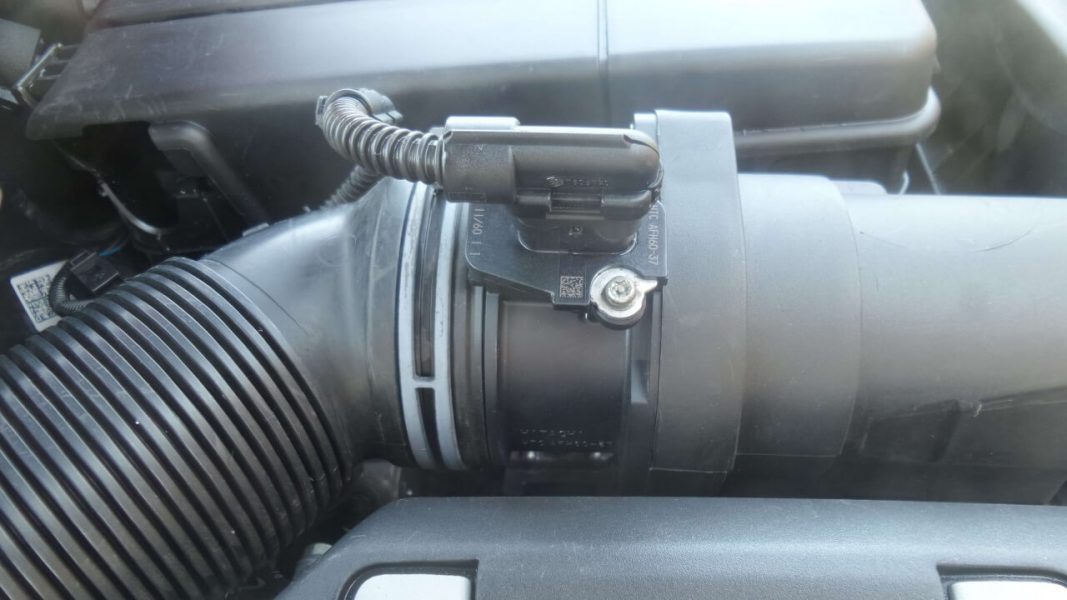
Air Mass Meter - Mass Air Flow and Intake Manifold Pressure Sensor MAP
Content
 More than one motorist, especially in the case of the legendary 1,9 TDi, has heard the name "mass air flow meter" or is popularly called "air weight". The reason was simple. Too often, a component failed and led, in addition to the burning light of the engine, to a significant drop in power or the so-called choking of the engine. The component was quite expensive in the early days of the TDi era, but fortunately has become significantly cheaper over time. In addition to the delicate design, careless replacement of the air filter "helped" it to shorten its life. The meter's resistance has improved significantly over time, but it can still fail from time to time. Of course, this component is present not only in the TDi, but also in other diesel and modern gasoline engines.
More than one motorist, especially in the case of the legendary 1,9 TDi, has heard the name "mass air flow meter" or is popularly called "air weight". The reason was simple. Too often, a component failed and led, in addition to the burning light of the engine, to a significant drop in power or the so-called choking of the engine. The component was quite expensive in the early days of the TDi era, but fortunately has become significantly cheaper over time. In addition to the delicate design, careless replacement of the air filter "helped" it to shorten its life. The meter's resistance has improved significantly over time, but it can still fail from time to time. Of course, this component is present not only in the TDi, but also in other diesel and modern gasoline engines.
The amount of flowing air is determined by cooling the temperature-dependent resistance (heated wire or film) of the sensor with flowing air. The electrical resistance of the sensor changes and the current or voltage signal is evaluated by the control unit. The air mass meter (anemometer) directly measures the mass quantity of air supplied to the engine, i.e. that the measurement is independent of the density of the air (as opposed to the measurement of volume), which depends on the pressure and temperature of the air (altitude). Since the fuel-air ratio is specified as a mass ratio, for example 1 kg of fuel per 14,7 kg of air (stoichiometric ratio), measuring the amount of air with an anemometer is the most accurate measurement method.
Advantages of measuring the amount of air
- Accurate determination of the mass air quantity.
- Fast response of the flow meter to changes in flow.
