P2256 O2 Sensor Negative Current Control Circuit High Bank 2 Sensor 1
Content
- P2256 O2 Sensor Negative Current Control Circuit High Bank 2 Sensor 1
- OBD-II DTC Datasheet
- What does this mean?
- What is the severity of this DTC?
- What are some of the symptoms of the code?
- What are some of the common causes for the code?
- What are some steps to troubleshoot the P2256?
- Related DTC discussions
- Need more help with the P2256 code?
P2256 O2 Sensor Negative Current Control Circuit High Bank 2 Sensor 1
OBD-II DTC Datasheet
O2 Sensor Negative Current Control Circuit Bank 2 Sensor 1
What does this mean?
This is a generic Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) applicable to many OBD-II vehicles (1996 and newer). This may include, but is not limited to, Mazda, VW, Acura, Kia, Toyota, BMW, Peugeot, Lexus, Audi, etc. Despite the general nature, the exact repair steps may vary depending on the year of manufacture, brand, models and transmissions.
A stored code P2256 means that the powertrain control module (PCM) has detected a negative current mismatch in the upstream oxygen (O2) sensor for engine bank number two. Bank two is a group of engines that does not have the number one cylinder. Sensor 1 is the top (pre) sensor. The negative current control circuit is the ground circuit.
The PCM uses input from the heated oxygen sensors (HO2S) to monitor the oxygen content in the exhaust gases for each engine bank, as well as the efficiency of the catalytic converter.
The oxygen sensors are constructed using a zirconia sensing element located in the center of a vented steel housing. Small platinum electrodes are soldered between the sensing element and the wires in the oxygen sensor harness connector. The O2 sensor harness connector connects to the controller network (CAN), which connects the oxygen sensor harness to the PCM connector.
Each HO2S has threads (or studs) in the exhaust pipe or manifold. It is positioned so that the sensing element is closer to the center of the pipe. Waste exhaust gases leave the combustion chamber (through the exhaust manifold) and pass through the exhaust system (including catalytic converters); leaks over oxygen sensors. Exhaust gases enter the oxygen sensor through specially designed air vents in the steel housing and swirl around the sensing element. Air drawn through the wire cavities in the sensor housing fills the tiny chamber in the center of the sensor. The heated air (in a tiny chamber) causes oxygen ions to produce energy, which the PCM recognizes as voltage.
Differences between the amount of O2 ions in the ambient air and the number of oxygen molecules in the exhaust cause the heated oxygen ions inside the HO2S to bounce very quickly and intermittently from one platinum layer to the next. As the pulsating oxygen ions move between the platinum layers, the HO2S output voltage changes. The PCM sees these changes in the HO2S output voltage as changes in the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas.
The voltage outputs from the HO2S are lower when more oxygen is present in the exhaust (lean state) and higher when less oxygen is present in the exhaust (rich state). This part of the HO2S uses low voltage (less than one volt).
In a separate section of the sensor, the HO2S is preheated using the battery voltage (12 volts). When the engine temperature is low, the battery voltage heats up the HO2S so it can start monitoring the oxygen in the exhaust gas more quickly.
If the PCM detects too high a voltage level and is not within acceptable parameters, P2256 will be stored and a Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) may illuminate. Most vehicles will require several ignition cycles (on failure) to turn on the warning light.
Typical oxygen sensor O2: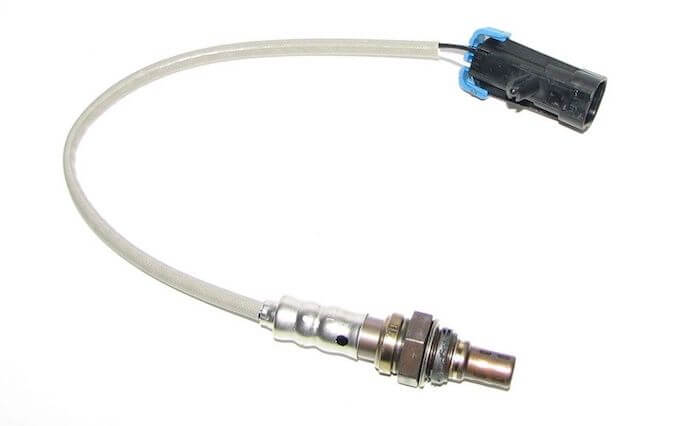 
What is the severity of this DTC?
A HO2S with a control circuit malfunction can result in very poor engine performance and various handling problems. The P2256 code should be classified as serious and corrected as soon as possible.
What are some of the symptoms of the code?
Symptoms of a P2256 trouble code may include:
- Decreased fuel efficiency
- Reduced engine performance
- Stored Misfire Codes or Lean / Rich Exhaust Codes
- Service engine lamp will light up soon
What are some of the common causes for the code?
Reasons for this code may include:
- Defective oxygen sensor / s
- Burnt, frayed, broken, or disconnected wiring and / or connectors
- Faulty PCM or PCM programming error
What are some steps to troubleshoot the P2256?
An accurate diagnosis of the P2256 code will require a diagnostic scanner, digital volt / ohmmeter (DVOM), and reliable vehicle information source.
Connect the scanner to the vehicle diagnostic port and get all stored codes and corresponding freeze frame data. You will want to write this information down just in case the code turns out to be intermittent. Then clear the codes and test drive the vehicle. At this time, one of two things will happen. Either P2256 will be cleared or the PCM will enter ready mode.
If the code is intermittent and the PCM enters ready mode, it may be more difficult to diagnose. The conditions that led to the storage of P2256 may need to worsen before an accurate diagnosis can be made. If the code is cleared, continue diagnostics.
Connector faceplate views, connector pinout diagrams, component layouts, wiring diagrams, and diagnostic block diagrams (related to the associated code and vehicle) can be found using your vehicle information source.
Visually inspect the HO2S related wiring and connectors. Replace cut, burnt, or damaged wiring.
Disconnect the HO2S in question and use the DVOM to test the resistance between the negative current control circuit and any voltage circuits. If there is continuity, suspect a faulty HO2S.
If the P2256 code continues to reset, start the engine. Allow it to warm up to normal operating temperature and idle (with the transmission in neutral or park). Connect the scanner to the vehicle diagnostic port and observe the oxygen sensor input in the data stream. Narrow down your data stream to include only relevant data for a faster response.
If the oxygen sensors are operating normally, the voltage across the oxygen sensors upstream of the catalytic converter will cycle continuously from 1 to 900 millivolts when the PCM enters closed loop mode. Post-Cat sensors will also cycle between 1 and 900 millivolts, but they will be mounted at a specific point and remain relatively stable (compared to pre-cat sensors). A HO2S that is not working properly should be considered defective if the engine is in good working order.
If the HO2S is displaying battery voltage or no voltage in the scanner data stream, use the DVOM to get real-time data from the HO2S connector. If the output remains the same, suspect an internal HO2S short that will require replacement of the HO2S.
- In most cases, you will correct this type of code by replacing the appropriate HO2S, but complete the diagnosis anyway.
Related DTC discussions
- There are currently no related topics in our forums. Post a new topic on the forum now.
Need more help with the P2256 code?
If you still need help with DTC P2256, post a question in the comments below this article.
NOTE. This information is provided for informational purposes only. It is not intended to be used as a repair recommendation and we are not responsible for any action you take on any vehicle. All information on this site is protected by copyright.
