P0068 MAP/MAF - Throttle Position Correlation
Content
OBD-II Trouble Code - P0068 - Data Sheet
MAP/MAF - Throttle Position Correlation
What does fault code 0068 mean?
This Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is a generic transmission code. It is considered universal as it applies to all makes and models of vehicles (1996 and newer), although the specific repair steps may differ slightly depending on the model.
General fault code P0068 refers to a problem with engine control. There is a mismatch between the sensors of the computer between the volumes of air entering the intake manifold.
The PCM relies on three sensors to indicate airflow volume to calculate fuel and timing tactics. These sensors include a mass air flow sensor, a throttle position sensor, and a manifold pressure (MAP) sensor. There are many sensors on the engine, but three are associated with this code.
The mass air flow sensor is located between the air cleaner and the throttle body. Its job is to signal the amount of air passing through the throttle body. To do this, a thin piece of resistance wire as thick as a hair is pulled through the inlet of the sensor.
The computer applies voltage to this wire to heat it up to a predetermined temperature. As the volume of air increases, more voltage is required to maintain the temperature. Conversely, as the air volume decreases, less voltage is required. The computer recognizes this voltage as an indication of the volume of air.
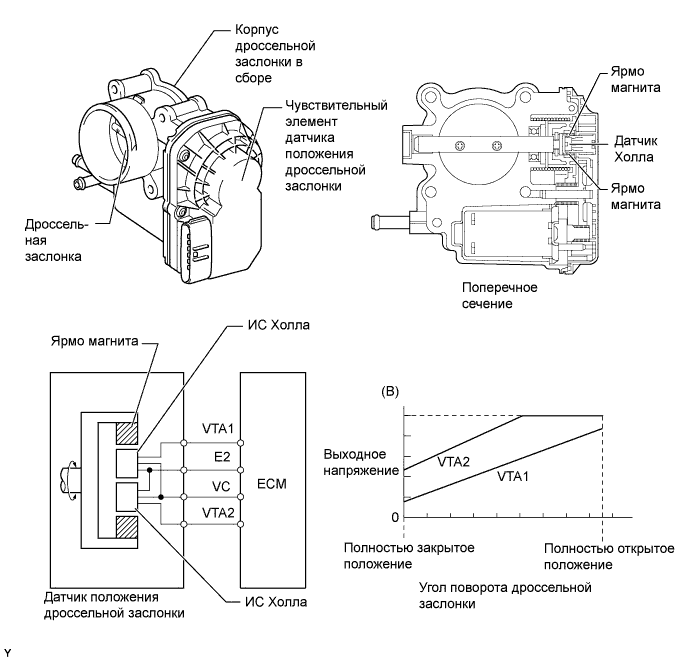
The throttle position sensor rests on the opposite side of the throttle body in the throttle body. When closed, the throttle valve prevents air from entering the engine. The air required for idling bypasses the throttle valve using the idle speed motor.
Most later car models use a floorboard throttle position sensor at the top of the accelerator pedal. When the pedal is depressed, a sensor attached to the pedal sends voltage to the electric motor, which controls the opening of the throttle valve.
In operation, the throttle position sensor is nothing more than a rheostat. When the throttle is closed at idle, the throttle position sensor registers very close to 0.5 volts, and when opened, as during acceleration, the voltage rises to about 5 volts. The transition from 0.5 to 5 volts should be very smooth. The engine computer recognizes this increase in voltage as a signal indicating the amount of airflow and opening speed.
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) plays a dual role in this scenario. It determines the manifold pressure, corrected for air density due to temperature, humidity and altitude. It is also connected to the intake manifold via a hose. When the throttle valve suddenly opens, the manifold pressure drops just as suddenly and rises again as the air flow increases.
The engine management computer requires all three of these sensors to accurately determine the injector opening times and the amount of ignition timing required to maintain the 14.5 / 1 fuel ratio. make correct settings and set DTC P0068.
Symptoms
Some symptoms of a P0068 code that a driver may experience may include rough engine idling during parking and deceleration, loss of power due to excess air that can enter the system, which can affect the air/fuel ratio, and obviously check engine indicator.
The symptoms displayed for the P0068 code will depend on the cause of the overload:
- The Service Engine or Check Engine light will illuminate.
- Rough Engine - The computer will set the above code and additional codes indicating a faulty sensor if the problem is electrical. Without proper airflow, the engine will run at a rough idle and, depending on the severity, it may not accelerate or have a serious malfunction. dead zone at idle. In short, it will work lousy
Causes of the P0068 code
Possible reasons for this DTC:
- Vacuum leaks between the MAF sensor and the intake manifold and loose or cracked hoses
- Dirty air cleaner
- Leakage in the intake manifold or sections
- Defective sensor
- Coked intake port behind the throttle body
- Bad or corroded electrical connectors
- Airflow obstruction
- Defective electronic throttle body
- Clogged hose from the intake manifold to the absolute gas pressure sensor
- Faulty mass air flow sensor or related wiring
- Faulty intake manifold absolute pressure sensor or related wiring
- Vacuum leak in the intake manifold, air intake system, or throttle body.
