Hinges of equal and unequal angular velocities
Content
- Cardan transmission with a hinge of unequal angular velocities
- Design and operation
- Cardan transmission with constant velocity joint
- Cardan transmission purpose and arrangement of the most important transmission mechanism
- Rigid hinge
- Annex a (informative) calculation of the critical speed of the cardan shaft
- Frequent malfunctions and their elimination
- Advantages and disadvantages of SHRUS
- Types of constant velocity joints
- Hinge: the main secret of the cardan
- Cardan transmission with elastic semi-cardan joint
- Photo report on the dismantling and installation of constant velocity joints on the VAZ 2110-2112
- Main malfunctions, their signs
- SHRUS crackles - how to determine which one, and what to do?
- Types of hinge joints
- Checking the condition of the propeller shaft
- Prospects for the development of the cardan transmission system
- Where is swivel applicable?
- Lubricants used for swivel joints
- Appendix b (reference) calculation of the cardan shaft imbalance
- Cardan: why is it needed?
Cardan transmission with a hinge of unequal angular velocities
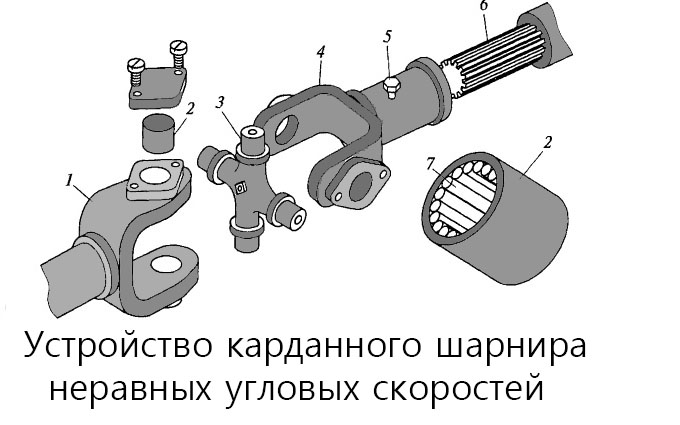
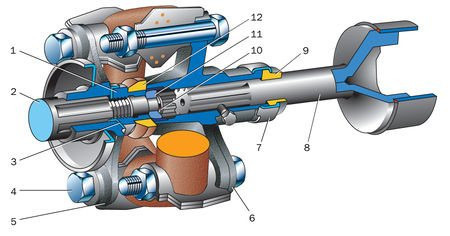
This type of transmission can be found in cars with rear or all-wheel drive. The device for such a transmission is as follows: hinges of unequal angular velocities are located on the cardan shafts. There are connecting elements at the ends of the transmission. If necessary, a connecting bracket is used.
The hinge combines a pair of studs, a cross and locking devices. Needle bearings are installed in the eyes of the forks, in which the cross member rotates.
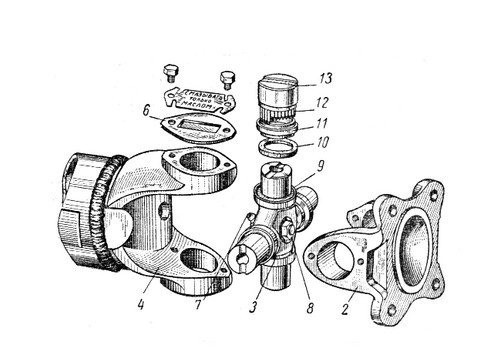
Bearings are not subject to repair and repair. They are filled with oil during installation.
A feature of the hinge is that it transmits uneven torque. The secondary axle periodically reaches and lags behind the main axle. To compensate for this shortcoming, various hinges are used in the transmission. The opposite forks of the hinge are located in the same plane.
Depending on the distance over which the torque must be transmitted, one or two shafts are used in the drive line. When the number of axles is equal to two, one of them is called intermediate, the second - rear. To fix the axles, an intermediate bracket is installed, which is attached to the car body.
The transmission line is connected to other elements of the vehicle using flanges, couplings and other connecting elements.
It is safe to say that the hinges of unequal angular velocities have low reliability and a relatively short service life. In modern conditions, cardan transmissions with CV joints are used.
