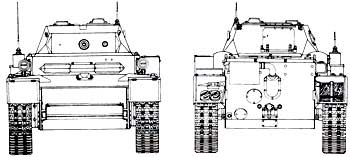
Reconnaissance tank T-II "Lux"
Reconnaissance tank T-II "Lux"Pz.Kpfw. II Ausf. L 'Luchs' (Sd.Kfz.123)
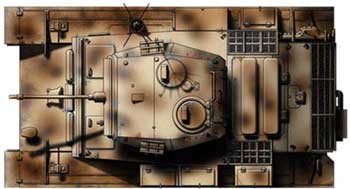
The hull of the tank is made without a rational inclination of the armor plates. A 20-mm automatic gun with a barrel length of 55 calibers is installed in a multifaceted turret using a cylindrical mask. A self-propelled flamethrower (special vehicle 122) was also produced on the basis of this tank. The Lux tank was a successful high-speed reconnaissance vehicle with good off-road capability, but due to poor armament and armor, it had limited combat capabilities. The tank was produced from September 1943 to January 1944. In total, 100 tanks were produced, which were used in tank reconnaissance units of tank and motorized divisions.
In July 1934, the "Waffenamt" (weapons department) issued an order for the development of an armored vehicle armed with a 20-mm automatic cannon weighing 10 tons. In early 1935, a number of firms, including Krupp AG, MAN (chassis only), Henschel & Son (chassis only) and Daimler-Benz, presented prototypes of the Landwirtschaftlicher Schlepper 100 (LaS 100) - an agricultural tractor. Prototypes of agricultural machines were intended for military testing. This tractor is also known under the names 2 cm MG “Panzerwagen” and (VK 6222) (Versuchkraftfahrzeug 622). The tractor, also known as the Panzerkampfwagen light tank, was designed to complement the Panzerkampfwagen I tank as a more heavily armed vehicle capable of firing armor-piercing and incendiary shells. Krupp was the first to present a prototype. The vehicle was an enlarged version of the LKA I tank (a prototype of the Krupp Panzerkampfwagen I tank) with enhanced armament. The Krupp machine did not suit the customer. The choice was made in favor of a chassis developed by MAN and a Daimler-Benz body. In October 1935, the first prototype, made not from armor, but from structural steel, was tested. Waffenamt ordered ten LaS 100 tanks. From the end of 1935 to May 1936, MAN completed the order by delivering ten of the required vehicles.
The prototype of the tank LaS 100 firm "Krupp" - LKA 2 Later they received the designation Ausf.al. Tank "Panzerkampfwagen" II (Sd.Kfz.121) was larger than "Panzerkampfwagen" I, but still remained a light vehicle, designed more for training tankers than for combat operations. It was considered as an intermediate type in anticipation of the entry into service of the Panzerkampfwagen III and Panzerkampfwagen IV tanks. Like the Panzerkampfwagen I, the Panzerkampfwagen II did not have a high combat effectiveness, although it was the main tank of the Panzerwaffe in 1940-1941. Weak from the point of view of the military machine, however, was an important step towards the creation of more powerful tanks. In good hands, a good light tank was an effective reconnaissance vehicle. Like other tanks, the chassis of the Panzerkampfwagen II tank served as the basis for numerous conversions, including the Marder II tank destroyer, the Vespe self-propelled howitzer, the Fiammpanzer II Flamingo (Pz.Kpf.II(F)) flamethrower tank, the amphibious tank and self-propelled artillery "Sturmpanzer" II "Bison".
Description. The armor of the Panzerkampfwagen II tank was considered very weak, it did not even protect against fragments and bullets. Armament, a 20-mm cannon, was considered adequate at the time the vehicle was put into service, but quickly became outdated. The shells of this gun could only hit normal, non-armored targets. After the fall of France, the issue of arming the Panzerkampfwagen II tanks with French 37 mm SA38 guns was studied, but things did not go beyond testing. Tanks "Panzerkampfwagen" Ausf.A / I - Ausf.F were armed with automatic guns KwK30 L / 55, developed on the basis of the FlaK30 anti-aircraft gun. The rate of fire of the KwK30 L / 55 gun was 280 rounds per minute. The Rheinmetall-Borzing MG-34 7,92 mm machine gun was paired with the cannon. The gun was installed in the mask on the left, the machine gun on the right.
