Battery Density
Content
The density of the electrolyte in the battery is a very important parameter for all acid batteries, and any car enthusiast should know: what density should be, how to check it, and most importantly, how to correctly raise the density of the battery (specific gravity of the acid) in each of the cans with lead plates filled with H2SO4 solution.
Checking the density is one of the points in the battery maintenance process, which also includes checking the electrolyte level and measuring the battery voltage. in lead batteries density is measured in g/cm3. She is proportional to the concentration of the solution, inversely dependent on temperature liquids (the higher the temperature, the lower the density).
By the density of the electrolyte, you can determine the condition of the battery. So that if the battery does not hold a chargethen you should check the condition of its fluid in every bank.
The density of the electrolyte affects the capacity of the battery and its service life.
It is checked by a densimeter (hydrometer) at a temperature of +25°C. If the temperature differs from the required one, the readings are corrected as shown in the table.
So, we figured out a little what it is, and what needs to be checked regularly. And what numbers to focus on, how much is good and how much is bad, what should be the density of the battery electrolyte?
What density should be in the battery
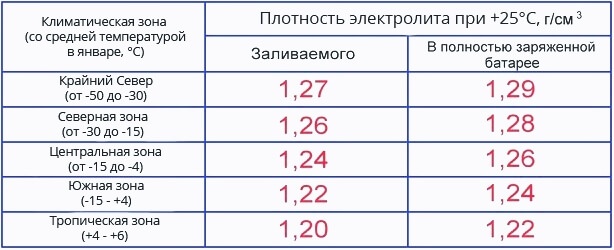
Maintaining the optimal electrolyte density is very important for the battery and it is worth knowing that the required values \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbare dependent on the climatic zone. Therefore, the density of the battery must be set based on a combination of requirements and operating conditions. For example, in a temperate climate, the density of the electrolyte should be at the level 1,25-1,27 g / cm3 ±0,01 g/cm3. In the cold zone, with winters down to -30 degrees, 0,01 g / cm3 more, and in the hot subtropical zone - by 0,01 g/cm3 less. In those regions where the winter is especially severe (up to -50 ° C), so that the battery does not freeze, you have to increase density from 1,27 to 1,29 g/cm3.
Many car owners are wondering: “What should be the density of the electrolyte in the battery in winter, and what should be in summer, or is there no difference, and should the indicators be kept at the same level all year round?” Therefore, we will deal with the issue in more detail, and it will help to produce it, battery electrolyte density table divided into climatic zones.
you also need to remember that, usually, the battery, being by car, charged no more than 80-90% its nominal capacity, so the density of the electrolyte will be slightly lower than when fully charged. So, the required value is chosen a little higher, from the one indicated in the density table, so that when the air temperature drops to the maximum level, the battery is guaranteed to remain operational and not freeze in the winter. But, regarding the summer season, increased density can threaten boiling.
Battery electrolyte density table
The density table is compiled relative to the average monthly temperature in the month of January, so that climatic zones with cold air down to -30 ° C and moderate ones with temperatures not lower than -15 do not require a decrease or increase in acid concentration. All year round (winter and summer) the density of the electrolyte in the battery should not be changed, but only check and make sure that it does not deviate from the nominal value, but in very cold areas, where the thermometer is often below -30 degrees (in the flesh up to -50), an adjustment is allowed.
The density of the electrolyte in the battery in winter
The density of the electrolyte in the battery in winter should be 1,27 (for regions with winter temperatures below -35, not less than 1.28 g/cm3). If the value is lower, then this leads to a decrease in the electromotive force and difficult starting of the internal combustion engine in cold weather, up to freezing of the electrolyte.
When the density in the battery is lowered in winter, you should not immediately run for a correction solution in order to raise it, it is much better to take care of something else - a high-quality battery charge using a charger.
Half-hour trips from home to work and back do not allow the electrolyte to warm up, and, therefore, it will be well charged, because the battery takes charge only after warming up. So the rarefaction increases from day to day, and as a result, the density also decreases.
For a new and serviceable battery, the normal interval for changing the density of the electrolyte (full discharge - full charge) is 0,15-0,16 g / cm³.
Remember that the operation of a discharged battery at sub-zero temperatures leads to freezing of the electrolyte and the destruction of lead plates!