Design and operation
In more detail, we will consider the design and principle of operation of CV joints using the example of a VAZ-2199 car.
This car is front-wheel drive, so CV joints are involved in the design of the transmission.
The exterior element of this car is made according to the "Beerfield" type.

At the end of the drive shaft coming out of the gearbox, there is an inner ring with 6 grooves.
The outer clamp has grooves on the inner surface. The clip itself is connected to the axle, on which there are splines inserted into the wheel hub.
The inner cage passes into the outer one, and the metal working balls are placed in the existing grooves of both cages. To prevent the balls from falling out, they are inserted into the separator.

This CV joint works like this: while driving, the wheel constantly moves relative to the car body due to independent suspension, while the angle between the drive shaft and the shaft inserted into the hub is constantly changing due to road irregularities.
The balls, moving along the grooves, provide a constant transmission of rotation when the angle changes.
The design of the inner “grenade”, which in this vehicle is of the GKN type, is the same as the outer one, but the outer clip is somewhat longer, this ensures a change in the length of the drive shaft.
When driving through bumps, the angle of the outer CV joint changes, and the wheel itself goes up. In this case, changing the angle affects the length of the cardan shaft.
In the case of using the GKN CV joint, the inner race, together with the balls, can penetrate deep into the outer race, thereby changing the length of the shaft.
The design of the separating splined ball joint is very reliable, but with one caveat. They are very sensitive to pollution.
The ingress of dust and sand into the "grenade" causes accelerated wear of the grooves and balls.
Therefore, the internal elements of this connection must be covered with anthers.

Damage to the boot will cause the CV joint grease to leak out and sand to enter.
It is very simple to identify a problem with these elements: when the wheels turn completely, and the leaders begin to move, characteristic clicks are heard.
Cardan transmission with constant velocity joint
This type of transmission is widely used in front wheel drive vehicles. With its help, the differential and the hub of the drive wheel are connected.
The transmission has two hinges, internal and external, connected by a shaft. CV joints are often used on rear-wheel drive vehicles, on all-wheel drive vehicles. The fact is that SHRUS are more modern and practical, besides, their noise level is much lower than that of SHRUS.
The most common available is the ball type constant velocity joint. The CV joint transmits torque from the drive shaft to the driven shaft. The angular velocity of torque transmission is constant. It does not depend on the angle of inclination of the axes.
SHRUS, or as it is popularly called "grenade", is a spherical body in which there is a clip. The balls rotate with each other. They move along special grooves.
As a result, the torque is uniformly transmitted from the drive shaft to the driven shaft, subject to a change in angle. The separator holds the balls in place. "Grenade" is protected from the effects of the external environment "dust cover" - a protective cover.
A prerequisite for the long service life of CV joints is the presence of lubrication in them. And the presence of lubrication, in turn, is ensured by the tightness of the hinge.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the safety of CV joints. If a crack or noise is heard in the "grenade", it must be changed immediately. Operating a vehicle with a faulty CV joint is extremely dangerous. In other words, the wheel can fall off. The reason that the cardan shaft becomes unusable is, in most cases, the wrong choice of speed and poor road surface.
Cardan transmission purpose and arrangement of the most important transmission mechanism
Studying the structure of cars, we, friends, constantly find original and interesting engineering solutions, sometimes simple or ingenious, and sometimes so complex that it is almost impossible for a non-specialist to cope with them.
In this article, we will try to get acquainted with the mechanism that performs an extremely important function - the transfer of rotation from the gearbox to the axle with drive wheels. This device is called -, cardan transmission, the purpose and device of which we have to find out.
Cardan: why is it needed?
So, what problems can arise if we want to transfer torque from the engine to the wheels? At first glance, the task is quite simple, but let's take a closer look.
The fact is that, unlike the engine and gearbox, the wheels, along with the suspension, have a certain course, which means that it is simply impossible to simply connect these nodes.
Engineers solved this problem with a transmission.

The key element of the mechanism is the so-called universal joint, which is the most ingenious engineering solution that allows you and me to enjoy a car journey.
It must be said that cardans are used in various parts of the machine. Basically, of course, they can be found in the transmission, but in addition, this type of transmission is related to the steering system.
