P1022 – Throttle Pedal Position Sensor/Switch (TPS) Circuit A Low Input
Content
P1022 – OBD-II Trouble Code Technical Description
Throttle Pedal Position Sensor/Switch (TPS) Circuit A Low Input
What does the fault code mean P1022?
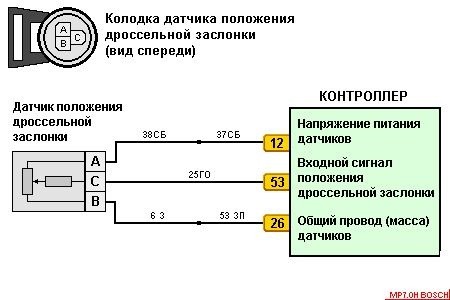
Trouble code P1022 usually indicates problems with the vehicle's throttle pedal position sensor (TPS). Specifically, a “circuit A low input” error message indicates that the signal coming from the TPS sensor is too low or not within the expected range.
The TPS measures the throttle opening angle and sends this information to the vehicle's Electronic Control Unit (ECU). A low input signal may be caused by a malfunction of the sensor itself, wiring or connection problems, or other electrical problems in the system.
To accurately identify and correct this problem, it is recommended that you consult the service manual for the specific make and model of your vehicle. Most cases will require diagnosis by a qualified auto mechanic or service center to determine the cause and make the necessary repairs.
Possible reasons
Trouble code P1022 indicates a low input signal from the throttle pedal position sensor (TPS). Here are some possible reasons that could cause this error to occur:
- TPS sensor malfunction: The sensor itself may be damaged or fail, resulting in an incorrect signal.
- Wiring problems: Opens, short circuits or damaged wiring can cause a low signal.
- Connection problems: Incorrect connection of the TPS sensor or connector may result in reduced signal.
- Circuit A fault: Circuit A problems may include damaged wiring or connections within the circuit, resulting in a low signal.
- Problems with the Electronic Control Unit (ECU): In rare cases, the problem may be due to a malfunction of the ECU itself, which processes the signals from the TPS sensor.
- Mechanical problems with the throttle valve: Sticks or problems with the throttle mechanism can cause incorrect signals from the TPS sensor.
To pinpoint the cause of the problem, it is recommended to conduct a thorough diagnosis using diagnostic tools such as a scan tool to read trouble codes, and possibly a multimeter to check electrical circuits. In most cases, you will need the help of a qualified auto mechanic or service center to fix the problem.
What are the symptoms of a fault code? P1022?
Symptoms for Trouble Code P1022 related to the Throttle Pedal Position Sensor (TPS) may include the following:
- Power Loss: A low signal from the TPS can result in loss of power when accelerating. The car may respond slowly when you press the gas pedal.
- Unstable idle: Incorrect signals from the TPS can affect engine idle stability. This can manifest itself in uneven engine operation or even stopping.
- Gearshift problems: A low TPS signal can affect the automatic transmission's performance, causing shifting instability or even failure to shift.
- Unstable idle mode: The vehicle may have difficulty maintaining a stable idle.
- Increased fuel consumption: Incorrect signals from the TPS can result in inefficient fuel combustion, which in turn can lead to increased fuel consumption.
- When the Check Engine light appears: Code P1022 activates the Check Engine light on the dashboard.
If you notice any of these symptoms or the Check Engine Light illuminates on your dashboard, it is recommended that you diagnose and repair the problem to avoid further damage and keep your vehicle running properly.
How to diagnose a fault code P1022?
Diagnosing trouble code P1022 requires a systematic approach and the use of specialized tools. Here are the steps you can take to identify and resolve the problem:
- Scanner for reading fault codes:
- Use your car diagnostic scanner to read trouble codes. This will help you get more detailed information about which specific codes are activated, including P1022.
- Write down the codes and any additional information that the scanner may provide.
- Visual check of wiring and connections:
- Inspect the wiring, connections, and connectors associated with the throttle pedal position sensor (TPS). Make sure the wiring is intact, the connectors are securely connected, and there are no signs of corrosion.
- TPS resistance test:
- Use a multimeter to measure the resistance across the TPS sensor leads. The resistance should change smoothly as the position of the gas pedal changes.
- Checking voltage on TPS:
- Using a multimeter, measure the voltage at the TPS sensor terminals. The voltage should also change smoothly in accordance with changes in the position of the gas pedal.
- Checking the throttle valve:
- Check the mechanical condition of the throttle valve. Make sure it moves freely and doesn't get stuck.
- Checking Circuit A:
- Check circuit A, including wiring and connectors, to identify any problems.
- TPS replacement:
- If all of the above steps do not identify the problem, it is possible that the TPS sensor itself is the source of the malfunction and requires replacement.
If you are not experienced in diagnosing and repairing vehicles, it is recommended that you contact a qualified auto mechanic or service center to further diagnose and repair the problem.
Diagnostic errors
Errors may occur when diagnosing the P1022 trouble code, especially if the process is not carried out systematically or if sufficient attention to detail is not paid. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Skip visual inspection:
- Error: Sometimes technicians may miss visually checking the wiring, connectors, and TPS sensor by focusing only on the scan tool.
- Recommendation: Carefully inspect all connections, connectors, and wiring before proceeding to more advanced diagnostic steps.
- Ignoring mechanical problems:
- Mistake: Some technicians may focus solely on the electrical side, neglecting to check the mechanical condition of the throttle body.
- Recommendation: Check that the throttle valve moves freely and is not stuck.
- Incorrect interpretation of TPS data:
- Error: Some technicians may misinterpret TPS data, resulting in incorrect conclusions.
- Recommendation: Carefully analyze the TPS data to ensure that it matches the expected values at various throttle pedal positions.
- Neglecting circuit check A:
- Error: Sometimes technicians may forget to perform a full test of the A circuit, focusing only on the TPS sensor.
- Recommendation: Check the condition of the entire A circuit, including wiring and connections.
- Immediately replacing the TPS sensor:
- Error: Some technicians may instantly assume that the problem is with the TPS sensor itself and replace it without sufficient diagnostics.
- Recommendation: Perform all necessary tests before replacing the TPS sensor to ensure that it is the source of the problem.
It is important to follow a systematic approach, including checking mechanical components, wiring and connections, and using diagnostic tools to avoid incorrect conclusions and eliminate the cause of the P1022 trouble code.
How serious is the fault code? P1022?
Trouble code P1022, associated with the throttle pedal position sensor (TPS), indicates problems with the engine management system. Although the error itself can be caused by a variety of reasons, it usually signals problems that can affect the performance and efficiency of the engine.
The severity of a P1022 code can vary depending on the specific circumstances and how quickly the problem is resolved. Here are a few aspects to consider:
- Loss of power and efficiency: Problems with the TPS can cause the engine to lose power and efficiency. This may affect the overall performance of the vehicle.
- Fuel consumption: Improper operation of the TPS can cause inefficient fuel combustion, which in turn can lead to increased fuel consumption.
- Idle speed and gear shifting instability: Problems with the sensor can also affect idle speed and automatic transmission performance.
- Stopping the engine: In some cases, if the TPS problem is severe, it can cause the engine to stall.
Overall, although P1022 is not a critical fault, resolving it is important to ensure proper engine operation and prevent additional problems. It is recommended to diagnose and eliminate the cause as soon as possible to avoid more serious consequences and ensure reliable operation of the vehicle.
What repair will help eliminate the code? P1022?