Full and usable battery capacity. How different are they? What is the best way to charge a car?
Content
 The battery in an electric or hybrid vehicle plays a major role. How does its power affect the distance that we can drive a car?
The battery in an electric or hybrid vehicle plays a major role. How does its power affect the distance that we can drive a car?
Total and usable battery capacity
Full battery capacity is the maximum battery capacity, the maximum that can be reached under certain conditions. Much more useful information is displayed in the usable battery capacity. This is the value of use that can actually be used.
What is the best way to charge the "electrician" - quickly or slowly? Or maybe super fast?
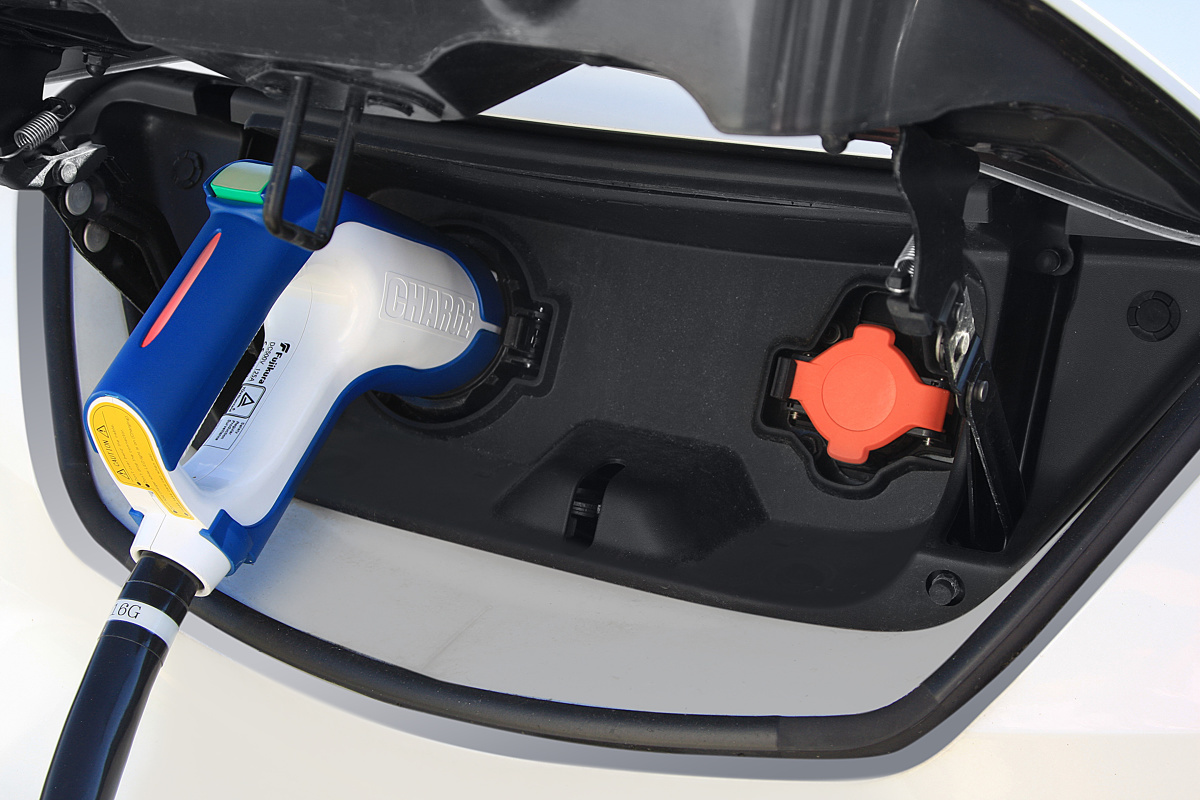
Charging a car at home is possible thanks to a converter - a device that converts alternating voltage into a constant voltage with a value that depends on the degree of discharge and the temperature of the battery. Such devices are included in the equipment of most cars available in our country. Home charging typically offers power between 3,7kW and 22kW. Such a “refueling” is the cheapest, but takes a lot of time - depending on the capacity of the batteries and their degree of wear, the type of car and the degree of discharge - it can be from several (7-8) to even several hours.
Several better options are offered by the so-called. semi-fast, up to 2 × 22 kW. Most often they can be found in underground garages, parking lots and public areas. Usually this is the so-called suspension. Wallbox or in a stand-alone version - Post. In Europe, the universal standard for AC charging connectors (the so-called Link Type 2) has been adopted.
What capacity of charging stations is available in Poland?
Other options are available for DC devices, i.e. devices that are charged with DC current, bypassing the AC/DC converter in the vehicle. The charging voltage and current are then regulated by the vehicle's electronic battery management system (BMS), which measures and analyzes the degree of discharge and the temperature of the cells. This requires communication between the vehicle and the charging station.
In Europe, two DC connector standards are most popular: CCS Combo, which is mainly used in European cars (BMW, VW, AUDI, Porsche, etc.) and CHAdeMO, which is usually used in Japanese ones (Nissan, Mitsubishi).
See also: driver's license. Can I watch the exam recording?
– The fastest way to charge your car is at Fast and UltraFast stations. The first uses direct current, with a power of 50 kW. Stations are installed and accessible on expressways and generally where short stopovers and high vehicle interchangeability are expected, so charging times must be short. The standard charging time for a 40 kWh battery does not exceed 30 minutes. Ultra-fast stations over 100kW allow more than one vehicle to be charged with DC power at stations under 50kW,” says Grzegorz Pioro, Technical Development Manager at SPIE Building Solutions. – HPC (High Performance Charging) fleets have the most power. Usually these are 6 terminals with a capacity of 350 kW each. Systems that reduce charging time to a few/few minutes are possible thanks to the development of lithium-ion battery technology, including solid electrolyte cells. However, it is worth remembering that fast and ultra-fast charging is less beneficial for the battery than slow charging, so in an effort to extend its life, you should limit the frequency of ultra-fast charging to situations in which it is required. adds Grzegorz Pioro, an electric vehicle expert.
Fast? It is cheap?
The most economical way to “refuel” is to charge at home, especially when using the night rate. In this case, the fare for 100 km is a few PLN, for example: for a Nissan LEAF that consumes 15 kWh / 100 km, at a price of 0,36 PLN / kWh, the fare for 100 km is 5,40 PLN. Charging at public stations increases operating costs. Estimated prices per kWh range from PLN 1,14 (using AC) to PLN 2,19 (DC fast charging at a 50 kW station). In the latter case, the fare for 100 km is about PLN 33, which is equivalent to 7-8 liters of fuel. Thus, even the most expensive charge is quite price-competitive compared to the cost of traveling that distance in an internal combustion vehicle. However, it is worth remembering that a statistical user in 85% of cases charges a car at home or in the office, using much cheaper energy than at DC charging stations.
– In the case of an underground garage in an office building or apartment building, cheap charging (with a power of 3,7-7,4 kW) that takes several hours is not a problem, because relatively long - more than 8 hours. For stations used in public places, with the possibility of being used as public, the price-speed ratio changes. Short downtime is more important, so 44 kW (2×22 kW) stations are used there. At present, relatively few vehicles will use 22 kW charging power, but the power of converters installed in cars is gradually increasing, which reduces time while keeping costs low, says Grzegorz Pioro from SPIE Building Solutions.
Read also: Testing Renault hybrids
