Why the car stalls at idle - the main causes and malfunctions
If the car stalls at low speeds, it is very important to quickly determine the cause of this behavior and carry out the appropriate repairs. Neglect of this problem often leads to emergencies.
If the car stalls at idle, but when you press the gas pedal, the engine runs normally, then the driver needs to urgently find and eliminate the cause of this behavior of the vehicle. Otherwise, the car may stall in the most inconvenient place, for example, before the appearance of a green traffic light, which sometimes leads to emergencies.
What is idle
The speed range of an automobile engine averages 800-7000 thousand per minute for gasoline and 500-5000 for the diesel version. The lower limit of this range is idling (XX), that is, those revolutions that the power unit produces in a warm state without the driver pressing the gas pedal.
Therefore, generators for diesel and gasoline engines differ from each other, because even in XX mode they must:
- charge the battery (battery);
- ensure the operation of the fuel pump;
- ensure the operation of the ignition system.

It looks like a car generator
That is, in idle mode, the engine consumes a minimum of fuel, and the generator supplies electricity to those consumers that ensure the operation of the engine. It turns out a vicious circle, but without it it is impossible to either accelerate sharply, or smoothly pick up speed, or slowly start moving.
How does the engine idle
To understand how XX differs from the operation of the engine under load, it is necessary to analyze in detail the operation of the power unit. A car engine is called a four-stroke engine because one cycle includes 4 cycles:
- admission;
- compression;
- working stroke;
- release.
These cycles are the same on all types of automotive engines, with the exception of two-stroke power units.
Inlet
During the intake stroke, the piston goes down, the intake valve or valves are open and the vacuum created by the movement of the piston sucks in air. If the power plant is equipped with a carburetor, then the passing air stream tears off microscopic droplets of fuel from the jet and mixes with them (Venturi effect), moreover, the proportions of the mixture depend on the air speed and the diameter of the jet.
Based on these readings, the ECU determines the optimal amount of fuel and sends a signal to the injectors connected to the rail, which are constantly under fuel pressure. By adjusting the duration of the signal to the injectors, the ECU changes the amount of fuel injected into the cylinders.

Mass air flow sensor (DMRV)
Diesel engines work differently, in them the high-pressure fuel pump (TNVD) supplies diesel fuel in small portions, moreover, in early generation models, the portion size depended on the position of the gas pedal, and in more modern ECUs, it takes into account many parameters. However, the main difference is that the fuel is injected not during the intake stroke, but at the end of the compression stroke, so that the air heated from high pressure immediately ignites the sprayed diesel fuel.
Compression
During the compression stroke, the piston moves up and the temperature of the compressed air rises. Not all drivers know that the higher the engine speed, the greater the pressure at the end of the compression stroke, although the piston stroke is always the same. At the end of the compression stroke in gasoline engines, ignition occurs due to the spark formed by the spark plug (it is controlled by the ignition system), and in diesel engines, sprayed diesel fuel flares up. This occurs shortly before reaching the top dead center (TDC) of the piston, and the response time is determined by the angle of rotation of the crankshaft is called the ignition timing (IDO). This term is even applied to diesel engines.
Working stroke and release
After the ignition of the fuel, the stroke of the working stroke begins, when, under the action of the mixture of gases released during the combustion process, the pressure in the combustion chamber increases and the piston pushes towards the crankshaft. If the engine is in good condition and the fuel system is properly configured, then the combustion process ends before the start of the exhaust stroke or immediately after the exhaust valves open.
Hot gases exit the cylinder, because they are displaced not only by the increased volume of combustion products, but also by the piston moving to TDC.
Connecting rods, crankshaft and pistons
One of the main disadvantages of a four-stroke engine is a small useful action, because the piston pushes the crankshaft through the connecting rod only 25% of the time, and the rest either moves with ballast or consumes kinetic energy to compress air. Therefore, multi-cylinder engines, in which the pistons push the crankshaft in turn, are very popular. Thanks to this design, the beneficial effect occurs much more often, and given that the crankshaft and connecting rods are made of iron alloys, including cast iron, the whole system is very inertial.