- Loose or damaged electrical connection associated with this system.
- Faulty or incorrectly installed valve position sensor or related wiring
Diagnostic steps and possible solutions
As an auto mechanic, let's start with the most common problems. You will need a volt/ohmmeter, a punch-hole gauge, a can of carburetor cleaner, and a can of air intake cleaner. Fix any problems as you find them and start the car to determine if the problem is fixed - if not, continue with the procedures.
With the engine off, open the hood and check the air filter element.
Look for loose clips or leaks in the line from the MAF sensor to the throttle body.
Inspect all vacuum lines on the intake manifold for blockages, cracks, or looseness that could cause loss of vacuum.
Disconnect each sensor and check the connector for corrosion and extruded or bent pins.
Start the engine and use a carburetor cleaner to find intake manifold leaks. A short shot of the carburetor cleaner over the leak will noticeably change the engine rpm. Keep the spray can at arm's length to keep the spray out of your eyes, or you'll learn a lesson just like grabbing a cat by the tail. You won't forget next time. Inspect all manifold connections for leaks.
Loosen the clamp on the pipe connecting the mass airflow to the throttle body. Look into the throttle body to see if it's covered in coke, a black greasy substance. If so, clamp the tube from the air intake bottle between the tube and the throttle body. Slide the nipple onto the throttle body and start the engine. Start spraying until the can runs out. Remove it and reconnect the hose to the throttle body.
Check mass air flow sensor. Remove the connector from the sensor. Switch on the ignition with the engine off. There are three wires, 12V power, sensor ground and signal (usually yellow). Use the red lead of a voltmeter to test the 12 volt connector. Keep the black wire on the ground. Lack of voltage - a problem with the ignition or wiring. Install the connector and check the grounding of the sensor. It must be less than 100 mV. If the sensor is supplying 12V and is out of range at ground, replace the sensor. This is the basic test. If upon completion of all tests it passes and the problem persists, mass air flow may still be bad. Check it out on a graphics computer like the Tech II.
Check the operation of the throttle position sensor. Make sure it is installed correctly and the bolts are tight. This is a 5-wire connector - dark blue for signal, gray for XNUMXV reference, and black or orange for PCM negative wire.
– Connect the red wire of the voltmeter to the blue signal wire and the black wire of the voltmeter to ground. Turn the key on with the engine off. If the sensor is OK, then when the throttle is closed, there will be less than 1 volt. As the throttle opens, the voltage rises smoothly to about 4 volts without dropouts or glitches.
Check the MAP sensor. Turn on the key and check the power control wire with the red wire of the voltmeter, and the black one with ground. With the key on and the engine off, it should be between 4.5 and 5 volts. Start the engine. It should have between 0.5 and 1.5 volts depending on altitude and temperature. Increase engine speed. The voltage should respond to throttle opening by dropping and rising again. If not, replace it.
COMMON ERRORS WHEN DIAGNOSING CODE P0068
Common mistakes in diagnosing a P0068 code may include replacing parts in the ignition or ignition fuel system, assuming a misfire is the problem, as this can cause the engine to perform similarly. Another failure to diagnose this problem may be to replace one or more sensors without checking their functionality before replacing. Before repair it is very important to check all faults.
HOW SERIOUS CODE P0068 IS?
Code P0068 may not be serious to begin with, but it can lead to a more serious vehicle condition. The engine will likely run until the problem is fixed. If the engine runs intermittently for a long period of time, engine damage may result. We recommend that you diagnose the problem and fix it as soon as possible to avoid further engine damage.
WHAT REPAIRS CAN FIX CODE P0068?
Repairs that can fix a P0068 code would include:
- Adjusting the mounting or installation of the mass air flow sensor, intake manifold absolute pressure sensor or throttle position sensor
- Mass Air Flow Sensor Replacement
- Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Replacement
- Repair or replace the wiring associated with these two sensors.
- Fix vacuum leak
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS REGARDING CODE P0068
It is recommended that code P0068 be cleared as soon as possible as this code can affect the vehicle's fuel economy. If there are vacuum leaks, the air-fuel mixture will not be correct, causing the engine to idle. While this results in the engine consuming less fuel, it also causes a loss of power, which consequently reduces fuel consumption.
Need more help with your p0068 code?
If you still need help with DTC P0068, post a question in the comments below this article.
NOTE. This information is provided for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be used as a repair recommendation and we are not responsible for any action you take on any vehicle. All information on this site is protected by copyright.
2 comment
Opel Corsa 1.2 2007
error code 068 has changed the lamb probe intake air temperature sensor spark plug ignition coil but error code 068 comes up again the car goes a little rvckit
Robert Macias
Is it possible that this code (P0068) causes the PRNDS indicators on a Golf Rabbit to all come on at the same time (I am told that this protects the gearbox)? I took him to check the gearbox, he told me that the gearbox is fine, but that it marks some codes, including this one, and that it is possible that correcting them also corrects the protection mode in which the gearbox enters .