The principle of operation of the turbocharger and its design
Content
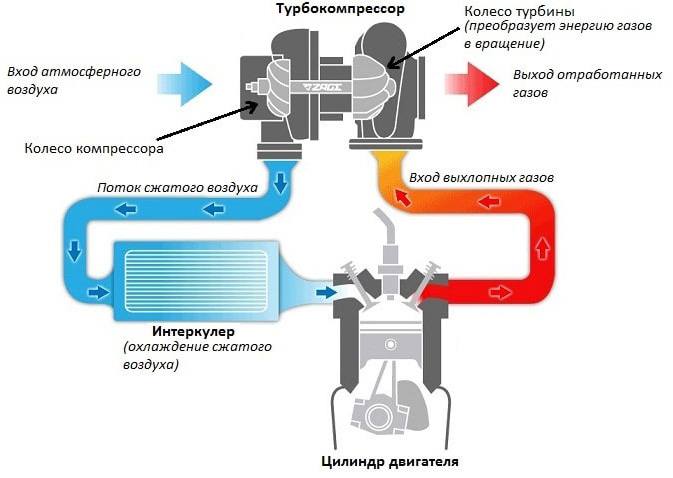
A turbocharger (turbine) is a mechanism used in cars to force air into the cylinders of an internal combustion engine. In this case, the turbine is driven solely by the flow of exhaust gases. The use of a turbocharger allows you to increase engine power up to 40% while maintaining its compact size and low fuel consumption.
How the turbine is arranged, the principle of its operation
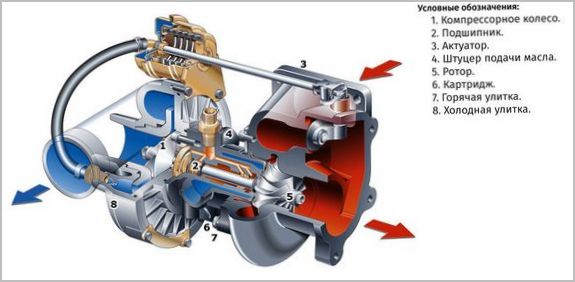
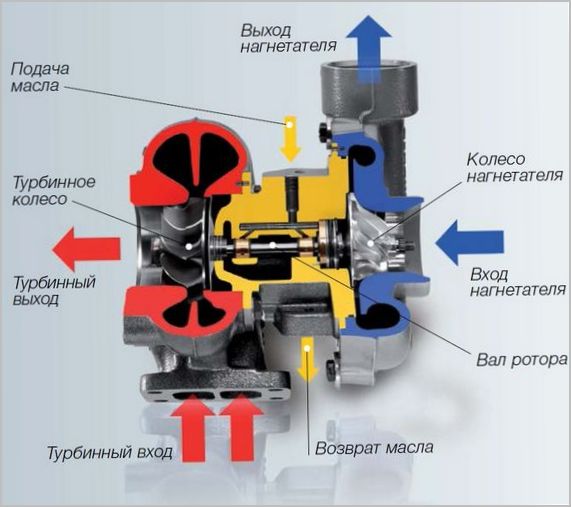
The standard turbocharger consists of:
- Корпус. Made from heat resistant steel. It has a helical shape with two differently directed tubes provided with flanges for installation in a pressurization system.
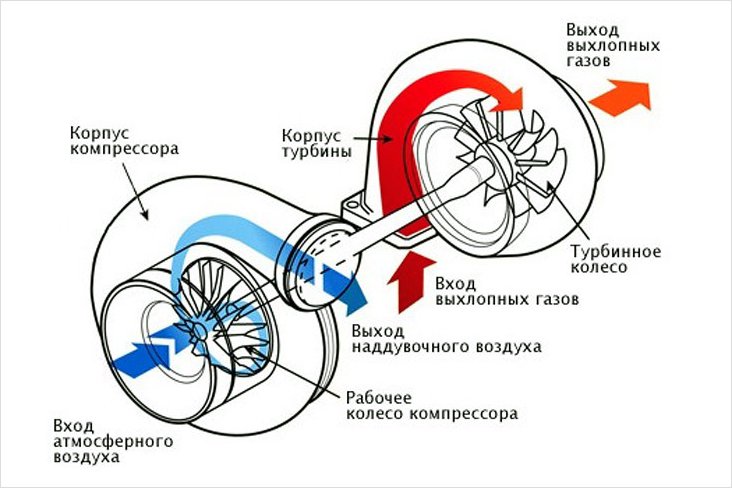
- Turbine wheel. It converts the energy of the exhaust into rotation of the shaft on which it is rigidly fixed. Made from heat resistant materials.