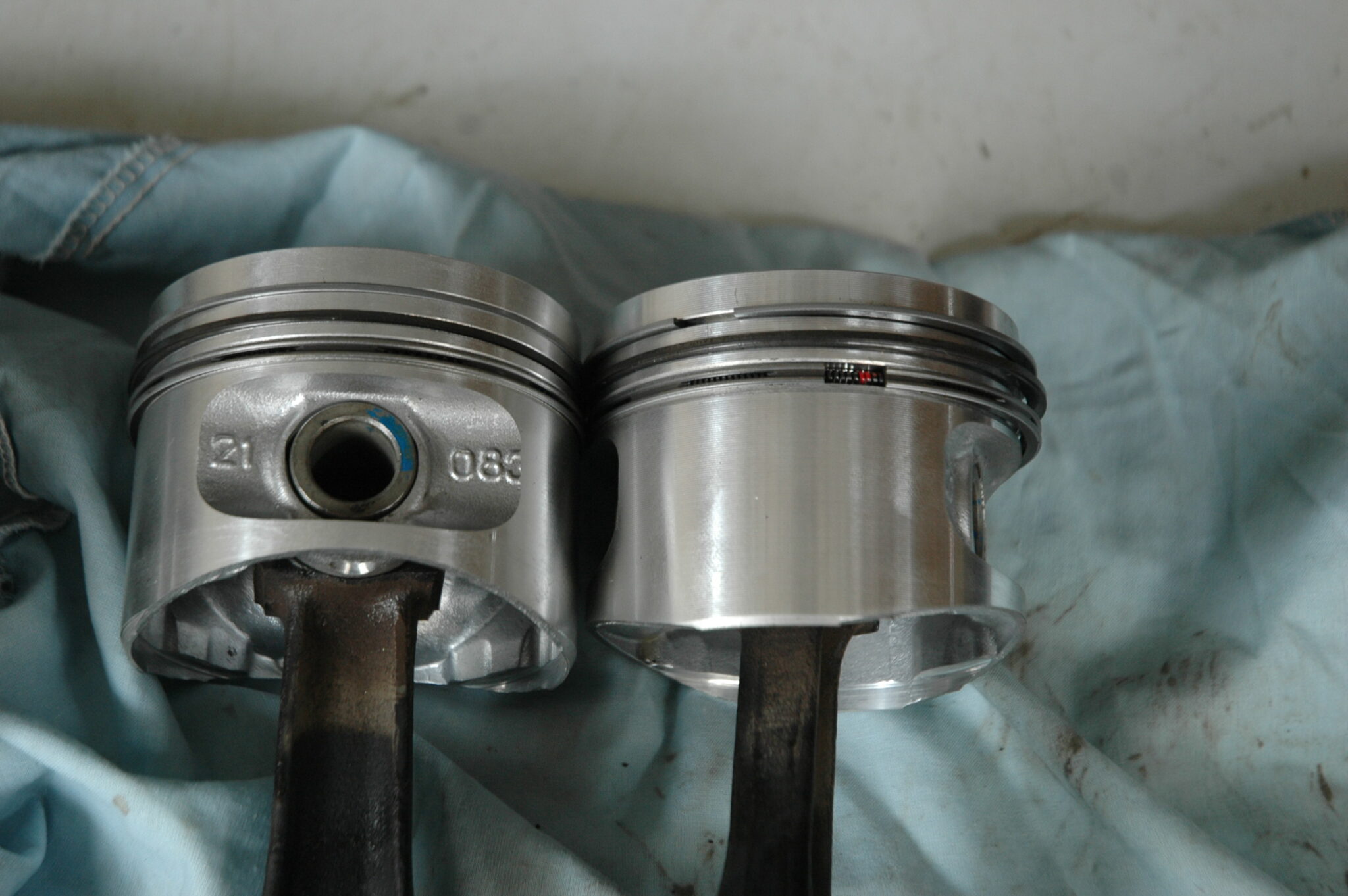

Pistons with rings and connecting rods
Work in XX mode
For efficient operation in the XX mode, it is necessary to create a fuel-air mixture with certain proportions, which, when burned, will release enough energy so that the generator can provide energy to the main consumers. If in operating modes the speed of rotation of the engine shaft is adjusted by manipulating the gas pedal, then in XX there are no such adjustments. In carburetor engines, the proportions of fuel in XX mode are unchanged, because they depend on the diameters of the jets. In injection engines, a slight correction is possible, which the ECU carries out using the idle speed controller (IAC).
