Different engine architectures?
There are several engine architectures, two of which are basic. Let's open them up and try to identify the advantages and disadvantages of each.

Engine in line
An inline engine is what is most often done in the automotive world, and it is certainly the one that your car is equipped with. Cylinders are aligned on one axis and move from bottom to top.
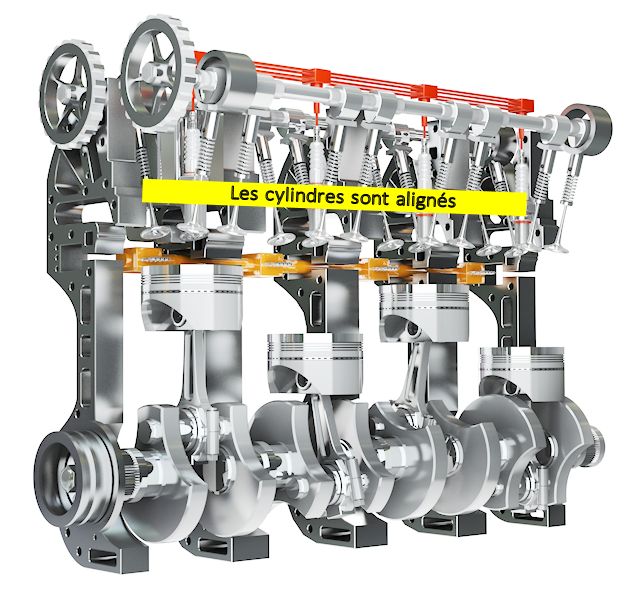
Here's what can be noted on the positive side:
- The simpler mechanics are therefore more economical to manufacture (and it is also the most common design in France).
- Generally more efficient (reduced) consumption on an in-line engine
- Smaller than a V-engine, but longer ... The transverse placement frees up maximum living space.
On the other hand:
- This type of engine takes up more space (in length rather than width) under the engine cover because the cylinders are more “spread out”, therefore a larger surface is required. Thus, the V-shaped design allows the cylinders to be stacked in a smaller volume, or rather in a more uniform volume.
- Internal masses are less balanced than in a V-engine. An inline engine usually requires an internal counterweight system called a balance shaft. However, it should be noted that the problem no longer exists with 6 cylinders in line, which then benefit from better balancing thanks to the multiplication of masses in motion.
engine on board
In the case of a flat engine, the pistons this time work horizontally (in the opposite direction) instead of up and down. Also, half of the pistons move in one direction and the other half in the opposite direction. There are two types of flat motors: Boxer and 180°V motor.
It is a Flat 6, equivalent to flat V6 (180 °)
Here is the engine Boxer, the difference is mainly at the level of fastening of the piston rods. Pay attention to your culture that this Boxer name was used by Porsche to refer to the Boxster (which therefore has a Boxer engine ...)
Here's a boxer from a Porsche Boxster.
Used in particular by Porsche and Subaru, this type of design is very rare in the automotive market.
Advantages:
- The advantage of this mechanism is usually a lower center of gravity. Since the engine is flat and located as low as possible, this reduces the height of the center of gravity.
- The balancing of the motor is good enough because the masses move in opposite directions.
Disadvantages:
- Maintenance and repair costs can be higher because this engine is more atypical (therefore less known to mechanics).
Engine in V
A V-shaped engine has two lines side by side, not one line. Its shape gave rise to the name: V.

The advantages of the V-shaped motor:
- The balancing of the moving masses is better, which makes it easier for engineers to control vibrations.
- Significantly lowered center of gravity with large V opening (if we got to 180 degrees, the engine would be flat)
- Shorter than in-line engine
Disadvantages:
- The more expensive and complex engine of this type is therefore more expensive to buy and maintain. Specifically at the distribution level, which then has to synchronize two lines (on a V-shaped engine) instead of one.
- Consumption that may be slightly higher
- Decreasing the angle of the V does not help reduce the center of gravity.
- Wider than an inline engine
VR engine
RVs are V-engines that have been reduced in angle to reduce the size of the engine. The best example remains the Golf 3 VR6, which didn't necessarily have a lot of room under the hood. The pistons are so close together that there is no need for two cylinder heads (one for each bank in the case of the V6). Therefore, it could be placed transversely in the Golf, knowing that it remains one of the rare compact cars on the market equipped with a 6-cylinder engine.
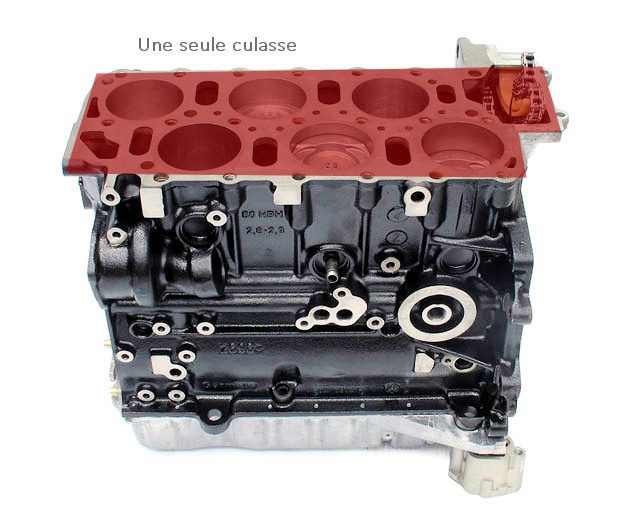