Hinge: the main secret of the cardan

Therefore, we will not waste time on unnecessary talk and move on to the essence of the problem. The transmission of a car, no matter what model it is, has a number of standard elements, namely:
- loops,
- driving, driven and intermediate bridges,
- supports,
- connecting elements and couplings.
The differences between these mechanisms, as a rule, are determined by the type of universal joint. There are such execution options:
- with a hinge of unequal angular velocities,
- with a constant velocity joint,
- with semi-cardan elastic joint.
When motorists pronounce the word "cardan", they usually mean the first option. The CV joint mechanism is most commonly found on rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive vehicles.
The operation of this type of cardan transmission has a feature, which is also its disadvantage. The fact is that due to the design details of the hinge, a smooth transmission of torque is impossible, but it turns out that this is done only cyclically: in one revolution, the driven shaft lags behind twice and twice ahead of the drive shaft.
This nuance is compensated by the introduction of another of the same hinge. The cardan drive device of this type is simple, like everything ingenious: the axles are connected by two forks located at an angle of 90 degrees and fastened with a cross.
More advanced are the options with CV joints of equal angular speeds, which, by the way, are often called CV joints; You must have heard this name.
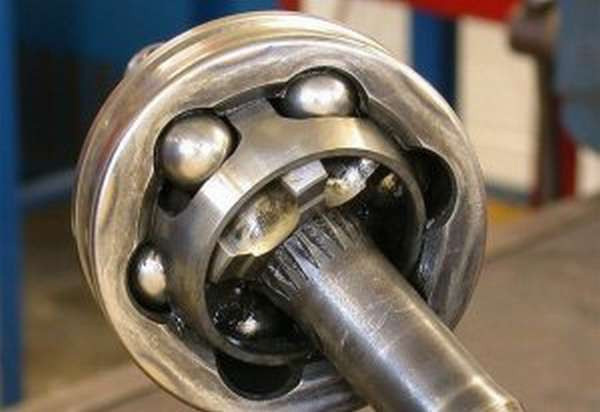

Cardan transmission, the purpose and device of which we are considering in this case, has its own nuances. Although its design is more complex, this is more than offset by a number of advantages. So, for example, the axes of this type of suspension always rotate uniformly and can form an angle of up to 35 degrees. The disadvantages of the mechanism can, perhaps, include a rather complicated assembly scheme.

The CV joint must always be sealed, as there is a special lubricant inside it. Depressurization causes leakage of this lubricant, and in this case, the hinge quickly becomes unusable and breaks. However, CV joints, with proper care and control, are more durable than their counterparts. You can find CV joints on both front-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles.
The design and operation of a cardan drive with an elastic semi-cardan also has its own characteristics, which, by the way, do not allow it to be used in modern car designs.
The transfer of rotation between the two shafts in this case occurs due to the deformation of the elastic element, such as a specially designed clutch. This option is considered extremely unreliable and therefore is not currently used in the automotive industry.
Well, friends, the purpose and design of the transmission, as well as the varieties that we have revealed in this article, turned out to be a fairly simple mechanism that brings a lot of benefits.
Rigid hinge
Rigid articular joints are represented by elastic semi-cardiac joints. This is a mechanism in which the torque from the drive shaft to the driven shaft, which has a different angle of location, is achieved due to the deformation of the link connecting them. The elastic link is made of rubber with possible reinforcement.
An example of such an elastic element is the Gibo coupling. It looks like a hexagonal element, on which metal coatings are vulcanized. The sleeve is pre-compressed. This design is characterized by good damping of torsional vibrations as well as structural shocks. Allows the articulation of rods with a divergence angle of up to 8 degrees and a rod movement of up to 12 mm in both directions. The main task of such a mechanism is to compensate for inaccuracies during installation.
The disadvantages of the assembly include increased noise during operation, manufacturing difficulties and a limited service life.