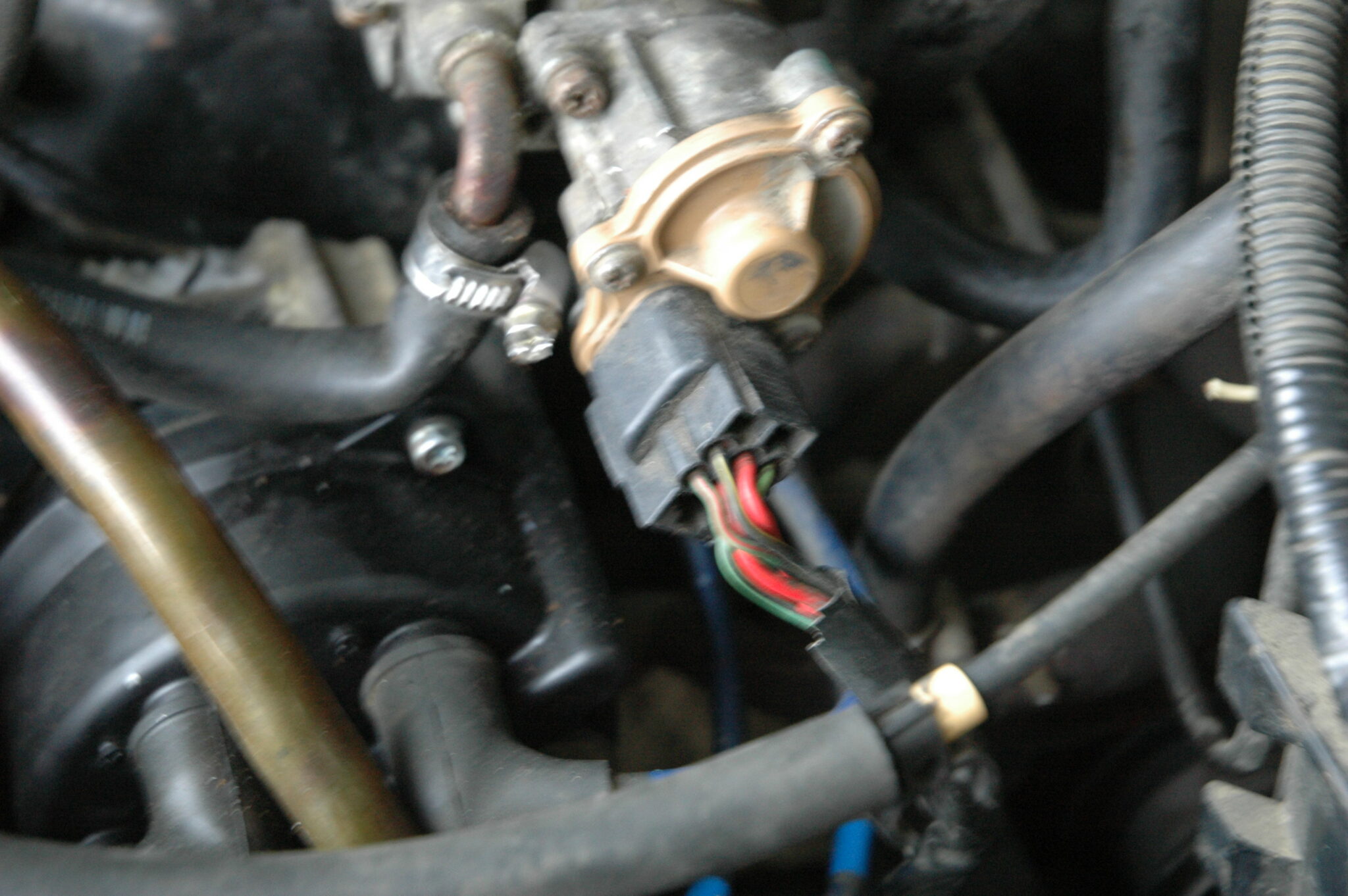

Idle speed regulator
In diesel engines of older types equipped with a mechanical injection pump, XX is regulated using the angle of rotation of the sector to which the gas cable is connected, that is, they simply set the minimum speed at which the engine runs stably. In modern diesel engines, XX regulates the ECU, focusing on sensor readings.
