carburetor breakdowns
Content
The task of the carburetor is to produce the correct mixture (1 part gasoline and 16 parts air). With this ratio, the mixture ignites efficiently, and the internal combustion engine operates at maximum power. When the first breakdowns of the carburetor appear, the engine starts to jerk, the idle speed disappears or the consumption of gasoline increases. Determining the cause of breakdowns can be difficult, so consider the main symptoms of malfunctions.
Signs of failure in the fuel system
The presence of possible failures in the operation of the car's power system can be judged by the characteristic signs of the behavior of the vehicle on the road:
- Failure - in the process of pressing the “gas” pedal, the car continues to move at an accelerated speed (or with a slowdown) for a short period of time (from 1 to 30 seconds), and only after a while begins to pick up speed;
- Jerk - resembles a failure, but it is more short-lived;
- Rocking - periodic dips;
- A twitch is a series of jerks that follow each other;
- Sluggish acceleration is a reduced rate of increase in vehicle speed.
In addition, you can judge the presence of malfunctions in the internal combustion engine power system by the following signs:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- The start of the internal combustion engine does not work;
- Reduced or increased idle speed;
- Difficulty in the process of starting a hot / cold internal combustion engine;
- Difficult operation of the internal combustion engine of a car in cold running mode.
Changes in gas distribution phases, wear of the camshaft cams, incorrect adjustment of heat gaps, reduced or uneven compression in the cylinders, and valve burnout significantly reduce vehicle power, cause vibration and increase fuel consumption.
the carburetor and its breakdowns also play an important role. Consider the most common carburetor breakdowns using the Solex as an example. How to properly clean, check and adjust the carburetor, using the VAZ 2109 as an example, is described in the article. So.
If the cylinder-piston group is worn out, crankcase gases, oil vapors and tarry gases can also enter the carburetor area, clog the filter element, and also settle on jets and other carburetor elements, thereby disrupting the operation of the internal combustion engine.
Typical carburetor failures
If the internal combustion engine does not start or stalls immediately after starting. Perhaps this is due to the fact that there is no fuel in the float chamber or the composition of the mixture is disturbed (for example, the mixture is too rich or vice versa).
ICE at idle is unstable or stalls regularly. With the correct operation of other carburetor systems, more breakdowns are possible due to the following factors:
- Clogged channels or idle jets;
- Malfunctions of the solenoid valve;
- Malfunctions of the elements of the EPHH and the control unit;
- Malfunctions and deformation of the rubber sealing ring - the "quality" screw.
Since the transition system of the first chamber interacts with the cold running system, at partial speeds, a failure is possible, and sometimes even a complete stop of the internal combustion engine during the soft start of the car. By flushing or purging the channels, the blockage can be eliminated, but it will need to be partially disassembled. you also need to change the faulty parts.
High idle speed
Low/high idle may cause:
- Faulty idle adjustment:
- Reduced / increased level of fuel in the chamber;
- Clogged air or fuel jets;
- Oxygen suction into the inlet pipeline or carburetor through connecting hoses or at joints;
- Partial opening of the air damper.
Difficult start of the internal combustion engine and fuel consumption
Difficulty starting a cold engine can cause incorrect adjustment of the trigger mechanism. Partial closing of the air damper can cause the mixture to become lean, which in turn will cause the absence of flashes in the cylinders, and incorrectly opening it after starting the internal combustion engine enriches the mixture sufficiently, so the internal combustion engine “chokes”.
Difficulty starting the car when the engine is warm may be caused by the fact that a rich mixture enters the cylinders due to the high level of fuel that is in the float chamber. The reason for this may be a violation of the adjustment of the fuel chamber or the fuel valve is not well sealed.
Excessive fuel consumption. Eliminating this "defect" is the most difficult, as it can be caused by various reasons. Initially, it is worth making sure that there is no increased resistance to the movement of the vehicle, which is facilitated by braking pads on drums or discs, violation of wheel mounting angles, deterioration of aerodynamic data when transporting bulky cargo on the roof, or loading a car. Driving style also plays an important role.
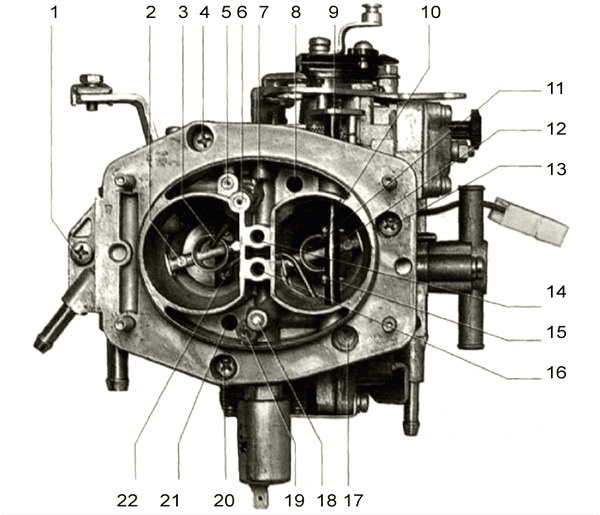
1, 4, 13, 17, 20 - screws securing the carburetor cover to the body; 2 - small diffuser (sprayer) of the main dosing system of the second chamber; 3 - econostat atomizer; 5 - air jet of the transition system of the second chamber; 6, 7 - plugs of econostat channels; 8, 21 - balancing holes of the float chamber; 9 - axis of the air damper; 10, 15 - screws for fastening the air damper; 11 - small diffuser (sprayer) of the second chamber; 12 - air damper; 14 - channel of the main air jet of the second chamber; 16 - channel of the main air jet of the first chamber; 18, 19 - plugs of idle channels; 22 - accelerator pump sprayer
Violations of the functionality of the carburetor can lead to high fuel consumption:
- breakdown of the EPHH system;
- Clogged air jets;
- Loose closing of the solenoid valve (leakage of fuel between the walls of the channel and the jet);
- Incomplete opening of the air damper;
- Economizer defects.
A deep dip to a complete stop of the internal combustion engine with an open throttle valve of one chamber can be triggered by clogging of the main fuel jet. If the internal combustion engine of the car is idling or in the mode of insignificant loads, then the fuel consumption of the internal combustion engine is quite small. Trying to enter the full load mode, the consumption of the fuel mass increases sharply, there is not enough patency for the fuel jets that are clogged, failures appear in the operation of the internal combustion engine.
car jerks while driving, as well as sluggish acceleration with a “smooth” pressing of the “gas” often provokes a low fuel level with incorrect adjustment of the float system. Rocking, dips and jerks of the car are common phenomena under increased loads, which disappear when switching to a cold run. usually, they are associated with interruptions in the fuel supply system, as well as the following factors:
- Fuel pump valves are not tight;
- The mesh filters of the fuel intake and carburetor are clogged;
Dips with a sharp press of "gas", which disappear when the car's internal combustion engine is running for five seconds, in the same mode can be caused by a breakdown of the accelerator pump.

