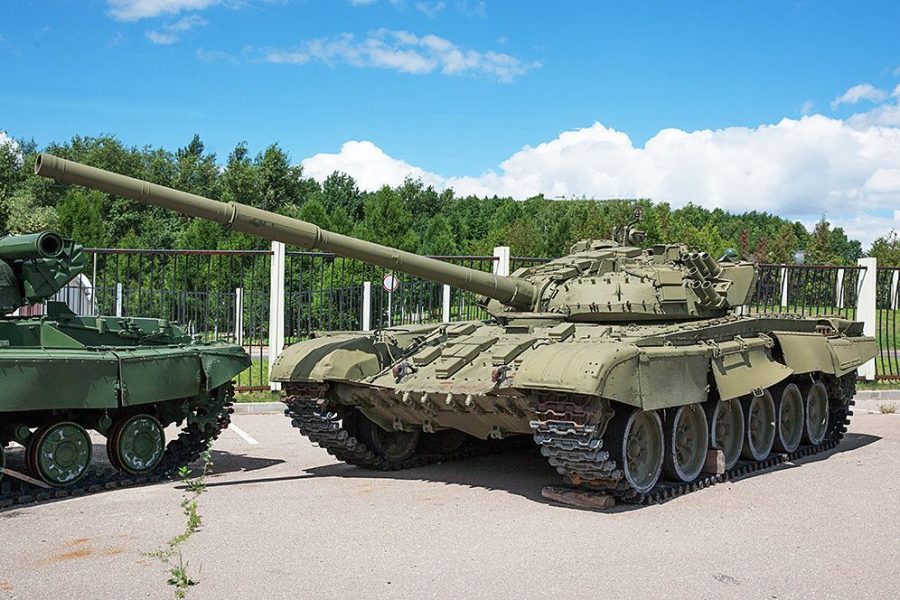
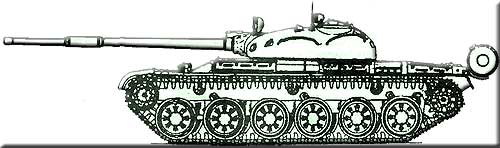
Main battle tank T-72
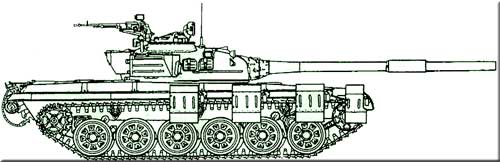
Main battle tank T-72Modifications to the T-72 main battle tank:
T-72 Tank
MBT T-72 was developed by Uralvagonzavod in Nizhny Tagil. Serial production of the tank is organized at a plant in Nizhny Tagil. From 1979 to 1985, the T-72A tank was in production. On its basis, an export version of the T-72M was produced, and then its further modification - the T-72M1 tank. Since 1985, the T-72B tank and its export version T-72S have been in production. Tanks of the T-72 series were exported to the countries of the former Warsaw Pact, as well as to India, Yugoslavia, Iraq, Syria, Libya, Kuwait, Algeria and Finland. On the basis of the T-72 tank, the BREM-1, the MTU-72 tank bridge layer, and the IMR-2 engineering barrier vehicle were developed and put into mass production. The history of the creation of the T-72 tankThe beginning of the process of creating the T-72 tank was laid by the decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR of August 15, 1967 “On equipping the Soviet Army with new T-64 medium tanks and developing capacities for their production”, in accordance with which it was planned to organize the serial production of T-64 tanks not only at the Kharkov Plant of Transport Engineering named after Malyshev (KhZTM), but also at other enterprises in the industry, including Uralvagonzavod (UVZ), where the T-62 medium tank was produced at that time. The adoption of this resolution was logically dictated by the development of Soviet tank building in the period of 1950-1960s. It was in those years that the top military-technical leadership of the country D.F. Ustinov, L.V. Smirnov, S.A. Zverev and P.P. Poluboyarov (marshal of the armored forces, from 1954 to 1969 - head of the armored forces of the Soviet Army) made an uncontested bet on the T-64 tank, developed in KB-60 (since 1966 - the Kharkov Design Bureau for Mechanical Engineering - KMDB) under the leadership of A. A. Morozov. Tank T-72 "Ural"
T-72 was adopted by the Soviet Army on August 7, 1973. The idea that A.A. Morozov, was to increase the level of the main tactical and technical characteristics of the tank without increasing its mass. A prototype tank, created in the framework of this idea - "object 20" - appeared in 430. On this machine, new technical solutions were applied, among which, first of all, it is necessary to include the installation of a two-stroke H-shaped engine 1957TD and the use of two small-sized five-speed gearboxes. These technical solutions made it possible to significantly reduce both the volume of the MTO and the entire reserved volume of the tank to unprecedentedly small values - 5 and 2,6 m3 respectively. In order to keep the tank's combat mass within 36 tons, steps were taken to lighten the chassis: small-diameter road wheels with internal shock absorption and aluminum alloy discs and shortened torsion bars were introduced. The weight savings obtained through these innovations made it possible to strengthen the armor protection of the hull and turret. From the very beginning of the tests of the “object 430”, the unreliability of the 5TD engine was revealed. The high thermal stress of the cylinder-piston group incorporated in its design, combined with increased resistance at the outlet, led to frequent disruptions in the normal functioning of the pistons and failure of the exhaust manifolds. In addition, it turned out that at the most probable air temperature (+25°C and below), the engine could not be started without preheating with a heater. A lot of design flaws were also revealed in the lightweight undercarriage of the tank. In addition, even at the design stage, the “object 430” began to lag behind the latest foreign models in terms of its performance characteristics. By 1960, considerable funds had already been spent on these works, and their termination would mean the recognition of the fallacy of all previous decisions. Just at this moment, A.A. Morozov presented the technical design of the tank "object 432". Compared to the “object 430”, it included many innovations, including: a 115-mm smooth-bore gun with a separate cartridge case; gun loading mechanism, which allowed to reduce the number of crew members to 3 people; combined armor of the hull and turret, as well as anti-cumulative side screens; boosted up to 700 hp two-stroke diesel 5TDF and much more. T-64 Tank