- Compressor wheel. It receives rotation from the turbine wheel and pumps air into the engine cylinders. The compressor impeller is often made of aluminum, which reduces energy losses. The temperature regime in this zone is close to normal and the use of heat-resistant materials is not required.
- Turbine shaft. Connects the turbine wheels (compressor and turbine).
- Plain bearings or ball bearings. Needed to connect the shaft in the housing. The design can be equipped with one or two supports (bearings). The latter are lubricated by the general engine lubrication system.
- bypass valve. PDesigned to regulate the flow of exhaust gases acting on the turbine wheel. This allows you to control the boost power. Valve with pneumatic actuator. Its position is controlled by the engine ECU, which receives a signal from the speed sensor.
The basic principle of operation of the turbine in gasoline and diesel engines is as follows:
- The exhaust gases are directed to the turbocharger housing where they act on the turbine blades.
- The turbine wheel begins to rotate and accelerate. Turbine rotation speed at high speeds can reach 250 rpm.
- After passing through the turbine wheel, the exhaust gases are discharged into the exhaust system.
- The compressor impeller rotates in sync (because it is on the same shaft as the turbine) and directs the compressed air flow to the intercooler and then to the engine intake manifold.
Turbine characteristics
Compared to a mechanical compressor driven by a crankshaft, the advantage of a turbine is that it does not draw energy from the engine, but uses energy from its by-products. It is cheaper to manufacture and cheaper to use.

Although technically the turbine for a diesel engine is essentially the same as for a gasoline engine, it is more common in a diesel engine. The main feature is the modes of operation. Therefore, less heat-resistant materials can be used for a diesel engine, since the exhaust gas temperature averages from 700 °C in diesel engines and from 1000 °C in gasoline engines. This means that it is not possible to install a diesel turbine on a gasoline engine.
On the other hand, these systems also have different levels of boost pressure. In this case, it should be taken into account that the efficiency of the turbine depends on its geometric dimensions. The pressure of the air blown into the cylinders is the sum of two parts: 1 atmospheric pressure plus the excess pressure created by the turbocharger. It can be from 0,4 to 2,2 atmospheres or more. Since the principle of operation of the turbine in a diesel engine allows more exhaust gas to be taken in, the design of a gasoline engine cannot be installed even in diesel engines.
Types and service life of turbochargers
The main disadvantage of the turbine is the "turbo lag" effect that occurs at low engine speeds. It represents a time delay in response to a change in engine speed. To overcome this shortcoming, various types of turbochargers have been developed:
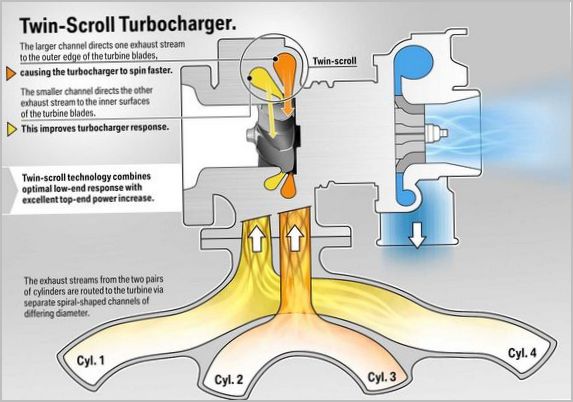
- Twin-scroll system. The design provides for two channels separating the turbine chamber and, as a result, the exhaust gas flow. This provides faster response times, maximum turbine efficiency and prevents clogging of the exhaust ports.
- Turbine with variable geometry (nozzle with variable geometry). This design is most commonly used in diesel engines. It provides a change in the cross-section of the inlet to the turbine due to the mobility of its blades. Changing the angle of rotation allows you to adjust the flow of exhaust gases, thereby adjusting the speed of the exhaust gases and the speed of the engine. In gasoline engines, variable geometry turbines are often found in sports cars.
The disadvantage of turbochargers is the fragility of the turbine. For gasoline engines, this is an average of 150 kilometers. On the other hand, the turbine life of a diesel engine is slightly longer and averages 000 kilometers. With prolonged driving at high speed, as well as with the wrong choice of oil, the service life can be reduced by two or even three times.
Depending on how the turbine works in a gasoline or diesel engine, performance can be assessed. The signal to check is the appearance of blue or black smoke, a decrease in engine power, as well as the appearance of a whistle and rattle. To avoid breakdowns, it is necessary to change the oil, air filters and carry out regular maintenance in time.