Understanding Electric Vehicle Batteries
Content
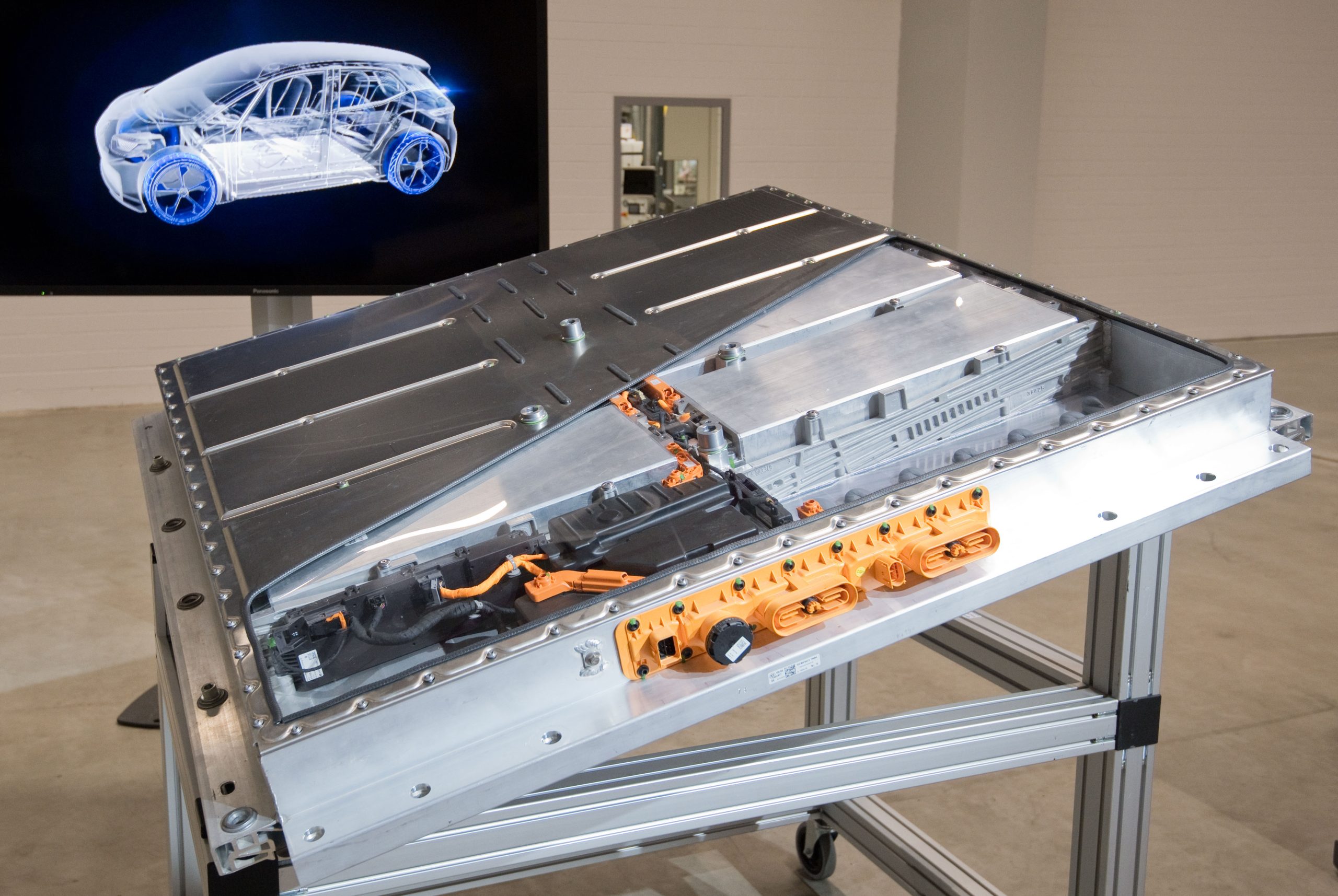
Electric vehicles contain rechargeable lithium-ion batteries designed to generate high power. They still weigh significantly less than their energy density suggests and reduce overall vehicle emissions. Plug-in hybrids have charging capabilities as well as compatibility with gasoline for refueling. Many non-hybrid electric vehicles advertise their "zero-emissions" capabilities.