The tank entered service in 1969 as the T-64A medium tank. At the beginning of 1962, an experimental chassis of the "object 432" was manufactured. After the installation of the technological tower, sea trials began. The first complete tank was ready in September 1962, the second - on October 10th. Already on October 22, one of them was presented at the Kubinka training ground to the country's top leadership. At the same time, N.S. Khrushchev received assurances about the imminent start of mass production of the new tank, as it soon turned out to be unfounded. In 1962-1963, six prototypes of the "object 432" tank were manufactured. In 1964, a pilot batch of tanks was manufactured in the amount of 90 units. In 1965, another 160 cars left the factory floors.
The T-64 tank was produced for a short time - until 1969 - in 1963, work began on the tank "object 434". It was carried out almost in parallel with the fine-tuning of the “object 432”: in 1964 a technical project was completed, in 1966-1967 prototypes were made, and in May 1968, the T-64A tank, armed with a 125-mm D-81 cannon, was put into service . The decision of the Council of Ministers of the USSR of August 15, 1967 also referred to the release of a “reserve” version of the T-64 tank. It was needed because of the lack of capacity for the production of 5TDF engines in Kharkov, which could not provide the volume of production of T-64 tanks at other plants in peacetime and wartime. The vulnerability of the Kharkiv version of the power plant from a mobilization point of view was obvious not only to opponents, but also to supporters, including A.A. Morozov himself. Otherwise, it is impossible to explain the fact that the design of the “reserve” version was carried out by A.A. Morozov since 1961. This machine, which received the designation "object 436", and after some refinement - "object 439", was developed rather sluggishly. Nevertheless, in 1969, four prototypes of the “object 439” tank were manufactured and tested with a new MTO and a V-45 engine, an improved version of the V-2 family diesel engine. Tank T-64A (object 434)
Medium tank T-64A (object 434) model 1969 By the early 1970s, serious doubts had accumulated in the Ministry of Defense about whether it was worth producing T-64 tanks with a 5TDF engine at all. Already in 1964, this engine stably worked out 300 hours at the stand, but under operating conditions on a tank, the engine's service life did not exceed 100 hours! In 1966, after interdepartmental tests, a warranty resource of 200 hours was established, by 1970 it had increased to 300 hours. In 1945, the V-2 engine on the T-34-85 tank worked out about the same, and often more! But even these 300 hours the 5TDF engine could not stand it. During the period from 1966 to 1969, 879 engines were out of order in the troops. In the fall of 1967, during tests in the Belarusian Military District, the engines of 10 tanks collapsed in just a few hours of work: the Christmas tree needles clogged the air cleaning cyclones, and then the dust rubbed the piston rings. In the summer of next year, new tests had to be carried out in Central Asia and a new air purification system was introduced. Grechko in 1971, before accelerated military tests of fifteen T-64 tanks, told the Kharkovites:
“Somehow, at an armored training ground, I decided to look at this tank. Climbed into the fighting compartment. I did not like the automatic loader and stacking of shots in the turret. The shots were located vertically along the shoulder strap of the tower and seriously limited access to the driver. In case of injury or concussion, it would be quite difficult to evacuate him from the tank. Sitting in the driver's seat, I felt like I was in a trap: there was metal all around, the ability to communicate with other crew members was very difficult. Arriving home, I instructed the design bureaus of Kovalev and Bystritsky to develop a new automatic loader for the T-62 tank. Comrades reacted to the work with great interest. The possibility of stacking shots in two rows, under a rotating floor, was found, which improved access to the driver and increased the survivability of the tank during shelling. By the end of 1965, we had completed the development of this machine, but it did not make sense to introduce it, since by that time the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR had issued a decree on putting the Kharkov tank into production with us ... Since the Kharkovites could not bring their tank to serial production conditions , we decided as soon as possible to install a 125-mm gun with an automatic loader worked out for us for a 115-mm gun in the T-62 tank. In terms of external dimensions, both guns were the same. Usually, we timed all our initiative works to coincide with some anniversaries. This work was dedicated to the 50th anniversary of the October Revolution. Soon, one prototype of the T-62 tank with a 125-mm gun was made. Experienced tank "object 167" 1961
