When charging the battery, one bank does not boil
Content
By connecting a discharged battery to an automatic charger, many motorists go out for several hours and automatically turn off, after which only the terminals remain and the battery is returned back under the hood.

If you carefully observe the charging process, you can find the following. When the necessary charge accumulates in the banks, that is, the compartments with plates and electrolyte, they gradually begin to boil. If this is a charger without auto-shutdown, boiling is fixed until the charger is turned on.
It is believed that with the correct course of the charging process, after charging is completed, all 6 compartments (banks) of 12b batteries begin. But it happens that one of the cans does not boil. Regarding this phenomenon, motorists are regulated by legitimate questions.
Why does boiling occur, and is it the norm
Battery banks are called compartments inside the battery. They contain packages of individual lead-based plates surrounded by an electrolyte. It is a mixture of distilled water and sulfuric acid.
If this is a standard car battery, there will be 6 such cans. Each of them gives out about 2,1 V, which in total allows you to get about 12,7 V when connected in series.
The effect of the application can be observed only on special serviced batteries, where there are plugs. In maintenance-free batteries, boiling is detected, which can be produced using methods, including the use of boiling.
It is important to understand that boiling in this case is not available. This is not due to the liquid boiling under the influence of high temperature, as happens when a conventional kettle of water rises. Here an electrochemical reaction takes place, as a result of which water from the electrolyte composition decomposes into 2 gases. These are hydrogen and oxygen. This happens at temperatures below 100 degrees Celsius, and sometimes even at negative temperatures. Gas bubbles burst out, which creates the effect of boiling.
All this suggests that charging can indeed be accompanied by such a phenomenon. If the electrolyte begins to boil, this is normal. This is like a hint that the battery has stopped charging, it has received a shortage
The electric current supplied to the battery during charging provokes electrochemical. It is the current that provokes the decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen. Bubbles rush up, and all this resembles the usual boiling of water.
The gas released during drilling of the electrolyte is highly explosive.
The charging procedure must be performed in a well-ventilated patient's body. Also, there were no flame sources near the loaded battery. In the event of an inadmissibility.
Seething becomes a signal that the battery has fully replenished the lost charge. If the signs are left to accumulate further, overcharging will already begin, followed by the release of water and suspicion of the concentration of sulfuric acid in a large number of electrolytes. When the water level drops, the amount of fluid in the battery decreases. Because of this, the plates are exposed, a short circuit, destruction is possible.
If it is necessary to increase the value of the electrolyte, it is necessary to bring the battery to a state of baldness. In this case, the water evaporates, and the concentration of acids remains unchanged.
The main thing here is not to overdo it. The electrolyte can be allowed to boil at a minimum current. If the seething is intense, this can lead to the destruction of the plate and the complete exit from the battery structure.
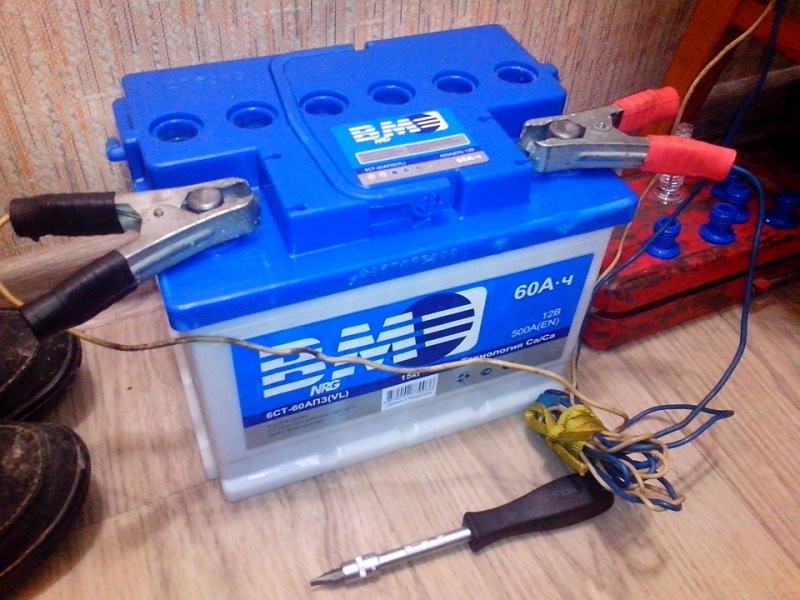

