The principle of operation and the composition of the air suspension
Content
With the automotive industry gradually shifting to the use of more compact and precise coil springs in most suspension applications instead of bulky coarse springs, it is logical to expect continued evolution of the running gear. Partially it has already happened - metal in elastic elements is often replaced with gas. Of course, enclosed under pressure in a strong shell. But a simple replacement of the springs with air springs was not enough, the new suspension implies the active use of electronic devices and actuators.

Common and Unique Air Suspension Assemblies
Features of the use of pneumatics as elastic elements led to the possibility of remote operational changes in the characteristics of the suspension. Starting from a simple change in the position of the body above the road in statics and ending with active control functions.
In general, having retained the classification of suspension types, air springs caused the appearance of a number of additional devices in the chassis. The amount of equipment depends on the specific implementation by different manufacturers. These can be electrical and mechanical compressors, valve platforms, electronic control units, and sometimes hydraulic kits. It is not difficult to give such systems the properties of adaptation and selection of characteristics from the driver's seat. And outwardly, it will largely resemble traditional dependent suspensions, two- and multi-link independents, MacPherson struts or simple torsion beams. Up to the complete interchangeability of parts, when you can simply remove the pneumatics and install coil springs in the same place.
The composition of the equipment and individual components
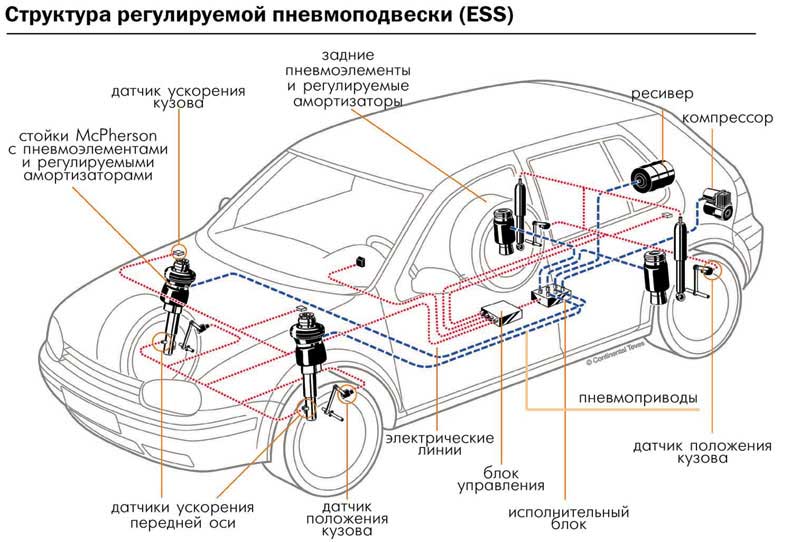
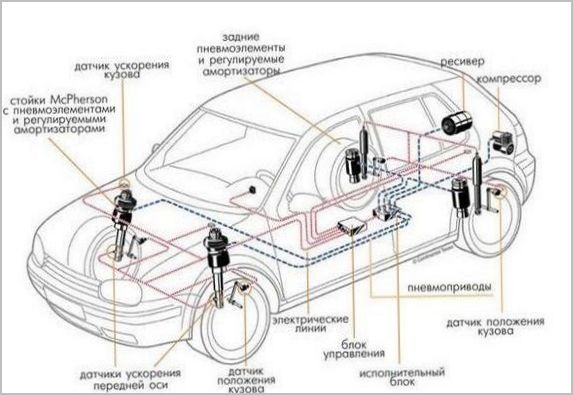
The purpose and functions of the basic elements have changed little in the course of the evolution of air suspension, only their design and control algorithms have been improved. The usual composition includes:
- air springs installed instead of springs or springs;
- an air compressor that maintains and regulates pressure in pneumatics;
- control and distribution air fittings with a system of electromagnetic valves;
- air filters and dryers;
- body height sensors for each wheel;
- control electronic unit;
- air suspension control panel.
It is possible to use other devices associated with the presence of additional functions.
Pneumatic cushions (cylinders)
The elastic suspension element is an air spring in the broadest sense of the word, theoretically a spring is also a spring. In practice, this is air under pressure in a rubber-metal case. Changing the geometry of the shell is possible in given directions, reinforcement prevents arbitrary deviation from the shape.

It is possible to integrate a pneumatic element with a damping shock absorber in a single construct of a telescopic air strut. This achieves the compactness of a single unit in the composition, for example, MacPherson-type suspension. Inside the rack there is a sealed chamber with compressed air and the usual hydraulics of a classic shock absorber.
Compressors and receivers
To compensate for leaks and prompt pressure changes in the pneumatic elements, the system is equipped with an autonomous compressor with an electric drive from the power driver of the control unit. The operation of the compressor is facilitated by the presence of an air storage - receiver. Due to the accumulation of compressed air in it, as well as bypassing the pressure from the cylinders, the compressor turns on much less frequently, which saves its resource, and also reduces the load on the air preparation units, its filtration and drying.

The pressure in the receiver is controlled by a sensor, according to the signals of which the electronics send commands to replenish the compressed gas reserves, including the compressor. When a decrease in clearance is required, the excess air is not discharged into the atmosphere, but enters the receiver.
Electronic regulation
Receiving information from ride height sensors, usually these are elements related to the position of suspension arms and rods, as well as pressure at different points, the electronic unit completely controls the position of the body. Thanks to this, the suspension acquires fundamentally new functions, it can be made adaptive to varying degrees.
To provide new features, controller connections with other vehicle systems have been introduced. He is able to take into account the trajectory of the car, the impact of the driver on the controls, the speed and nature of the road surface. It becomes quite simple to optimize the behavior of the chassis, giving it a lower center of gravity to increase stability at high speed, to minimize body roll, thereby increasing the safety of the car as a whole. And off-road, on the contrary, increase the ground clearance, allow extended articulation of the axles. Even when parked, the car will become more driver-friendly by lowering the height of the body for easier loading.
Practical use of the advantages of air suspension
Starting with a simple ride height adjustment, car designers began to introduce advanced features into the suspension. This made it possible, among other things, to introduce pneumatics as an option on car models that are basically equipped with a conventional suspension. With subsequent extended advertising of new features and return on investment in development.

It became possible to separately control the suspensions on the sides of the car and along the axles. Several fixed settings are offered for selection in the car's main menu. In addition, a customized setting is available for advanced users with memory retention.
The possibilities of pneumatics are especially important for freight transport, where there is a large difference in mass for a loaded and empty car or road train. There, clearance control systems have become indispensable, no springs can be compared with the capabilities of air springs.
For high-speed cars, it is important to adapt the suspension to work on highways. The lower ground clearance not only improves stability, but also improves aerodynamics, increasing fuel economy and driving performance.
Off-road vehicles on pneumatics, especially those whose use is not limited to extreme conditions, are able to significantly increase the geometric cross-country ability when it is really required. Lowering the body to a safe level as speed increases, which happens automatically.
Comfort is also fundamentally improved. The properties of gas under pressure are several times more preferable than any spring metal. Suspension characteristics in any conditions, even if adaptation is not used, will be completely determined by shock absorbers, the properties of which are much easier and more accurately programmed during setup and manufacture. And the disadvantages in the form of complication and the associated reliability have long been determined not by fundamental features, but by the resource laid down by the manufacturer.