According to the table of the dependence of the freezing point of the electrolyte on its density, you can find out the minus threshold of the thermometer column at which ice forms in your battery.
g / cm³ | 1,10 | 1,11 | 1,12 | 1,13 | 1,14 | 1,15 | 1,16 | 1,17 | 1,18 | 1,19 | 1,20 | 1,21 | 1,22 | 1,23 | 1,24 | 1,25 | 1,28 |
° C | -8 | -9 | -10 | -12 | -14 | -16 | -18 | -20 | -22 | -25 | -28 | -34 | -40 | -45 | -50 | -54 | -74 |
As you can see, when charged to 100%, the battery will freeze at -70 °C. At 40% charge, it freezes already at -25 ° C. 10% will not only make it impossible to start the internal combustion engine on a frosty day, but will completely freeze in 10 degree frost.
When the density of the electrolyte is not known, the degree of discharge of the battery is checked with a load plug. The voltage difference in the cells of one battery should not exceed 0,2V.
Readings of the load plug voltmeter, B | Battery discharge degree, % |
1,8-1,7 | 0 |
1,7-1,6 | 25 |
1,6-1,5 | 50 |
1,5-1,4 | 75 |
1,4-1,3 | 100 |
If the battery is discharged by more than 50% in winter and more than 25% in summer, it must be recharged.
The density of the electrolyte in the battery in summer
In summer, the battery suffers from dehydration., therefore, given that increased density has a bad effect on lead plates, it is better if it is 0,02 g/cm³ below the required value (especially in the southern regions).
In summer, the temperature under the hood, where the battery is often located, is significantly increased. Such conditions contribute to the evaporation of water from the acid and the activity of electrochemical processes in the battery, providing high current output even at the minimum allowable electrolyte density (1,22 g/cm3 for a warm humid climate zone). So that, when the electrolyte level gradually dropsthen its density increases, which accelerates the processes of corrosion destruction of electrodes. That is why it is so important to control the liquid level in the battery and, when it drops, add distilled water, and if this is not done, then overcharging and sulfation threaten.
If the battery is discharged due to the driver's inattention or other reasons, you should try to restore it to its working condition using a charger. But before charging the battery, they look at the level and, if necessary, top up with distilled water, which could evaporate during operation.
After some time, the density of the electrolyte in the battery, due to its constant dilution with distillate, decreases and falls below the required value. Then the operation of the battery becomes impossible, so it becomes necessary to increase the density of the electrolyte in the battery. But in order to find out how much to increase, you need to know how to check this very density.
How to check battery density
In order to ensure the correct operation of the battery, electrolyte density should check every 15-20 thousand km run. The measurement of density in the battery is carried out using a device such as a densimeter. The device of this device consists of a glass tube, inside which is a hydrometer, and at the ends there is a rubber tip on one side and a pear on the other. in order to check, you will need to: open the cork of the battery can, immerse it in the solution, and draw in a small amount of electrolyte with a pear. A floating hydrometer with a scale will show all the necessary information. We will consider in more detail how to correctly check the density of the battery a little lower, since there is also such a type of battery as maintenance-free, and the procedure is somewhat different in them - you will not need absolutely any devices.
Density indicator on a maintenance-free battery
The density of a maintenance-free battery is displayed by a color indicator in a special window. Green indicator testifies that Everything is okay (degree of charge within 65 - 100%) if the density has fallen and recharging required, then the indicator will the black. When the window displays white or red bulb, then you need urgent topping up with distilled water. But, by the way, the exact information about the meaning of a particular color in the window is on the battery sticker.
Now we continue to understand further how to check the density of the electrolyte of a conventional acid battery at home.
Checking the density of the electrolyte in the battery
So, in order to be able to correctly check the density of the electrolyte in the battery, first of all we check the level and, if necessary, correct it. Then we charge the battery and only then proceed to the test, but not immediately, but after a couple of hours of rest, since immediately after charging or adding water there will be inaccurate data.
It should be remembered that the density directly depends on the air temperature, so refer to the correction table discussed above. Having taken the liquid from the battery can, hold the device at eye level - the hydrometer must be at rest, float in the liquid, without touching the walls. Measurement is made in each compartment, and all indicators are recorded.
Table for determining the battery charge by electrolyte density.