- No errors caused by changes in air pressure.
- No errors caused by changes in intake air temperature.
- Easy installation of an air flow meter with no moving parts.
- Very low hydraulic resistance.
Air volume measurement with heated wire (LH-Motronic)
In this type of petrol injection, an anemometer is included in the common part of the intake manifold, the sensor of which is a stretched heated wire. The heated wire is kept at a constant temperature by passing an electric current that is about 100 ° C higher than the temperature of the intake air. If the motor draws in more or less air, the temperature of the wire changes. Heat generation must be compensated for by changing the heating current. Its size is a measure of the amount of air drawn in. The measurement takes place approximately 1000 times per second. If the hot wire breaks, the control unit goes into emergency mode.

Since the wire is in the suction line, deposits can form on the wire and affect the measurement. Therefore, every time the engine is turned off, the wire is briefly heated to about 1000 ° C based on a signal from the control unit, and deposits on it burn.
Platinum heated wire with a diameter of 0,7 mm protects the wire mesh from mechanical stress. The wire can also be located in the bypass duct leading to the inner duct. Contamination of the heated wire is prevented by covering it with a glass layer and by the high air velocity in the bypass channel. Incineration of impurities is no longer required in this case.
Measuring the amount of air with a heated film
A resistance sensor formed by a heated conductive layer (film) is placed in an additional measuring channel of the sensor housing. The heated layer is not subject to contamination. The intake air passes through the air flow meter and thus affects the temperature of the conductive heated layer (film).
The sensor consists of three electrical resistors formed in layers:
- heating resistor RH (sensor resistance),
- resistance sensor RS, (sensor temperature),
- heat resistance RL (intake air temperature).
Thin resistive platinum layers are deposited on a ceramic substrate and connected to the bridge as resistors.
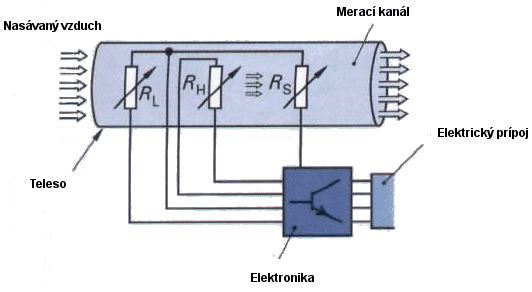
The electronics regulate the temperature of the heating resistor R with variable voltage.H so that it is 160 ° C higher than the intake air temperature. This temperature is measured by the resistance RL depends on the temperature. The temperature of the heating resistor is measured with a resistance sensor RS... As the air flow increases or decreases, the heating resistance cools more or less. The electronics regulate the voltage of the heating resistor via the resistance sensor so that the temperature difference reaches 160 ° C again. From this control voltage, the sensor electronics generate a signal for the control unit corresponding to the air mass (mass flow).

In the event of a malfunction of the air mass meter, the electronic control unit will use a substitute value for the opening time of the injectors (emergency mode). The substitute value is determined by the position (angle) of the throttle valve and the engine speed signal - the so-called alpha-n control.
Volumetric air flow meter
In addition to the mass air flow sensor, the so-called volumetric, a description of which can be seen in the figure below.
If the engine contains a MAP (manifold air pressure) sensor, the control system calculates air volume data using engine speed, air temperature and volumetric efficiency data stored in the ECU. In the case of MAP, the scoring principle is based on the amount of pressure, or rather vacuum, in the intake manifold, which varies with engine load. When the engine is not running, the intake manifold pressure is the same as the ambient air. The change takes place while the engine is running. Engine pistons pointing to bottom dead center suck in air and fuel and thus create a vacuum in the intake manifold. The highest vacuum occurs during engine braking when the throttle is closed. A lower vacuum occurs in the case of idling, and the smallest vacuum occurs in the case of acceleration, when the engine draws in a large amount of air. MAP is more reliable but less accurate. MAF - Airweight is accurate but more prone to damage. Some (especially powerful) vehicles have a Mass Air Flow (Mass Air Flow) and MAP (MAP) sensor. In such cases, the MAP is used to control the boost function, to control the exhaust gas recirculation function, and also as a backup in the event of a mass air flow sensor failure.