Boiling of battery fluid is normal. But at the same time, it is not entirely normal if this does not happen in one of the compartments.
Because of what one bank does not boil
It turns out that when charging the battery, one bank for some reason does not boil. This caused suspicion and questions from the car owner.
There are several main reasons. Moreover, in some cases, the restoration of battery tissue is no longer possible. There are problems for this.
As for the reasons, due to one can in a car battery does not boil, they can be taken into account:
- The section closed, some foreign object got into the compartment, the plates in the jar crumbled. All this does not allow sections to receive a charge, like all other banks.
- Balance imbalance. This is due to the fact that the level or concentration of electrolyte in one compartment is different. The jar needs a little time to boil more too.
- Banal end of battery life. The jar has completely crumbled, the electrolyte in it has become cloudy, and it will no longer be able to work normally.
Statistics show that in about 50% of cases, returning the battery to work in such a situation is possible.
Trying to restore the battery or not is a personal matter for everyone.
How to act correctly
Now more specifically about what to do if one of your battery banks for one reason or another
In this regard, experts give a few recommendations:
- Section restoration. If you do not boil 2 Banks when charging a car battery, Rebuilding sections is almost pointless. If the problem is only in one compartment, it's worth a try. The quality index for the external object. Washing with distilled water helps a lot. Moreover, this way you can clean the entire battery, then fill it with fresh electrolyte and put it on charge.
- Discharge. The essence of the method is to completely discharge the battery memory. This will balance the balance between them. You can do this by force, or wait for a natural discharge, which is very long. After that, install the battery on the charger, select the desired mode. Quite often, after such a manipulation, charging is already going on in all compartments in the same way.
- Buying a new battery. Having dismantled the compartment with a cloudy electrolyte, where the lead plates dissolve literally before our eyes, Nothing can be faked. Such content is not provided. There is a high probability that the shedding of the plate has begun in other compartments.
Flushing and recovery tasks are far from flat. This requires several complex operations, strictly observe safety precautions.
Having found out why exactly one bank in the next battery does not boil, you can understand whether it makes sense to restore, or the most likely and only true outcome of a new purchase of a power source.

Charging that you are faced with a situation where, when charging the battery, some 1 can. In this case, there is a certain algorithm of actions. It looks like advice:
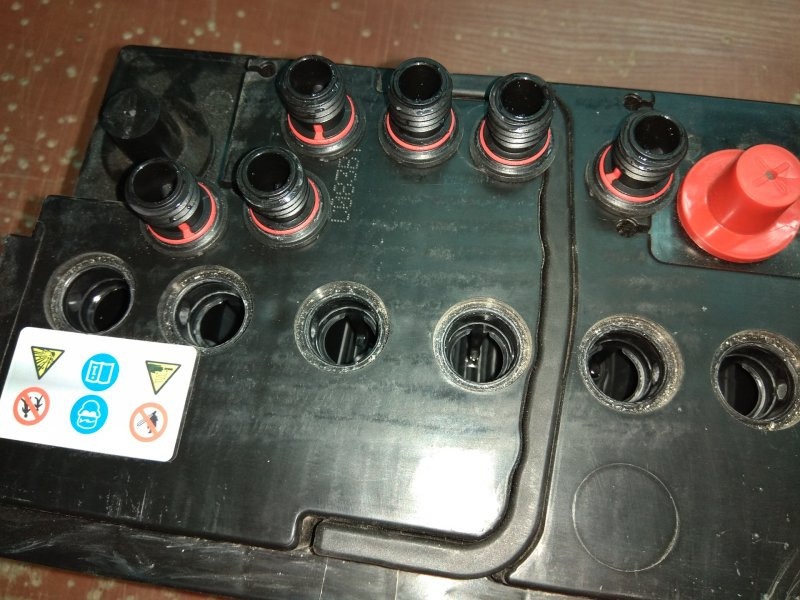
- Unscrew the lids from the cans of the battery being serviced by the assigned flashlight, shine it towards you. Look at the state of the electrolyte. Maintenance-free batteries usually have a clear plastic area. Through it, you can also understand the state of the liquid. If the volume is opaque, arm yourself with a bulb or syringe, extract a small amount of liquid and look at it.
- If the liquid turned out to be transparent, this turned out to be a good characteristic. Here, for sure, there is a problem of seething in the closure of banks, or in its undercharging. If the electrolyte is cloudy, then it is almost certain that the lead plates have crumbled. This provoked a change in the color of the working fluid. In its normal state, the electrolyte looks like ordinary water.
- In a transparent state of the electrolyte, a charger may appear to equalize the charge Sxbo all. To do this, the battery must be completely discharged, and then the charge current must be applied.
- If, after such an attempt, copying is still not observed on one bank, options 2 are the purchase of a new battery, Or disassemble the old language In the second case, it is necessary to cut the upper part, From the features from the problematic compartment of the plate case, look at them for possible closure. If there is no short circuit, put the plates in place, fill with electrolyte to the desired level and, as a result of soldering, close the case.
Some may conclude that there is nothing terrible and dangerous in the absence of the seething effect of just one section.
In fact this is not true. If one section does not work, the amount of reserves is about 2,1 V of power from the available 12,6–12,7. When the charging current from the generator is absorbed in this state, this can provoke boiling of the electrolyte, Chinese overcharging, and failure of the remaining sections. Plus, the generator itself and its components suffer.
It is not always possible to restore a rechargeable car battery if one of the cans fails. It all depends on what exactly caused this situation.
What experts do not recommend doing is destroying the battery case. In serviced batteries, it is only allowed to unscrew the banks. It is difficult to predict what the breakdown of the top cover and its subsequent soldering will lead to. But almost certainly do not forget about the expected service life.
Objectively, the most likely outcome will be to hand over the worn-out battery for recycling and search for a new appearance of quality with the estimated potential of the car.