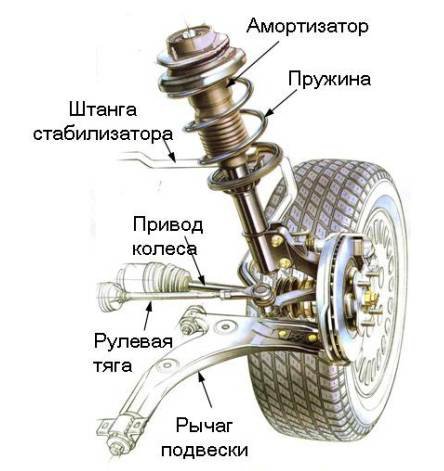
Car suspension: device, principle of operation
The suspension of a car is an important element of the chassis. Its main purpose is the connecting link between the road, wheels and body. We can also distinguish three functions that the suspension performs, and it does not matter what type of vehicle we are talking about - a racing car, a motorcycle, a medieval carriage:
- connection of wheels with a body;
- absorption of vibrations that appear during the interaction of tires with the surface of the roadway;
- ensuring the mobility of the wheels relative to the body, due to which a certain smoothness is achieved.
On our website Vodi.su, we have already touched on this topic, talking about shock absorbers or MacPherson struts. In fact, there are a huge variety of suspension types, there are two main subspecies:
- dependent suspension - the wheels of one axle are rigidly connected to each other;
- independent - the wheel can move relative to the body without affecting the position of the other coaxial wheel.
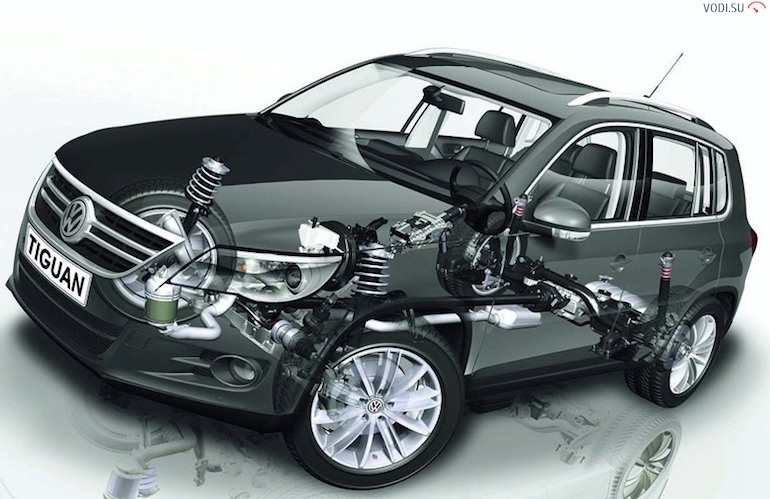