Annex a (informative) calculation of the critical speed of the cardan shaft
Annex A (informative)
For a cardan shaft with a steel pipe, the critical speed n, min, is calculated by the formula
(A.1)
where D is the outer diameter of the pipe, cm, d is the inner diameter of the pipe, cm;
L - the maximum distance between the axes of the cardan shaft hinges, cm;
where n is the frequency of rotation of the cardan shaft in gear (natural frequency of transverse vibrations of the shaft according to the first form), corresponding to the maximum speed of the vehicle, min
1 This calculation does not take into account the elasticity of the supports.
2 For cardan gears with an intermediate support, the value L is taken equal to the distance from the hinge axis to the axis of the bearing of the intermediate support. The critical speed of the shaft, made in the form of thrust between the cardan joints, is calculated at d equal to zero. The critical speed of the cardan shaft, consisting of a pipe and a rod, is calculated based on the given value of the pipe length L cm, calculated by the formula
,(A.2) where L is the length of the shaft tube, cm; l is the length of the pipe replacing the axle link, cm. The length of the pipe l replacing the axle link is calculated by the formula (A.3) where l is the length of the axle link, cm; d is the diameter of the cardan shaft rod, cm. The critical frequency of rotation of the cardan shaft, taking into account the elasticity of its supports in the transmission, is set experimentally by the vehicle developer. The frequency of rotation of the cardan in the transmission, corresponding to the maximum possible speed of the vehicle, should not exceed 80% of the critical frequency, taking into account the elasticity of the supports.
Frequent malfunctions and their elimination
All failures can be divided according to the emerging signs of failure:
- Vibration during movement - the bearings of the cross or sleeves are worn out, the balance of the shaft is disturbed;
- Knocks at start-up: grooves of splines are worn out, fixing bolts are loosened;
- Oil leakage from bearings - seals are worn out.
To eliminate the above problems, the “cardans” are disassembled and the failed parts are replaced. If there is an imbalance, the shaft must be dynamically balanced.
Advantages and disadvantages of SHRUS
Among the obvious advantages of the CV joint is the fact that during transmission with the help of this hinge there is practically no power loss compared to other similar mechanisms, other advantages are its low weight, relative reliability and ease of replacement in the event of a breakdown.
The disadvantages of CV joints include the presence of an anther in the design, which is also a container for lubrication. The CV joint is located in a place where it is almost impossible to avoid its contact with foreign objects. The trunk can break, for example, when driving on a too deep rut, when hitting an obstacle, etc. As a rule, the car owner only finds out about this when dirt has already entered the boot through a crack in the boot, causing severe wear. If you are sure that this happened recently, you can remove the CV joint, flush it, replace the boot and fill with new grease. If the problem arose a long time ago, then the CV joint will definitely fail ahead of time.
Types of constant velocity joints
The design options for the ball joint, although they were the most common in the passenger car industry, were not the only possible ones.

Ball joint
Tripod CV joints have found practical application for passenger cars and light commercial vehicles, in which rotating rollers with a spherical working surface play the role of balls.

SHRUS tripod
For trucks, cam (rusk) loops of the “tract” type, consisting of two studs and two shaped disks, have become widespread. Forks in such designs are quite massive and can withstand heavy loads (which explains the area of their use).
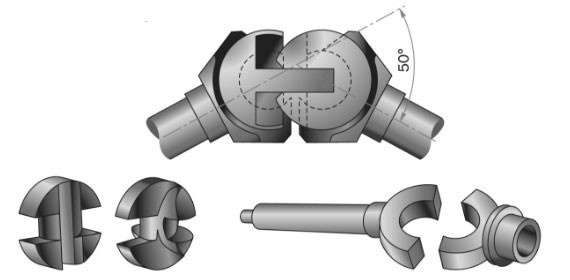
Cam (biscuit) SHRUS
It is necessary to mention another version of the CV joint - dual cardan joints. In them, the uneven transmission of the angular velocity of the first gimbal is compensated by the second gimbal.

Double universal joint of equal angular speeds
As mentioned above, the angle between the axes of the two axes in this case should not exceed 20⁰ (otherwise increased loads and vibrations appear), which limits the scope of such a design mainly for road construction equipment.
Internal and external CV joints
In addition to differences in design, CV joints are divided, depending on the place of their installation, into external and internal.