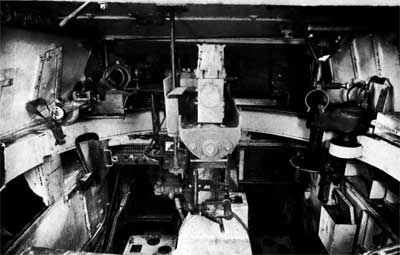
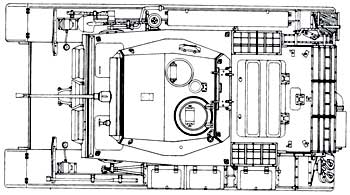
The gun was supplied with various options for the TZF4 optical sight. On early modifications, there was a commander's hatch in the roof of the turret, which was replaced by a turret in later versions. The turret itself is offset to the left relative to the longitudinal axis of the hull. In the fighting compartment, 180 shells were placed in clips of 10 pieces each and 2250 cartridges for a machine gun (17 tapes in boxes). Some tanks were equipped with smoke grenade launchers. The crew of the tank "Panzerkampfwagen" II consisted of three people: commander/gunner, loader/radio operator and driver. The commander was seated in the tower, the loader stood on the floor of the fighting compartment. Communication between the commander and the driver was carried out by means of a speaking tube. The radio equipment included a FuG5 VHF receiver and a 10-watt transmitter. The presence of a radio station gave the German tanker a tactical advantage over the enemy. The first “twos” had a rounded frontal part of the hull, in later vehicles the upper and lower armor plates formed an angle of 70 degrees. The gas tank capacity of the first tanks was 200 liters, starting with the Ausf.F modification, tanks with a capacity of 170 liters were installed. Tanks heading to North Africa were equipped with filters and fans, the abbreviation "Tr" (tropical) was added to their designation. During operation, many "twos" were finalized, and in particular, additional armor protection was installed on them.
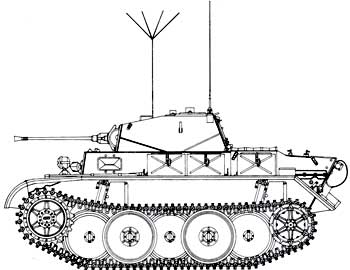
The last modification of the “Panzerkamprwagen” II tank was the “Lux” - “Panzerkampfwagen” II Auf.L (VK 1303, Sd.Kfz.123). This light reconnaissance tank was produced by the MAN and Henschel factories (in small quantities) from September 1943 to January 1944. It was planned to produce 800 vehicles, but only 104 were built (data are also given on 153 tanks built), chassis numbers 200101-200200. The MAN company was responsible for the development of the hull, the hull and turret superstructures were the Daimler-Benz company. “Lux” was a development of the VK 901 (Ausf.G) tank and differed from its predecessor in a modernized hull and chassis. The tank was equipped with a 6-cylinder Maybach HL66P engine and a ZF Aphon SSG48 transmission. The mass of the tank was 13 tons. Cruising on the highway - 290 km. The crew of the tank is four people: commander, gunner, radio operator and driver. The radio equipment included a FuG12 MW receiver and an 80W transmitter. Communication between the crew members was carried out through a tank intercom.