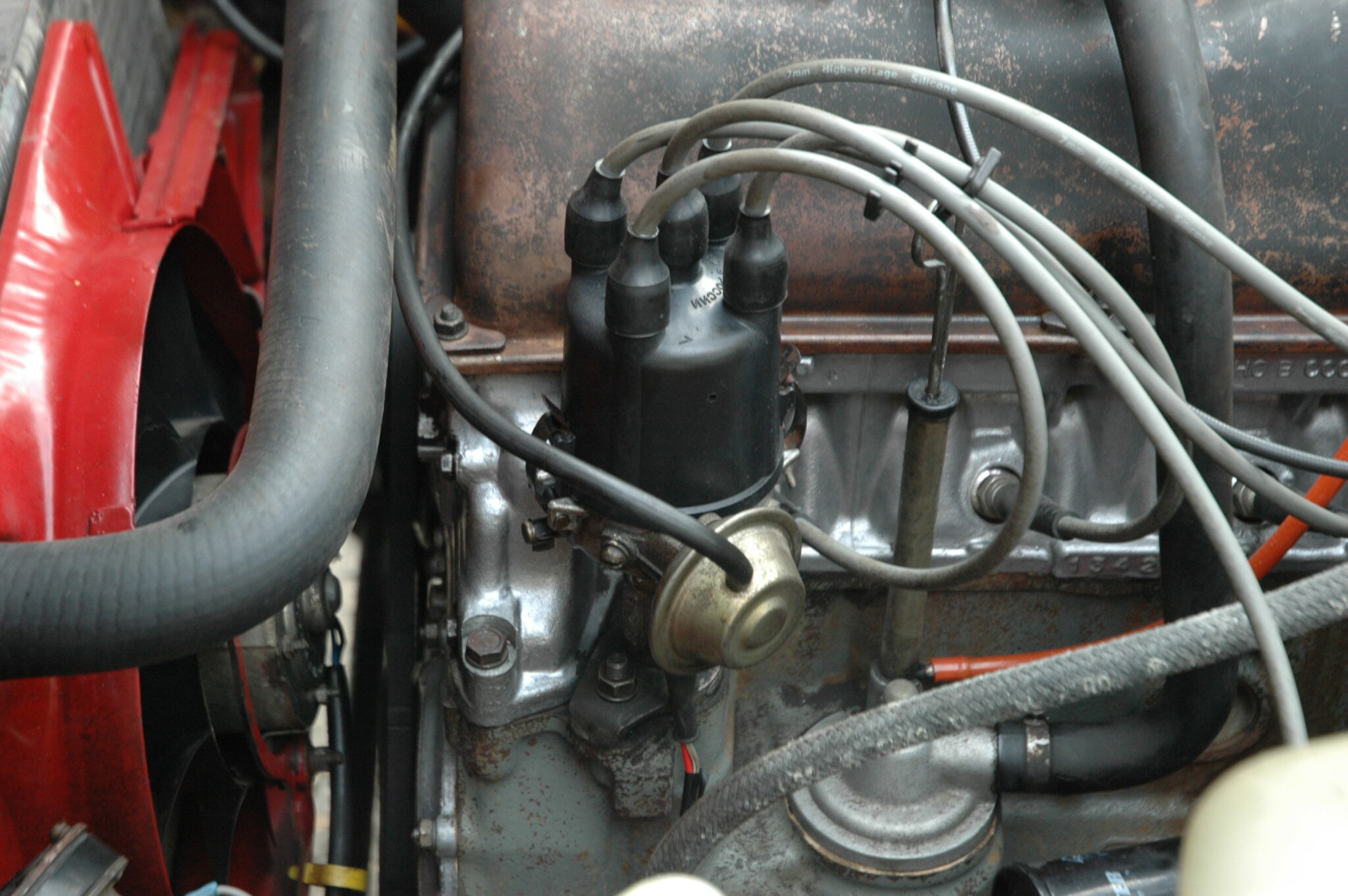
The distributor and vacuum corrector of the ignition determine the UOZ of the carburetor engine
One of the important parameters for the stable operation of the power unit in idle mode is the UOP, which must correspond to a certain value. If you make it smaller, the power will drop, and given the minimum fuel supply, the stable operation of the power unit will be disturbed and it will begin to shake, in addition, even a smooth pressure on the gas can lead to engine shutdown, especially with a carburetor.
