P02BC cylinder 9, injector limited
Content
P02BC cylinder 9, injector limited
OBD-II DTC Datasheet
Blockage of an injector for cylinder 9
What does this mean?
This is a generic powertrain diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and is commonly applied to OBD-II vehicles. This may include, but is not limited to, Ford vehicles (Transit, Focus, etc.), Land Rover, Mitsubishi, Maybach, Dodge, Subaru, etc. Despite the general nature, the exact repair steps may vary depending on year of manufacture, brand, model and transmission. configuration.
If your OBD-II equipped vehicle has stored the P02BC code, it means that the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected a possible restriction in the fuel injector for a specific cylinder of the engine, in this case cylinder # 9.
Automotive fuel injectors require precise fuel pressure in order to deliver the exact amount of fuel in a precisely atomized pattern to the combustion chamber of each cylinder. The requirements of this precise circuit require each fuel injector to be free of leaks and restrictions.
The PCM monitors factors such as fuel trim required and exhaust oxygen sensor data, in conjunction with crankshaft position and camshaft position, to detect a lean mixture and pinpoint which engine cylinder is malfunctioning.
The data signals from the oxygen sensors warn the PCM of the lean oxygen content in the exhaust gases and which engine block is affected. Once it is determined that there is a lean exhaust mixture on a particular engine block, the position of the camshaft and crankshaft helps determine which injector is having the problem. Once the PCM determines a lean mixture is present and detects a damaged fuel injector on cylinder # 9, a P02BC code will be stored and a malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) may illuminate.
Some vehicles may require multiple failure cycles for the MIL to illuminate.
Cross-section of a typical fuel injector: 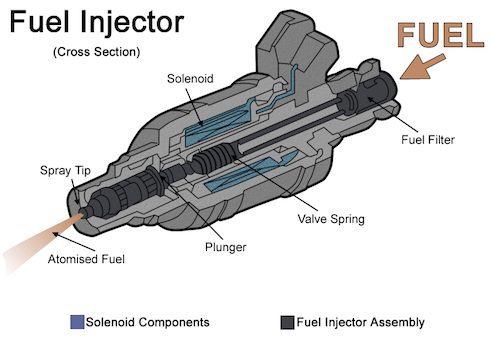
What is the severity of this DTC?
P02BC should be classified as heavy, as a lean fuel mixture can damage the cylinder head or engine.
What are some of the symptoms of the code?
Symptoms of a P02BC trouble code may include:
- Reduced engine performance
- Reduced fuel efficiency
- Lean exhaust codes
- Misfire codes can also be saved
What are some of the common causes for the code?
Reasons for this P02BC fuel injector code may include:
- Defective and / or clogged fuel injector
- Open or short circuit in the chain (s) of the fuel injector
- Defective oxygen sensor (s)
- PCM or programming error
- Malfunction of the mass air flow (MAF) or manifold air pressure (MAP) sensor
What are some P02BC troubleshooting steps?
MAF and MAP related codes must be diagnosed and repaired before attempting to diagnose the P02BC code.
I like to start my diagnosis with a general inspection of the fuel rail area. I would focus on the fuel injector in question (cylinder # 9). Externally inspect for corrosion and / or leaks. If there is severe corrosion on the outside of the fuel injector in question, or if it leaks, suspect that it has failed.
If there are no obvious mechanical problems in the engine compartment, several tools will be required to make an accurate diagnosis:
- Diagnostic Scanner
- Digital Volt / Ohmmeter (DVOM)
- Car stethoscope
- Reliable source of vehicle information
Then I connected the scanner to the car diagnostic port and got all stored codes and freeze frame data. This will be helpful as my diagnosis progresses. Now I would clear the codes and test drive the vehicle to see if the P02BC is reset.
If the P02BC code returns immediately, use an injector balance scanner to verify that the misfire is an injector problem. Once you've done that, go to step 1.
Step 1
With the engine running, use a stethoscope to listen to the appropriate fuel injector. An audible clicking sound should be heard, repeating in a pattern. If there is no sound, go to step 2. If it is taut or intermittent, suspect that the # 9 injector is faulty or clogged. If necessary, compare the sounds from the injector of this cylinder with other sounds for comparison.
Step 2
Use the DVOM to check the voltage and ground impulse with the engine running. Most manufacturers use a constant battery voltage system at one terminal of the fuel injector and a ground pulse (from the PCM) applied to the other terminal at the appropriate time.
If no voltage is detected at the corresponding fuel injector connector, use the DVOM to test system fuses and relays. Replace fuses and / or relays if necessary.
I like to test fuses in a system with a circuit under load. A defective fuse that appears to be OK when the circuit is not loaded (key on / engine off) may fail when the circuit is loaded (key on / engine running).
If all system fuses and relays are OK and no voltage is present, use your vehicle information source to trace the circuit to the ignition switch or fuel injection module (if applicable).
Note. Use caution when checking / replacing high pressure fuel system components.
Related DTC discussions
- There are currently no related topics in our forums. Post a new topic on the forum now.
Need more help with the P02BC code?
If you still need help with DTC P02BC, post a question in the comments below this article.
NOTE. This information is provided for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be used as a repair recommendation and we are not responsible for any action you take on any vehicle. All information on this site is protected by copyright.

