore, there are five more squadrons. There are only two squadrons left in Air Force Reserve Command - the 93rd Fighter Squadron of the 482nd Fighter Wing at Homestead Air Force Base in Florida, using the F-16 Block 30 and flying the same version of the 457th Fighter Squadron of the 301st Wing. . Hunting lodge in Fort Worth, Texas. In addition to the Air National Guard, the US Air Force maintains 20 F-16 squadrons.