This is due to the fact that the air supply first increases, that is, the mixture becomes even leaner and only then additional fuel enters.
Why does it stall at idle
There are many reasons why the car stalls at idle or the engine floats at idle, but they are all related to the operation of the systems and mechanisms described above, because the driver cannot influence this parameter in any way from the cab, he can only press the gas pedal, translating engine to another mode of operation. We have already talked about various malfunctions of the power unit and its systems in these articles:
- VAZ 2108-2115 the car is not gaining momentum.
- Why does the car stall on the go, then it starts and goes on.
- The car starts up hot and stalls - causes and remedies.
- The car starts and immediately stalls when cold - what could be the reasons.
- Why the car twitches, troit and stalls - the most common causes.
- Why does a car with a carburetor stall when you press the gas pedal.
- When you press the gas pedal, the car with the injector stalls - what are the causes of the problem.
Therefore, we will continue to talk about the reasons why the car stalls at idle.
Air leaks
This malfunction almost does not appear in other modes of operation of the power unit, because much more fuel is supplied there, and a slight decrease in speed under load is not always noticeable. On injection engines, air leakage is indicated by the “lean mixture” or “detonation” error. Other names are possible, but the principle is the same.
In addition, with this malfunction, the engine often troits and gains momentum poorly, and also consumes noticeably more fuel. A frequent manifestation of the problem is a barely or strongly audible whistle, which increases with increasing speed.

Poor tightening of the clamps or damage to the air hoses leads to air leakage
Here are the main places where air leakage occurs, due to which the car stalls at idle:
- vacuum brake booster (VUT), as well as its hoses and adapters (all cars);
- intake manifold gasket (any engines);
- gasket under the carburetor (carburetor only);
- vacuum ignition corrector and its hose (carburetor only);
- spark plugs and nozzles.
Here is an algorithm of actions that will help detect a problem on an engine of any type:
- Carefully inspect all hoses and their adapters associated with the intake manifold. With the engine running and warm, swing each hose and adapter and listen, if a whistle appears or the operation of the motor changes, then you have found a leak.
- After making sure that all vacuum hoses and their adapters are in good condition, listen to see if the power unit is troiting, then gently press the gas pedal or the carburetor / throttle / injection pump sector. If the power unit has earned much more stable, most likely the problem is in the manifold gasket.
- After making sure that the intake manifold gasket is intact, try to restore stable operation with quality and quantity screws, if they do not improve the behavior of the power unit, then the gasket under the carburetor is damaged, its sole is bent, or the fixing nuts are loose.
- After making sure that everything is in order with the carburetor, remove the hose from it that goes to the vacuum ignition corrector, a sharp deterioration in the operation of the power unit indicates that this part is also in order.
- If all the checks did not help to find the place of air leakage, due to which the idle speed drops and the car stalls, then carefully clean the wells of the candles and nozzles, then pour them with soapy water and press the gas strongly, but briefly. Abundant bubbles that have appeared indicate that air is leaking through these parts and their seals need to be replaced.

The vacuum brake booster and its hoses can also suck in air.
If the result of all checks is negative, then the cause of the unstable XX is something else. But it is still better to start diagnosing with this check in order to immediately exclude the most likely causes. Remember, even if the car is more or less stable at idle, but stalls when you press the gas, then almost always the reason lies in air leakage, so the diagnosis should be started by finding the place of leakage.
Ignition system malfunctions
The problems with this system include:
- weak spark;
- no spark in one or more cylinders.
Checking spark strength on a carburetor engine
Measure the voltage at the battery, if it is below 12 volts, turn off the engine and remove the terminals from the battery, then measure the voltage again. If the tester shows 13–14,5 volts, then the generator needs to be checked and repaired, because it does not generate the required amount of energy, if less, replace the battery and check the operation of the engine. If it began to work more stable, then most likely due to low voltage a weak spark was obtained, which inefficiently ignited the air-fuel mixture.