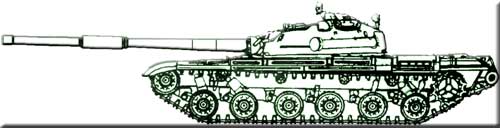
The chassis of this vehicle served as the basis for the creation of the undercarriage of the T-72 tank. Together with the engine design bureau of the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant, led by I.Ya. Trashutin, the possibility of forcing the engine of the V-2 family to a power of 780 hp was studied. due to boost. On one of the prototypes (“object 167”), a reinforced six-roller undercarriage was installed and tested. The role of "object 167" in the fate of the future "seventy-two" is very significant. The following were installed on this tank: a 700-horsepower V-26 diesel engine with a reinforced transmission, a new undercarriage (6 support and 3 support rollers on board) with increased smoothness, a new generator, a hydro-servo control system for transmission units and an anti-radiation lining. Since the introduction of these innovations increased the mass of the vehicle, in order to keep it within the limits of up to 36,5 tons, the armor protection had to be somewhat weakened. The thickness of the lower frontal hull plate was reduced from 100 to 80 mm, the sides - from 80 to 70 mm, the stern plate - from 45 to 30 mm. The first two tanks "object 167" were made in the fall of 1961. They successfully passed first full-scale factory and then field tests in Kubinka. The tank was recommended for adoption, but Deputy Minister of Defense Marshal V.I. Chuikov and Deputy Chairman of the State Committee for Defense Technology S.N. Makhonin gave him a generally unsatisfactory rating. In particular, a partial loss of interchangeability with the T-55 and T-62 tanks was noted as the main drawback. In the Nizhny Tagil Design Bureau, this reproach was taken seriously and they tried to create a car with greater continuity of the chassis. This is how the “object 166M” appeared. This machine differed from the serial T-62 mainly in the installation of the V-36F engine with an HP 640 power. and improved suspension. The undercarriage included five support and three support rollers on board. The track rollers were identical to those used on the “object 167”. Despite the fact that the speed of movement increased compared to the T-62, tests showed the futility of this version of the chassis. The advantage of the six-roller design became apparent. Neither the “object 167” nor the “object 166M” were up to the level of the “object 434” and could not be considered as a full-fledged alternative to the Kharkov tank. Only the “object 167M” or T-62B became such an alternative. The project of this tank was considered by the Scientific and Technical Council of the State Committee for Combating the War on February 26, 1964. The new car, announced by L.N. Kartsev as a modernization of a serial tank, differed significantly from the T-62. It had a hull and a turret with combined armor protection of the frontal projection, an “object 167” undercarriage, a 125-mm D-81 smoothbore gun with a “Rain” stabilizer, a carousel-type automatic loader, and a B-2 engine with a power of 780 hp. with a supercharger, improved radiators, air filters, fuel and oil systems, as well as reinforced transmission units. However, the meeting rejected the project for a new tank. Nevertheless, by the end of 1967, a number of components of the main battle tank were tested and tested at Uralvagonzavod. On one of the serial T-62 tanks, an automatic loader (the theme “Acorn”) was installed and tested, coupled with a 125-mm gun. This machine received the in-plant designation T-62Zh. The first sample of the tank "object 172" was made in the summer of 1968, the second - in September. They differed from the T-64A tank in a completely reconfigured fighting compartment, since the electro-hydro-mechanical loading mechanism of the T-64 tank was replaced by an electromechanical automatic loader with a pallet ejection mechanism, and the installation of the Chelyabinsk V-45K engine. All other components and assemblies were transferred from the Kharkov tank, or rather, they remained in place, since the first “172 objects” were converted “sixty-fours”. By the end of the year, both tanks passed a full cycle of factory tests and a run-in at the training ground of the Turkestan military district. The dynamic characteristics of the tanks were quite high: the average speed on the highway was 43,4-48,7 km / h, the maximum reached 65 km / h. Experienced tank