Common elements for all types of suspension are:
- elements due to which elasticity is achieved (springs, springs, torsion bars);
- elements of the distribution of the direction of force (longitudinal, transverse, double levers), these elements also provide fastening of the entire suspension system to the load-bearing body or frame of the vehicle;
- damping elements - do not allow the car to sway, that is, we are talking about shock absorbers, which, as we remember, are oil, pneumatic, gas-oil;
- anti-roll bars - a bar connecting both wheels of one axle is attached with racks;
- fasteners - silent blocks, ball bearings, metal bushings.
All these details in the process of driving on roads have a huge load, and this load is the greater, the worse the quality of the roads. Over time, all this is reflected in the quality of the ride: the car’s wheel alignment is disturbed, controllability is impaired, the car begins to “nod off” when braking, fits worse into turns, sways or rolls too much.
To avoid all these problems, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics in time, replace silent blocks, stabilizer struts, replace shock absorbers, etc.
Main types of suspensions
Both dependent and independent suspension types are still in use today. The most common dependent type is the suspension on longitudinal springs. This option is used in trucks, buses and SUVs, because it has a huge margin of safety, unlike the MacPherson strut suspension that is popular today.
In pre-war times, suspension on transverse springs was very popular. It was used on the first Ford models. It is worth saying that the Wartburg cars that were in demand at the time, produced in the GDR, were equipped with just such a spring system.
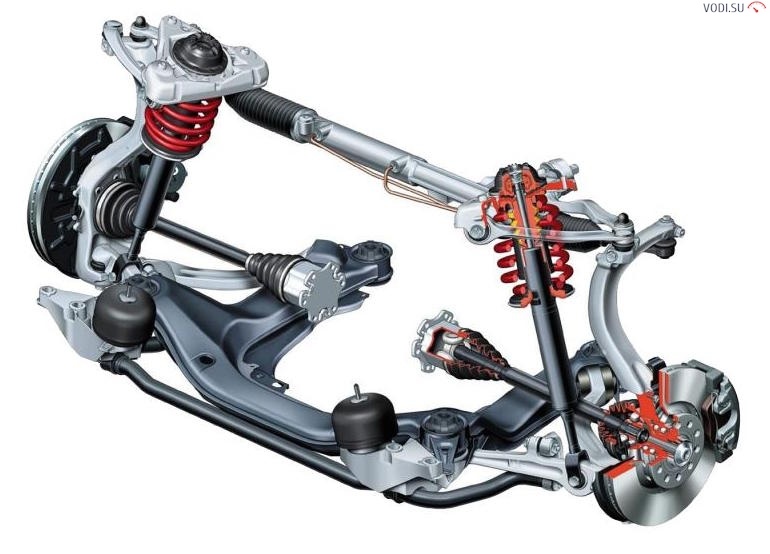
Other types of dependent suspensions include:
- suspension with control arms - still used on sports cars, trucks and passenger buses;
- with a push pipe or drawbar - used on Ford cars, it was reliable, but it was abandoned due to a complex device;
- De Dion - the drive wheels are connected by a sprung beam, the rotation to the wheels is transmitted from the gearbox through the axle shafts with hinges. This system is highly reliable, it is used on Ford Ranger, Smart Fortwo, Alfa Romeo and many other car models.
Torsion-link suspension refers to semi-dependent. It began to be installed on the first generations of the Volkswagen Golf and Scirocco. A torsion bar is a metal tube, inside of which there are elastic rods that work in torsion. Torsion bars are used as an element of elasticity or anti-roll bar.
Independent pendants are also invented a huge number of types. One of the simplest - with swinging axle shafts. The axle shafts also emanate from the gearbox, elastic elements are also used here: torsion bars, springs, springs. It was ideally suited for small-capacity non-fast cars, such as the ZAZ-965, but later they began to abandon it everywhere.
Wishbone suspension is used on the vast majority of passenger cars today. In fact, the wheels are not interconnected, but are attached to levers, which in turn are movably attached to the body.
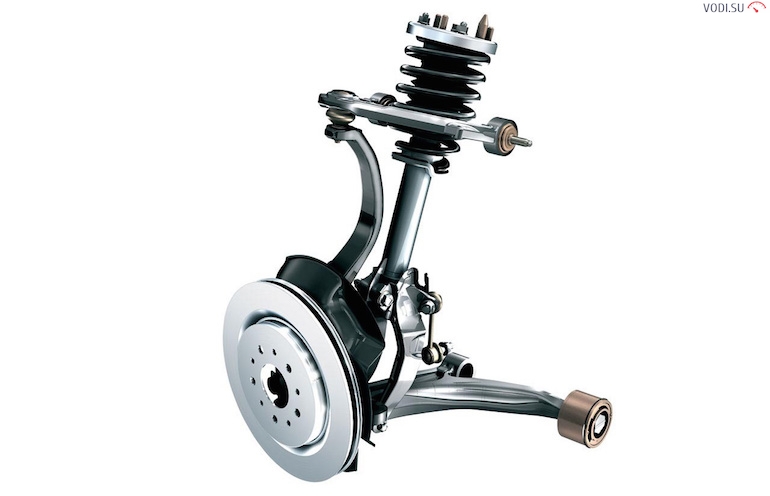

Later, such a system was repeatedly refined:
- longitudinal levers;
- oblique levers;
- double wishbones;
- multi-link suspension.
In principle, the MacPherson strut suspension is one of the types of this design, which was further developed by installing a candle - a guide strut with a shock absorber.
Well, do not forget that today active types of suspension are gaining popularity, for example, on air springs. That is, the driver can control various parameters using control devices. Adaptive suspension is a complex system equipped with a mass of sensors that collect information about speed, road surface quality, wheel position, and based on these data, the optimal driving mode is selected.


Watch this video on YouTube
Loading…