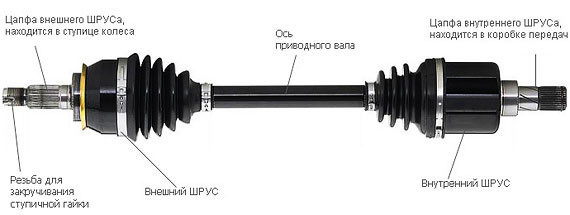
The inner CV joint connects the gearbox to the axle shaft, and the outer CV joint connects the axle shaft to the wheel hub. Together with the cardan shaft, these two joints make up the vehicle's transmission.
The most common type of external joint is the ball joint. The inner CV joint not only provides a large angle between the axles, but also compensates for the movement of the cardan shaft when it moves relative to the suspension. Therefore, a tripod assembly is often used as an internal joint in passenger cars.
A necessary condition for the normal operation of the CV joint is the lubrication of the moving parts of the hinge. The tightness of the working space in which the lubricant is located is ensured by anthers that prevent abrasive particles from entering the working surfaces. Given the high load of parts, only types of lubricants specially designed for such units are used.
Hinge: the main secret of the cardan
It is quite obvious that the cardan transmission, the purpose and device of which we are considering today, is an extremely important unit.
Therefore, we will not waste time on unnecessary talk and move on to the essence of the problem. The transmission of a car, no matter what model it is, has a number of standard elements, namely:
- loops;
- driving, driven and intermediate shafts;
- supports;
- connecting elements and couplings.
The differences between these mechanisms, as a rule, are determined by the type of universal joint. There are such execution options:
- with a hinge of unequal angular velocities;
- with a hinge of equal angular velocities;
- with semi-cardan elastic joint.
When motorists pronounce the word "cardan", they usually mean the first option. The CV joint mechanism is most commonly found on rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive vehicles.
The operation of this type of cardan transmission has a feature, which is also its disadvantage. The fact is that due to the design details of the hinge, a smooth transmission of torque is impossible, but it turns out that this is done only cyclically: in one revolution, the driven shaft lags behind twice and twice ahead of the drive shaft.
This nuance is compensated by the introduction of another of the same hinge. The cardan drive device of this type is simple, like everything ingenious: the axles are connected by two forks located at an angle of 90 degrees and fastened with a cross.
More advanced are the options with CV joints of equal angular speeds, which, by the way, are often called CV joints; You must have heard this name.
Cardan transmission, the purpose and device of which we are considering in this case, has its own nuances. Although its design is more complex, this is more than offset by a number of advantages. So, for example, the axes of this type of suspension always rotate uniformly and can form an angle of up to 35 degrees. The disadvantages of the mechanism can, perhaps, include a rather complicated assembly scheme.
The CV joint must always be sealed, as there is a special lubricant inside it. Depressurization causes leakage of this lubricant, and in this case, the hinge quickly becomes unusable and breaks. However, CV joints, with proper care and control, are more durable than their counterparts. You can find CV joints on both front-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles.
The design and operation of a cardan drive with an elastic semi-cardan also has its own characteristics, which, by the way, do not allow it to be used in modern car designs.
The transfer of rotation between the two shafts in this case occurs due to the deformation of the elastic element, such as a specially designed clutch. This option is considered extremely unreliable and therefore is not currently used in the automotive industry.
Well, friends, the purpose and design of the transmission, as well as the varieties that we have revealed in this article, turned out to be a fairly simple mechanism that brings a lot of benefits.
In the next post, we'll talk about something equally useful. Which one of? Subscribe to the newsletter and be sure to find out!
Cardan transmission with elastic semi-cardan joint
An elastic semi-cardan joint facilitates the transmission of torque between shafts located at a slight angle. This is due to the deformation of the elastic bond.
An example is the Guibo flexible coupling. This is a hexagonal compressed elastic element. The flanges of the drive and driven shafts are attached to it and torque is transmitted.
Photo report on the dismantling and installation of constant velocity joints on the VAZ 2110-2112
First of all, when the car is still on the ground, it is necessary to pry off the protective cap from the hub nut and remove it. Then, using a powerful lever and a 32 head, unscrew the hub nut, but not completely:
After that, we unscrew all the bolts on the wheel and remove it, having previously raised the front of the car with a jack. After that, finally unscrew the hub nut and remove the washer.