Temperature | Charging | ||
of 100% | of 70% | Discharged | |
above +25 | 1,21 - 1,23 | 1,17 - 1,19 | 1,05 - 1,07 |
below +25 | 1,27 - 1,29 | 1,23 - 1,25 | 1,11 - 1,13 |
Density versus voltage according to charge
A strongly reduced density in one of the cells indicates the presence of defects in it (namely, a short circuit between the plates). But if it is low in all cells, then this indicates a deep discharge, sulfation, or simply obsolescence. Checking the density, combined with measuring the voltage under load and without, will determine the exact cause of the breakdown.
When you need to check the density of the electrolyte in order to determine the degree of charge of the battery, you can do this without removing the battery from under the hood of the car; you will need the device itself, a multimeter (for measuring voltage) and a table of the ratio of measurement data.
Charge percentage | Electrolyte density g/cm³ (**) | Battery voltage V (***) |
100% | 1,28 | 12,7 |
80% | 1,245 | 12,5 |
60% | 1,21 | 12,3 |
40% | 1,175 | 12,1 |
20% | 1,14 | 11,9 |
0% | 1,10 | 11,7 |
If necessary, density adjustments are made. It will be necessary to select a certain volume of electrolyte from the battery and add corrective (1,4 g / cm3) or distilled water, followed by 30 minutes of charging with rated current and exposure for several hours to equalize the density in all compartments. Therefore, we will talk further about how to correctly raise the density in the battery.
How to increase the density in a battery
It is necessary to raise the density when it was necessary to repeatedly adjust the level with distillate or it is not enough for the winter operation of the battery, as well as after repeated long-term recharge. A symptom of the need for such a procedure will be a reduction in the charge / discharge interval. In addition to correctly and fully charging the battery, there are a couple of ways to increase the density:
- add a more concentrated electrolyte (the so-called corrective);
- add acid.

How to correctly check and increase the density in the battery.
To increase and adjust the density of the electrolyte in the battery, you will need:
1) hydrometer;
2) measuring cup;
3) a container for dilution of a new electrolyte;
4) pear enema;
5) corrective electrolyte or acid;
6) distilled water.
The essence of the procedure is as follows:
- A small amount of electrolyte is taken from the battery bank.
- Instead of the same amount, we add a corrective electrolyte, if it is necessary to increase the density, or distilled water (with a density of 1,00 g / cm3), if, on the contrary, its decrease is required;
- then the battery must be put on recharging, in order to charge it with the rated current for half an hour - this will allow the liquid to mix;
- Having disconnected the battery from the device, it will also be necessary to wait at least an hour / two, so that the density in all banks evens out, the temperature drops and all gas bubbles come out in order to eliminate the error in the control measurement;
- Re-check the density of the electrolyte and, if necessary, repeat the procedure for selecting and adding the required liquid (also increase or decrease), reducing the dilution step, and then measure it again.
in order to understand how to increase the density in the battery, or maybe vice versa - you need a decrease in the specifically measured battery compartment, it is desirable to know what is the nominal volume in it in cubic centimeters. For example, the volume of electrolyte in one bank of a machine battery for 55 Ah, 6ST-55 is 633 cm3, and 6ST-45 is 500 cm3. The proportion of electrolyte composition is approximately as follows: sulfuric acid (40%); distilled water (60%). The table below will help you achieve the required electrolyte density in the battery:
electrolyte density formula
Please note that this table provides for the use of a correction electrolyte with a density of only 1,40 g / cm³, and if the liquid is of a different density, then an additional formula must be used.
For those who find such calculations very complicated, everything can be done a little easier by applying the golden section method:
We pump out most of the liquid from the battery can and pour it into a measuring cup in order to find out the volume, then add half that amount of electrolyte, shake it to mix. If you are also far from the required value, then also add a fourth of the previously pumped out volume with electrolyte. So it should be topped up, each time halving the amount, until the goal is reached.
How to raise the density in the accumulator if it fell below 1.18
When the density of the electrolyte is less than 1,18 g/cm3, we cannot do with one electrolyte, we will have to add acid (1,8 g/cm3). The process is carried out according to the same scheme as in the case of adding an electrolyte, only we take a small dilution step, since the density is very high and you can skip the desired mark already from the first dilution.
The average service life of modern batteries, subject to the rules of operation (to prevent deep discharges and overcharging, including through the fault of the voltage regulator), is 4-5 years. So it makes no sense to perform manipulations, such as: drilling the case, turning it over to drain all the liquid and completely replace it - this is complete "game" - if the plates have fallen, then nothing can be done. Keep an eye on the charge, check the density in time, properly maintain the car battery and you will be provided with the maximum lines of its work.