Experienced tank "object 172" 1968 Work with tanks "object 172" (a total of 20 units were manufactured) continued until the beginning of February 1971. By this time, the components and assemblies developed in Nizhny Tagil had been brought to a high level of reliability. The automatic loaders had one failure for 448 loading cycles, that is, their reliability approximately corresponded to the average survivability of the 125-mm D-81T gun (600 rounds with a caliber projectile and 150 with a sub-caliber projectile). The only problem of the “object 172” was the unreliability of the chassis “due to the systematic failure of hydraulic shock absorbers, road wheels, pins and tracks, torsion bars and idlers.” Then in the UVZ design bureau, which since August 1969 was headed by V.N. Venediktov, it was decided to use on the “object 172” the chassis from the “object 167” with rubber-coated road wheels of increased diameter and more powerful tracks with an open metal hinge, similar to the tracks of the T-62 tank. The development of such a tank was carried out under the designation "object 172M". The engine, boosted to 780 hp, received the B-46 index. A two-stage cassette air cleaning system was introduced, similar to that used on the T-62 tank. The mass of the “object 172M” increased to 41 tons. But the dynamic characteristics remained at the same level due to an increase in engine power by 80 hp, fuel tank capacity by 100 liters and track width by 40 mm. From the T-64A tank, only positively proven structural elements of the armored hull with combined and differentiated armor and transmission were retained. From November 1970 to April 1971, the “object 172M” tanks went through a full cycle of factory tests and then on May 6, 1971 were presented to the Ministers of Defense A.A. Grechko and the defense industry S.A. Zverev. By the beginning of summer, an initial batch of 15 vehicles was produced, which, together with the T-64A and T-80 tanks, went through many months of testing in 1972. After the end of the tests, a “Report on the results of military tests of 15 172M tanks manufactured by Uralvagonzavod in 1972” appeared. "1. The tanks passed the test, but the track life of 4500-5000 km is insufficient and does not provide the required tank mileage of 6500-7000 km without replacing the tracks. 2. Tank 172M (warranty period - 3000 km) and the V-46 engine - (350 m / h) worked reliably. During further tests up to 10000-11000 km, most of the components and assemblies, including the V-46 engine, worked reliably, but a number of serious components and assemblies showed insufficient resources and reliability. 3. The tank is recommended for adoption into service and mass production, subject to the elimination of identified shortcomings and verification of the effectiveness of their elimination before mass production. The scope and timing of improvements and inspections must be agreed between the Ministry of Defense and the Ministry of Defense Industry.” “Object 172M”
Experimental tank "object 172M" 1971 By a resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR of August 7, 1973, the “object 172M” was adopted by the Soviet Army under the name T-72 “Ural”. The corresponding order of the Minister of Defense of the USSR was issued on August 13, 1973. In the same year, an initial batch of 30 machines was produced. Back – Forward >> |

 • T-72 (1973) - basic sample;
• T-72 (1973) - basic sample;


 But all these were not serial tanks. In March 1963 and May 1964, the "object 432" was presented for state tests, but he did not pass them. Only in the fall of 1966 did the state commission consider it possible to put the tank into service under the designation T-64, which was formalized by a resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR of December 30, 1966. All 250 vehicles manufactured in 1964-1965 were decommissioned four years later.
But all these were not serial tanks. In March 1963 and May 1964, the "object 432" was presented for state tests, but he did not pass them. Only in the fall of 1966 did the state commission consider it possible to put the tank into service under the designation T-64, which was formalized by a resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR of December 30, 1966. All 250 vehicles manufactured in 1964-1965 were decommissioned four years later.
 As part of the modernization of serial tanks at the UVZ design bureau under the leadership of L.N. Kartsev, a prototype of the T-62 tank with a 125-mm D-81 cannon and a new autoloader, the so-called cabinless type, was developed and manufactured. L.H. Kartsev describes these works and his impressions of getting acquainted with the automatic loader of the T-64 tank
As part of the modernization of serial tanks at the UVZ design bureau under the leadership of L.N. Kartsev, a prototype of the T-62 tank with a 125-mm D-81 cannon and a new autoloader, the so-called cabinless type, was developed and manufactured. L.H. Kartsev describes these works and his impressions of getting acquainted with the automatic loader of the T-64 tank