Spark plug
In addition, we recommend that you conduct a complete check of the engine, because the inefficient operation of the ignition at voltages above 10 volts is often a manifestation of various malfunctions.
Spark test in all cylinders (also suitable for injection engines)
The main sign of the absence of a spark in one or more cylinders is the unstable operation of the power unit at low and medium speeds, however, if you spin it up to high, then the motor runs normally without load. After making sure that the spark strength is sufficient, start and warm up the power unit, then remove the armored wires from each candle one by one and monitor the behavior of the motor. If one or more cylinders are not functioning, then removing the wire from their candles will not change the engine's operating mode. Having identified the defective cylinders, turn off the engine and unscrew the candles from them, then insert the candles into the corresponding tips of the armored wires and put the threads on the engine.
Start the engine and see if a spark appears on the candles, if not, install new candles, and if there is no result, turn off the engine again and insert each armored wire into the coil hole in turn and check for a spark. If a spark appears, then the distributor is faulty, which does not distribute high-voltage pulses to the corresponding candles and therefore the machine stalls at idle. To fix the problem, replace:
- coal with a spring;
- distributor cover;
- slider.

Checking and removing spark plug wires
On injection motors, swap the wires with those that work exactly. If, after connecting the armored wire to the coil, a spark does not appear, replace the entire set of armored wires, and also (preferably, but not necessary) put new candles.
Incorrect valve adjustment
This malfunction occurs only on vehicles whose engines are not equipped with hydraulic lifters. Regardless of whether the valves are clamped or knocking, in XX mode the fuel burns inefficiently, so the car stalls at low speeds, because the kinetic energy released by the power unit is not enough. To make sure that the problem is in the valves, compare the fuel consumption and dynamics before the problem with idling and now, if these parameters have worsened, the clearance must be checked and, if necessary, adjusted.
To check on a cold engine, remove the valve cover (if any parts are attached to it, for example, a throttle cable, then first disconnect them). Then, turning manually or with a starter (in this case, disconnect the spark plugs from the ignition coil), set the valves of each cylinder one by one to the closed position. Then measure the gap with a special probe. Compare the values obtained with those indicated in the operating instructions for your car.