Then we unscrew the two screws holding the ball joint from below:
After that, you can tilt the steering knuckle to the side and remove one end of the CV joint from the hub:
If it is necessary to replace the outer CV joint, it can already be knocked out of the shaft with a hammer, but this must be done carefully so as not to damage anything. And the ideal option, of course, is the complete removal of the unit
To do this, using a bracket, you need to pry off the inner CV joint and disconnect it from the gearbox:
As a result, it is possible to completely remove the CV joint from the VAZ 2110 gearbox and remove the transmission assembly to the outside. Then, using a vice and a hammer, we disconnect all the necessary CV joints, both internal and external.
Be sure to pay attention to the condition of the anthers. If they are damaged, they must be replaced with new ones.
Installation is carried out in the reverse order and in the same video that was presented at the beginning of the article, everything is perfectly visible. It is also worth mentioning the cost of new parts. So, the price of an external CV joint on a VAZ 2110 can be from 900 to 1500 rubles. For an intern, you will have to pay from 1200 to 2000 rubles.
In the 80s of the last century, an important stage began in the mass production of passenger cars - the transition from the classic design with a cardan shaft and a rear axle to a front-wheel drive. Front-wheel drive with MacPherson struts has proven to be a simple and reliable system with a number of advantages:
- increased handling and cross-country ability due to the weight of the front of the car;
- stable directional stability of the machine, especially on slippery surfaces;
- increase in the usable area of the cabin due to the compact dimensions of the engine compartment and the absence of a cardan shaft;
- reduced vehicle weight due to the absence of a gearbox and rear-wheel drive elements;
- increasing the safety of the structure and increasing the dimensions of the trunk due to the installation of a fuel tank under the rear seat.
However, to transfer rotation to the drive wheels, a number of vulnerable parts and assemblies were introduced into the design. The main heavily loaded transmission element on front-wheel drive vehicles are constant velocity joints (CV joints).
Main malfunctions, their signs
The most durable mechanism in the design is the axis itself. It is cast from a durable alloy that can withstand extreme loads. Therefore, you will have to try very hard to damage it. As a rule, these are mechanical damages in an accident.
In general, the main faults can be divided into several types:
- Vibration: When starting or driving, strong or weak vibrations may occur. This is the first sign of damage to the spider bearings. Also, the problem may indicate improper balancing of the shaft, this happens after its mechanical damage.
- Knock - A characteristic knock when moving from one place will mean that the mounting bolts or splines have worn out. In this case, it is best to immediately contact the service station to check the integrity of the connection.
- Oil Leak: You may find small drops of oil in areas where bearings and seals are located.
- Squeaks - may appear at the moment you press the accelerator pedal. In most cases, squeaks can be associated with hinge failure. With the appearance of corrosion, the crosses can get stuck and damage the bearings.
- Malfunction of the movable bearing - you can determine the problem by the characteristic creak in the area of \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbthe moving part of the shaft. During normal operation, the mechanism should not make any sounds, all movements are smooth. If a crack is heard, the bearing is most likely out of order. The problem is solved only by the complete replacement of the defective part.
In rare cases where mechanical damage to the main shaft occurs, incorrect geometry can cause severe vibration. Some craftsmen recommend manually correcting the geometry of the pipe, but this is the wrong decision, which can lead to rapid wear of the entire structure. The best solution is to completely replace the damaged elements.
SHRUS crackles - how to determine which one, and what to do?
Hello dear motorists! A car enthusiast can be considered a real person only when he is really concerned about the condition of the car's components and assemblies, and every new knock, creak and other signs of car breakdowns haunt him.
Driving a car can only be called comfortable if all the elements are in good working order.
However, each part, especially working under load and with friction like a CV joint, has its own working life.
Sooner or later, the material wears out, loses its properties, which leads to failure of the part. This is objective. And the “hint” of the approaching breakdown of the part itself must be taken seriously. It is better not to wait for the car to stop on a long trip, but to immediately start troubleshooting and troubleshooting.
Owners of front-wheel drive vehicles are familiar with such an unpleasant phenomenon as the CV joint squeak. Given that the front suspension of a car, in addition to its main functions, must also ensure the transmission of rotation from the differential gears to the drive wheels, it is equipped with unique devices - CV joints, which briefly sounds like a "CV joint".