Electric vehicles (Evs) get their name from the use of electricity instead of gasoline. "Refueling" is translated as "charging" the car's battery. The mileage you get from a full charge depends on the EV manufacturer. A car with 100 miles driving 50 miles every day will have a so-called "deep discharge" of its battery, which is depleted by 50% every day - this is difficult to make up with most home charging stations. For a trip of the same distance, a car with a higher full charge range would be more ideal because it gives a "surface discharge". Smaller discharges reduce the overall degradation of the electric battery and help it last longer.
Even with the smartest purchase intentions, an EV will eventually need a battery replacement, just like a battery-powered SLI (Start, Light, and Ignition) vehicle. Conventional car batteries are nearly 100% recyclable, and electric batteries approach that with a 96% recycle rate. However, when it comes time to replace your electric vehicle's battery, if it's not covered by the car's warranty, it could be the highest price you pay for car maintenance.
Replacing electric vehicle batteries
To begin with, due to the high price of an electric battery (it takes up a large part of your payment for the electric car itself), buying a replacement can be costly. To counteract this situation, most electric vehicle manufacturers provide a battery repair or replacement warranty. Within a few miles or years, and if the battery no longer charges above a certain percentage (usually 60-70%), it is eligible for a replacement with manufacturer support. Be sure to read the fine print when getting services - not all manufacturers will refund the cost of work done on a battery by a technician outside the company. Some popular electric vehicle warranties include:
- BMW i3: 8 years or 100,000 miles.
- Ford Focus: 8 years or 100,000 – 150,000 miles depending on condition.
- Chevy Bolt EV: 8 years or 100,000 miles.
- Nissan Leaf (30 kW): 8 years or 100,000 miles (24 kW only covers 60,000 miles).
- Tesla Model S (60 kW): 8 years or 125,000 miles (85 kW includes unlimited miles).
If it appears that your electric vehicle is no longer holding a full charge or seems to be draining faster than expected, the battery or battery service may be required. A qualified mechanic can often do the job and may even offer you compensation for your old battery. Most of its components can be recycled and repurposed for future use. Make sure your vehicle's warranty covers non-manufacturer work to save on service costs.
Factors Affecting Battery Life
Lithium batteries for electric vehicles work cyclically. The charge and subsequent discharge are counted as one cycle. As the number of cycles increases, the battery's ability to hold a full charge will decrease. Fully charged batteries have the highest possible voltage, and built-in battery management systems prevent voltage from exceeding the operating range and temperature. In addition to the cycles for which a battery is designed for a significant amount of time, factors that negatively affect the long life of a battery include:
- Extremely high or low temperatures.
- Overcharge or high voltage.
- Deep discharges (battery discharge) or low voltage.
- Frequent high charging currents or discharges, which means too many fast charges.
How to increase battery life
To extend the life of your electric vehicle battery, follow these 7 tips:
- 1. Do not leave the battery fully charged. Leaving it fully charged will stress the battery too often and drain it faster.
- 2. Store in a garage. If possible, keep your electric vehicle in a garage or temperature-controlled room to avoid extreme temperatures.
- 3. Plan walks. Preheat or cool down your electric vehicle before going outside, unless you have disconnected the vehicle from your home charging station. This practice will help you avoid using up battery power while driving.
- 4. Use economy mode if available. Electric vehicles with "eco mode" cut off the car battery during a stop. It acts as an energy-saving battery and helps minimize your vehicle's overall energy consumption.
- 5. Avoid speeding. Battery efficiency tends to drop when you go over 50 mph. When applicable, slow down.
- 6. Avoid hard braking. Hard braking uses the car's normal brakes. Regenerative brakes activated by gentle braking conserve battery power, but friction brakes do not.
- 7. Plan a vacation. Set the charge level to 50% and leave the electric vehicle plugged in for long trips if possible.
Electric vehicle batteries are constantly being improved with each new car model. Thanks to further developments, they are becoming more efficient and cost-effective. Innovations in battery life and design are driving the popularity of electric vehicles as they become more affordable. Charging stations are popping up in new locations across the country to serve the car of the future. Understanding how EV batteries work allows you to maximize the efficiency that an EV owner can get.