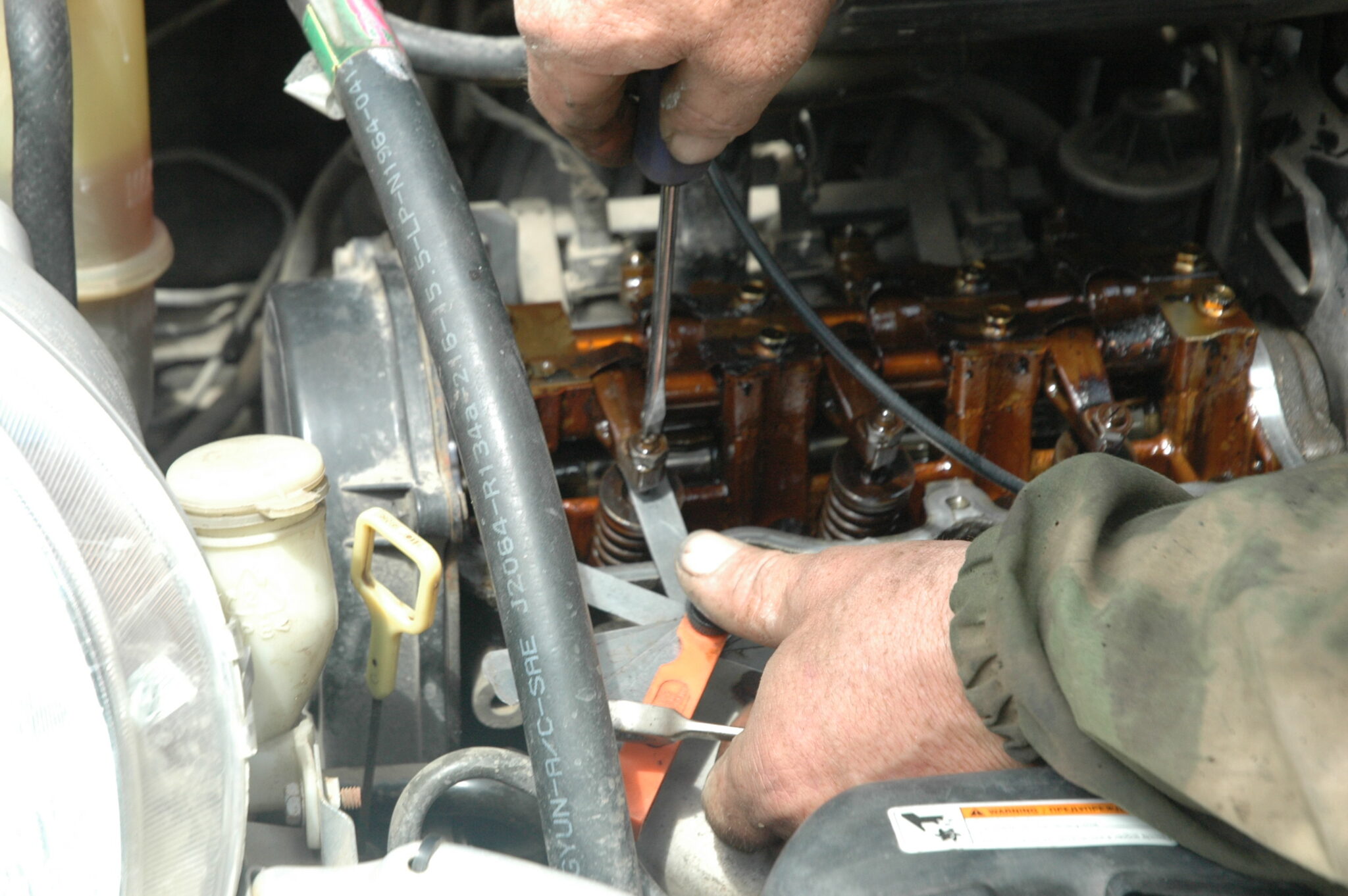

Adjustment of valves
For example, for the ZMZ-402 engine (it was installed on the Gazelle and the Volga), the optimal intake and exhaust valve clearances are 0,4 mm, and for the K7M engine (it is installed on Logan and other Renault cars), the thermal clearance of the intake valves is 0,1– 0,15, and exhaust 0,25–0,30 mm. Remember, if the car stalls at idle, but more or less stable at high speeds, then one of the most likely causes is the wrong thermal valve clearance.
Incorrect carburetor operation
The carburetor is equipped with an XX system, and many cars have an economizer that cuts off the fuel supply when driving in any gear with the gas pedal fully released, including when braking the engine. To check the operation of this system and confirm or exclude its malfunction, reduce the angle of rotation of the throttle with the gas pedal fully released until it closes. If the idle system is working properly, then there will be no change other than a slight decrease in speed. If the car stalls at idle when performing such manipulations, then this carburetor system is not working properly and needs to be checked.

Carburetor
In this case, we recommend contacting an experienced fueler or carburetor, because it is impossible to create a single instruction for all types of carburetors. In addition, in addition to a malfunction of the carburetor itself, the reason that the car stalls at idle may be the forced idle economizer valve (EPKhH) or the wire that supplies voltage to it.
The motor is a source of strong vibrations that fully affect the carburetor and EPHX valve, so it is likely that electrical contact may be lost between the wire and valve terminals.
Incorrect operation of the regulator XX
The idle air control operates a bypass (bypass) channel through which fuel and air enter the combustion chamber past the throttle, so the engine runs even when the throttle is fully closed. If XX is unstable or the car stalls at idle, there are only 4 possible reasons:
- clogged channel and its jets;
- faulty IAC;
- unstable electrical contact of the wire and IAC terminals;
- ECU malfunction.
Conclusion
If the car stalls at low speeds, it is very important to quickly determine the cause of this behavior and carry out the appropriate repairs. Neglecting this problem often leads to emergencies, for example, it is necessary to leave the intersection abruptly in order to make a jerk and avoid a collision with an approaching vehicle, but, after a sharp pressure on the gas, the engine stalls.