Light reconnaissance tanks "Lux" operated both on the Eastern and Western fronts as part of the armored reconnaissance units of the Wehrmacht and the SS troops. Tanks intended to be sent to the Eastern Front received additional frontal armor. A small number of cars were equipped with additional radio equipment. It was planned to equip the Luks tanks with 50 mm KWK39 L/60 cannons (the standard armament of the VK 1602 Leopard tank), but only a variant with a 20 mm KWK38 L/55 cannon with a rate of fire of 420-480 rounds per minute was produced. The gun was equipped with a TZF6 optical sight. There is information, which, however, is not documented, that 31 Lux tanks nevertheless received 50-mm Kwk39 L / 60 guns. The construction of armored evacuation vehicles "Bergepanzer Luchs" was supposed, but not a single such ARV was built. Also, the project of an anti-aircraft self-propelled gun based on the extended chassis of the Luks tank was not implemented. VK 1305. The ZSU was supposed to be armed with one 20-mm or 37-mm Flak37 anti-aircraft gun.
Exploitation. "Twos" began to enter the troops in the spring of 1936 and remained in service with the German units of the first line until the end of 1942. However, it is officially considered that the Anschluss of Austria and the occupation of Czechoslovakia became the first cases of combat use of tanks. As the main battle tank, the "two" took part in the Polish campaign of September 1939. After the reorganization in 1940-1941. Panzerwaffe, Panzerkampfwagen II tanks entered service with reconnaissance units, although they continued to be used as main battle tanks. Most of the vehicles were withdrawn from the units in 1942, although individual Panzerkampfwagen II tanks were encountered at the front in 1943 as well. The appearance of “twos” on the battlefield was noted in 1944, during the allied landings in Normandy, and even in 1945 (in 1945, 145 “twos” were in service).
1223 Panzerkampfwagen II tanks took part in the war with Poland, at that time the “twos” were the most massive in the panzerwaf. In Poland, German troops lost 83 Panzerkampfwagen II tanks. 32 of them - in the battles on the streets of Warsaw. Only 18 vehicles took part in the occupation of Norway. 920 "twos" were ready to participate in the blitzkrieg in the West. In the invasion of German troops in the Balkans, 260 tanks were involved. To participate in Operation Barbarossa, 782 tanks were allocated, a significant number of which became victims of Soviet tanks and artillery. The Panzerkampfwagen II tanks were used in North Africa until the surrender of parts of the Africa Corps in 1943. The actions of the "twos" in North Africa turned out to be the most successful due to the maneuverable nature of the hostilities and the weakness of the enemy's anti-tank weapons. Only 381 tanks took part in the summer offensive of the German troops on the Eastern Front.
In Operation Citadel, even less so. 107 tanks. As of October 1, 1944, the German armed forces had 386 Panzerkampfwagen II tanks. Tanks "Panzerkampfwagen" II were also in service with the armies of the countries allied with Germany: Slovakia, Bulgaria, Romania and Hungary. Currently, Panzerkampfwagen II Lux tanks can be seen in the British Tank Museum in Bovington, in the Munster Museum in Germany, in the Belgrade Museum and in the Aberdeen Proving Ground Museum in the USA, in the French Tank Museum in Samyur, one tank is in Russia in Kubinka. Tactical and technical characteristics of the tank "Lux"
Sources:
|

 The development of the tank was started by MAN in 1939 to replace the T-II tank. In September 1943, the new tank was put into mass production. Structurally, it was a continuation of the development of the T-II tanks. In contrast to the previous samples on this machine, a staggered arrangement of road wheels was adopted in the undercarriage, support rollers were eliminated and high-lying fenders were used. The tank was carried out according to the usual layout for German tanks: the power compartment was at the rear, the combat compartment was in the middle, and the control compartment, transmission and drive wheels were in front.
The development of the tank was started by MAN in 1939 to replace the T-II tank. In September 1943, the new tank was put into mass production. Structurally, it was a continuation of the development of the T-II tanks. In contrast to the previous samples on this machine, a staggered arrangement of road wheels was adopted in the undercarriage, support rollers were eliminated and high-lying fenders were used. The tank was carried out according to the usual layout for German tanks: the power compartment was at the rear, the combat compartment was in the middle, and the control compartment, transmission and drive wheels were in front.