This detail is very important and quite complex in design, so it is expensive and requires increased attention. If the CV joint creaks, then without hesitation it is necessary to repair the car and change it.
Why does the CV joint crunch?
Experienced drivers can determine the location of a car breakdown by ear. Such skills are acquired over time, but the abbreviation of the GC can never be confused.
To understand the nature of this characteristic noise, we must remember how the CV joint works. The task of the CV joint is to transfer rotation from one axle to another, subject to a continuous change in the angle between them.
This property is due to the need not only to turn the drive wheel, but also to give it the ability to rotate and move up and down on a spring.
The CV joint consists of the following main elements:
- the outer body is bowl-shaped with six semicircular grooves inside and a semi-axis outside;
- inner cage in the form of a spherical fist, as well as with six slots and a splined half shaft connection;
- there are 6 balls between the inner walls of the container and the cage in the separator.
All elements are made with such precision that they do not have any backlash during assembly. The clip through the balls transfers the force to the body and rotates it, and the movement of the balls along the grooves allows you to change the angle between the semi-axes.
Over time, work is formed at the point of contact of the balls with other elements, a reaction appears. The free movement of the balls (rolling) creates a sound very similar to crunching.
Considering that two CV joints are installed on each wheel, when alarming symptoms appear, it becomes difficult to understand which CV joint creaks: internal or external, right or left.
Types of hinge joints
There are several types of loops. The classification of this mechanical element can be carried out according to the number of combined structural elements:
- Simple. Connect one or two elements.
- Hard. Combine three or more items.
In addition, hinges can be movable and fixed:
- Refurbished. Connection point is fixed. The rod rotates around an axis.
- Mobile. Both the axle and the attachment point rotate.
But the biggest classification of these mechanical elements lies in the ways in which the structural elements move. This classification divides them into hinges:
- Cylindrical. The movement of two elements occurs relative to a common axis.
- Ball. Movement occurs around a common point.
- Cardan. Such a complex mechanism includes several elements. Several loops are placed on a common cross. Which, in turn, are connected to other elements of the mechanism.
- SHRUS. A complex mechanism that contributes to the transmission of traction and performs rotational movements.
- Lasted. Often used in modern mechanisms. It has a hemispherical design. Hinge elements are located at different angles. The transmission of torque occurs due to the deformation of the link. To do this, it is made of durable rubber. A material with shock-absorbing properties allows you to work with such a holistic design.
Checking the condition of the propeller shaft
It is necessary to check the cardan in the following cases:
- during acceleration, additional noise appears;
- there was an oil leak near the checkpoint;
- knocking when shifting gears
- at speed more vibration is transmitted to the bodywork.
Diagnostics must be carried out by lifting the car on a lift or using jacks (for information on how to choose the desired modification, see a separate article). It is important that the drive wheels are free to rotate.

Here are the nodes to check.
- Fixation. The connections between the intermediate support and the flange must be tightened with a screw with a lock washer. Otherwise, the nut will loosen, causing excessive play and vibration.
- Elastic coupling. Often fails, as the rubber part compensates for axial, radial and angular displacements of the parts to be joined. You can check the malfunction by slowly turning the central shaft (in the direction of rotation and vice versa). The rubber part of the coupling must not be broken; there must be no play at the place where the bolts are attached.
- Extendable fork Free lateral movement in this assembly occurs due to the natural wear of the spline connection. If you try to turn the shaft and coupling in the opposite direction, and there is a slight play between the fork and the shaft, then this assembly should be replaced.
- A similar procedure is carried out with loops. A large screwdriver is inserted between the protrusions of the forks. It plays the role of a lever with which they try to turn the axis in one direction or another. If play is observed during the swing, the spider should be replaced.
- Suspension bearing. Its serviceability can be checked by holding the shaft in front with one hand and behind with the other and shaking it in different directions. In this case, the intermediate support must be firmly fixed. If play is noticeable in the bearing, then the problem is solved by replacing it.
- Balance. Performed if the diagnostics did not reveal any malfunctions. This procedure is performed on a special stand.