Two "V-profiles" have been glued to reduce the size of the engine.
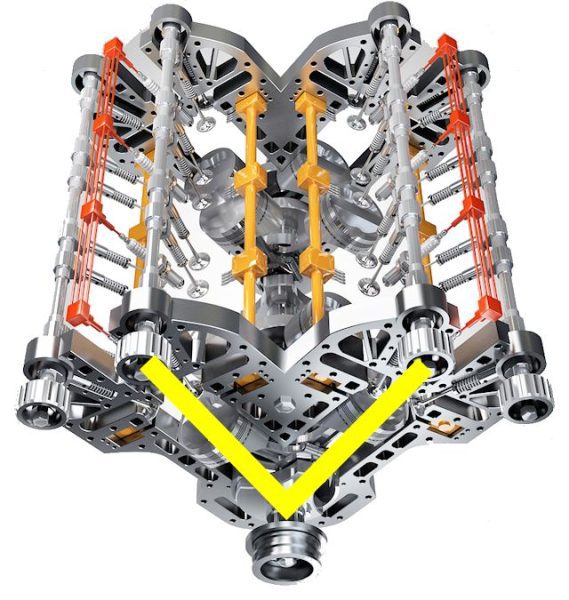
Motor W
The W engines, known primarily as 12-cylinder (W12) engines, are a kind of twin-V engine. At the end of the day, the shape looks like the letter W, but that's not entirely true.
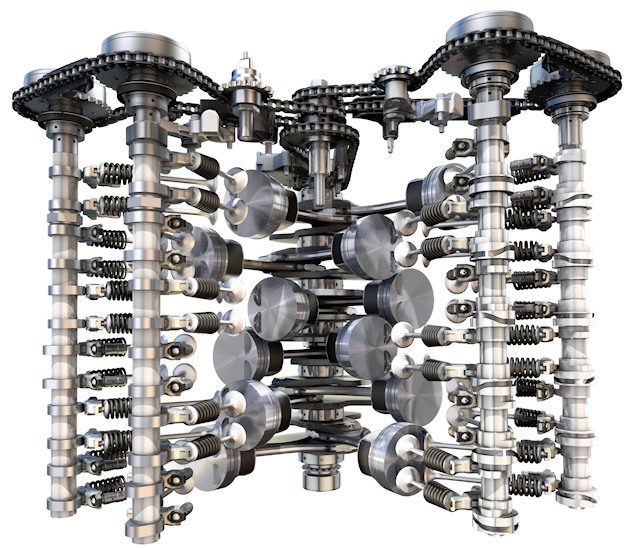
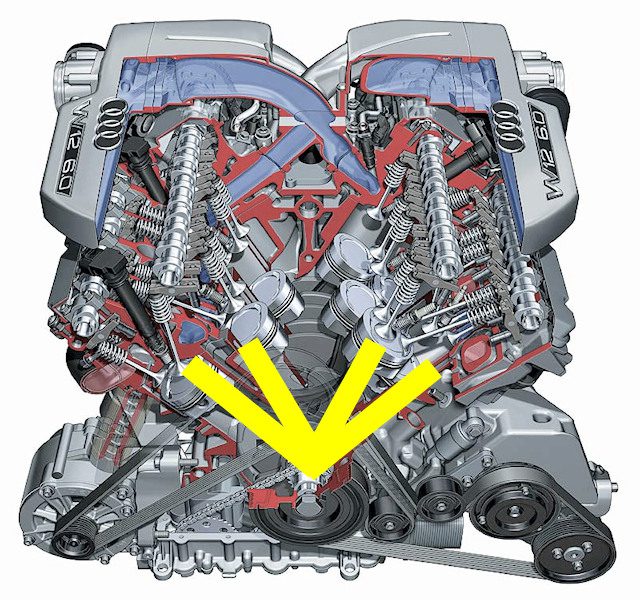
In fact, this is not exactly the letter W, but two letters V, nested one inside the other, as shown by the yellow figure that repeats the stroke of the cylinders. Ultimately, this is a good way to accommodate as many cylinders as possible while taking up as little space as possible.
Rotary engine
Undoubtedly, this is the most original design of all. Indeed, there is no piston here, but a new combustion chamber system.
Advantages:
- Reduced weight thanks to a simple design requiring fewer parts than a “conventional” engine.
- The engine that runs faster, more nervousness
- Very good motor balancing, so vibrations are greatly reduced, especially when compared to other architectures.
- The noise is very well controlled and the approval is very good
Disadvantages:
- A very special engine, not every mechanic will necessarily take care of it (it all depends on the problem being solved)
- The segmentation system is not necessarily perfect, and maintaining good compression over a long period of time can be more difficult than with a "standard" engine.
- More economical ...
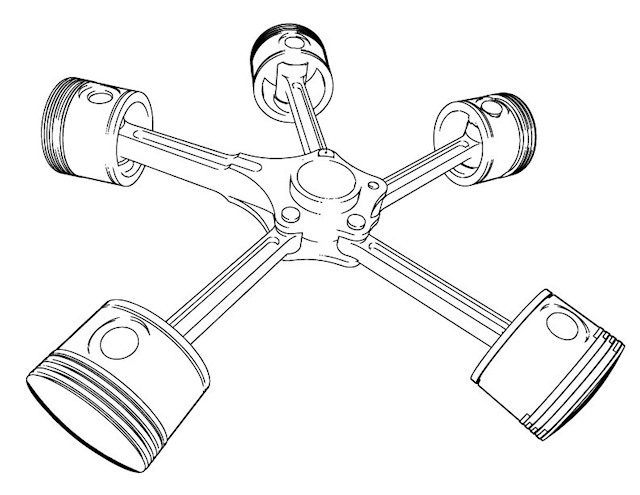
Star engine
I will not dwell on this, because it concerns aviation. But here's what it looks like for your general knowledge: