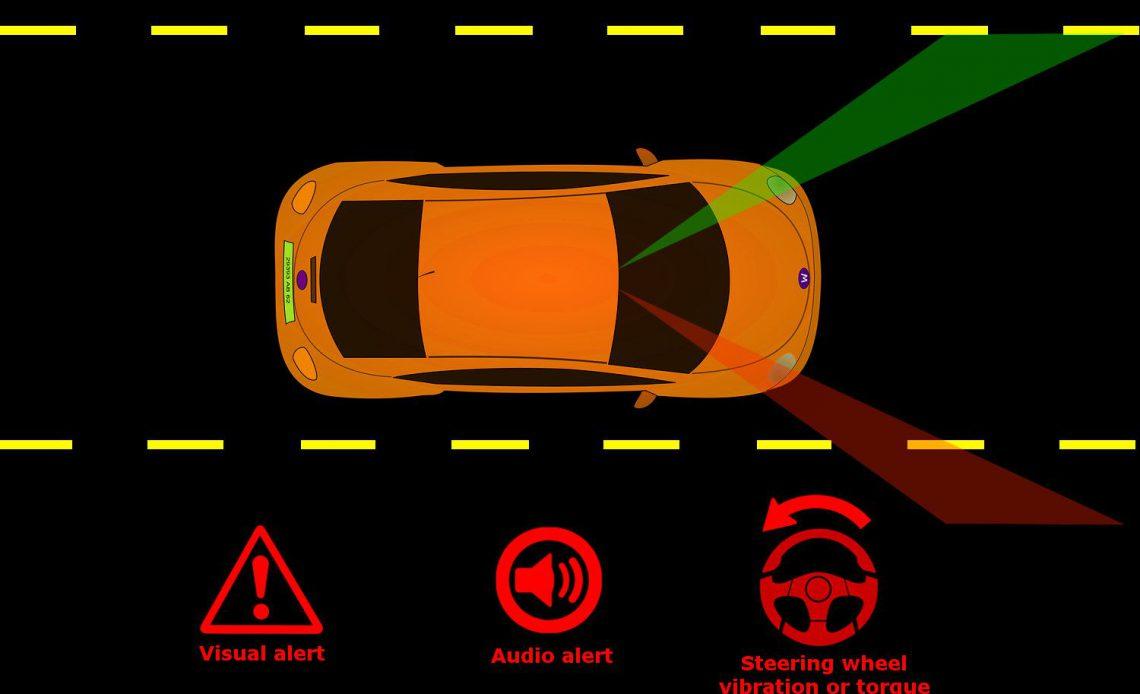
Lane Departure Warning Explanation

The technology is so noticeable that it is available even on the most affordable models.
If there is any doubt that autonomous cars will ever roam our road network, then the technology behind lane control systems should make even the most non-believers ready to greet our robot overlords.
Our vehicles can already accelerate, brake, drive through traffic, maintain a safe distance from the vehicle in front, park, read and recognize road signs, and warn us if they themselves need service, but the ability to follow and stay within road markings the lane, whether you're driving in straight lines or around corners, is the biggest piece of the offline puzzle that falls into place.
It started, as always, in technology-driven Japan back in 1992, when Mitsubishi introduced a rudimentary video camera system that could track lane markings and alert the driver if they sensed the car was moving out of the lane. Offered on non-Australian Debonair, it was the world's first lane departure warning system - a technology that is so prominent in the Australian new car market today that it's available on everything from the affordable Hyundai Sante Fe to the much less affordable Mercedes-Benz. AMG GLE 63.
This makes a future without drivers absolutely inevitable.
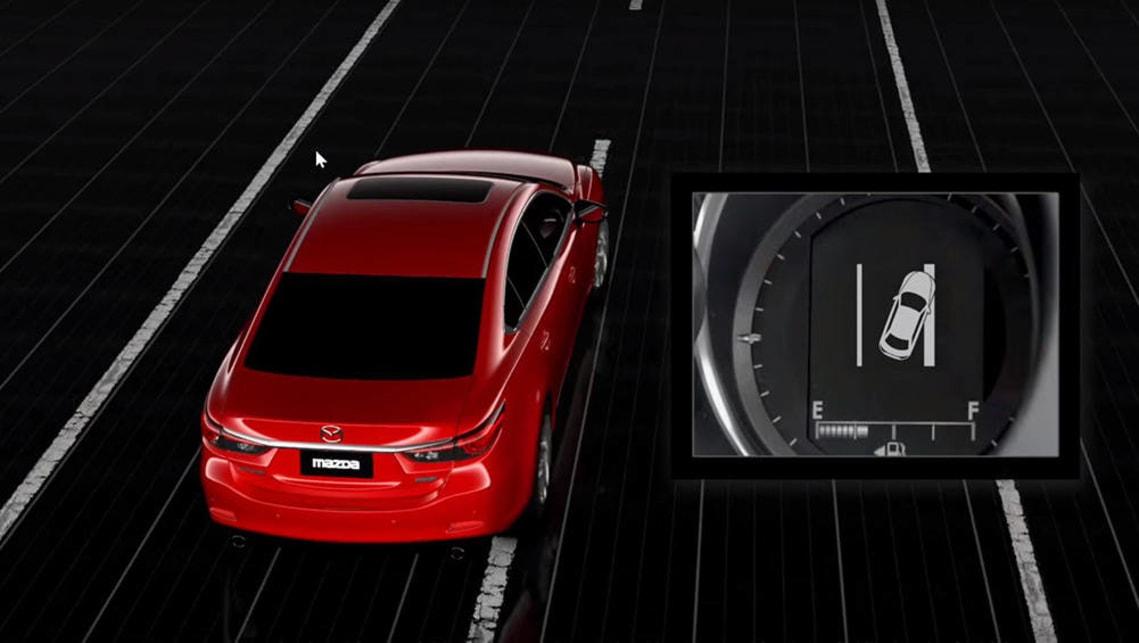
The technology behind the system hasn't changed much over the years: a camera, usually mounted above the windshield, scans the road ahead, recognizing dotted or straight lines to the left and right of your vehicle. . If you start to deviate from the lines or cross them without using the indicator, the warning part is triggered, be it a horn, a light on the dashboard, or a slight vibration on the steering wheel.
It will be another 12 years before the technology develops to the point where it can not only identify human error, but take steps to correct it. This breakthrough came in 2004 with the system installed on the Toyota Crown Majesta. He used the electric power steering motor to turn the wheel in the opposite direction to keep you on the straight and narrow road if he sensed you were moving out of your lane.
Also known as lane keep assist, lane keep assist, or lane keep assist, this technology is not without its detractors. Some say lane keeping is an essential skill for all drivers, and if you can't do it yourself, then you're better off on the bus. While others lament the sensitivity of the technology as they struggle with their own steering when their car incorrectly judges they are leaving the lane. However, most systems can be disabled, leaving you in complete control.
This technology took off again with the launch of Tesla's highly publicized Autopilot mode in 2015. Using 12 ultrasonic sensors located around the Model S sedan, Autopilot mode allows the car to take on a range of functions that once required a human driver, including steering. its speed, steering, brakes and even lane changes. While not a complete solution - you can't just jump into a car in your driveway and tell it to run, the system will only kick in under certain circumstances - a driverless future seems absolutely inevitable.
And when that happens, human drivers, like all legacy technology, will become redundant.
Do you greet our robot overlords? Tell us what you think in the comments below.