Prospects for the development of the cardan transmission system
The classic SHNUS has some technological disadvantages. The speed of rotation of its axes changes in the process of movement. In this case, the driven shaft can accelerate and decelerate at the same speed as the driving shaft. This leads to accelerated wear of the mechanism, and also creates an additional load on the rear axle. In addition, the operation of the hinge is accompanied by vibration. The purpose of the driveline can be performed by a bridge equipped with CV joints (front and rear). Similar systems are already used in some SUVs today. Also, the CV joint can be equipped with a cardan from a VAZ-2107 car and other "classics". Repair kits are available for sale.
The use of a CV joint allows you to eliminate the shortcomings inherent in the classic cross. The shaft rotation speed is equalized, the vibration disappears, the CV does not require balancing after repair, the torque transfer angle is increased to 17.
Where is swivel applicable?
The scope of such structures depends on their type. In practice, the use of one or another hinge depends on the degree of freedom (number of independent parameters). Complex type systems have three such parameters for rotation and three for movement. The higher this hinge value, the more options you have in use.
Simple cylindrical hinges are very common in everyday life. This type of connection of structural elements is inherent in scissors, pliers, mixers, and other doors mentioned above also have this element in their design.
The ball joint is well represented in the automotive industry and other areas where it is necessary to transfer power from one shaft to various pieces of equipment.
Cardan shafts have the same scope as the previous design. They are used when it is necessary to transfer forces between elements that form an angle with each other.
CV joints are an integral part of front-wheel drive vehicles.
Lubricants used for swivel joints
- Lithium based. Reliable thick greases with high retention characteristics. Reduce the load on nodal connections up to ten times. It neutralizes dust and is compatible with almost all resin shoe materials. The downside is that they have poor corrosion protection and will attack some plastics.
- Based on molybdenum disulfide. Lubricants with a long service life of up to one hundred thousand kilometers. Excellent lubricating and anti-corrosion properties. Does not destroy plastic. The disadvantage is that when moisture enters the lubricant loses its properties.
- Barium based. Good lubricants with the benefits of lithium molybdenum disulphide. They are also not afraid of moisture. The disadvantage is the destruction at low temperatures and the high price.
Appendix b (reference) calculation of the cardan shaft imbalance
Appendix B (informative)
And more interesting: photo features of the history of the UAZ-469 car
B.1 The unbalance of the cardan shaft depends on its mass, the play of the hinges and the mechanism for changing the length.
B.2 Unbalance D, g cm, in the cross section of the transmission support is calculated by the formulas: - for a shaft without a mechanism for changing the length
(B.1)
– for a shaft with a mechanism for changing the length
(B.2) where m is the mass of the cardan shaft per support, g; e is the total displacement of the shaft axis, due to axial clearances in the hinge between the ends of the cross and the bottoms of the bearings and the radial clearance in the crosshead-crosshead connection, cm; e is the displacement of the axis of the axis due to gaps in the mechanism for changing the length, cm. The mass m is determined by weighing on the scales placed under each support of the horizontal axis. The total displacement of the e-axis, cm, is calculated by the formula (B.3)
where H is the axial clearance in the hinge between the ends of the cross and the bottoms of the bearings, cm;
D is the inner diameter of the bearing along the needles, cm; D is the diameter of the transverse neck, cm. Axis offset e, cm, for a movable spline joint centered on the outer or inner diameter, e is calculated by the formula
(B.4) where D is the diameter of the slotted hole of the sleeve, cm; D is the diameter of the splined shaft, see Note: for a cardan shaft without a length change mechanism, e=0. The minimum or maximum imbalance D is calculated taking into account the tolerance field of the cardan shaft coupling elements.
Cardan: why is it needed?
So, what problems can arise if we want to transfer torque from the engine to the wheels? At first glance, the task is quite simple, but let's take a closer look. The fact is that, unlike the engine and gearbox, the wheels, along with the suspension, have a certain course, which means that it is simply impossible to simply connect these nodes. Engineers solved this problem with a transmission.
It allows you to transfer rotation from one node to another, located at different angles, as well as to balance all their mutual fluctuations without compromising the transmitted power. This is the purpose of the transfer.
The key element of the mechanism is the so-called universal joint, which is the most ingenious engineering solution that allows you and me to enjoy a car journey.
It must be said that cardans are used in various parts of the machine. Basically, of course, they can be found in the transmission, but in addition, this type of transmission is related to the steering system.
