
4-Wire Ignition Coil Schematic (Complete Guide)
Content
This article will provide the necessary information about the 4-wire ignition coil circuit.
The ignition coil is the heart of the ignition system, and improper ignition coil wiring can cause electronic ignition to malfunction, resulting in cylinder misfire. So you should be able to correctly identify the 4 pins when using a 4 wire ignition coil. In this short article, I will tell you everything I know about the circuit of a four-wire ignition coil and how it works.
The ignition coil can produce very high voltage (about 50000V) using a 12V battery voltage. A 4-wire ignition coil has four pins; 12V IGF, 5V IGT and ground.
I will cover more about this electronic ignition process in the article below.
What does an ignition coil do?
The ignition coil converts the low voltage of 12V into a higher voltage. Depending on the quality of the two windings, this voltage can reach 50000V. This voltage is then used to produce the spark required for the combustion process in the engine (with spark plugs). So you can refer to the ignition coil as a short step-up transformer.
Quick-Tip: Some mechanics use the term "spark coil" to refer to an ignition coil.
Diagram of a 4-wire ignition coil
When it comes to ignition coils, they come in many variations. For example, you can find 2-wire, 3-wire or 4-wire ignition coils in different car models. In this article, I will talk about a 4-wire ignition coil. So why is the 4-wire ignition coil so special? Let's find out.
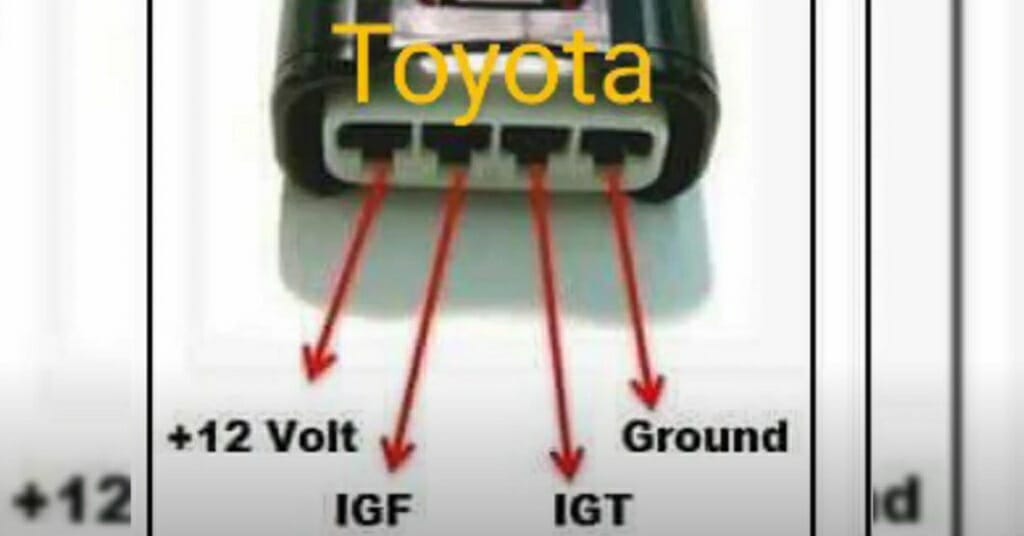

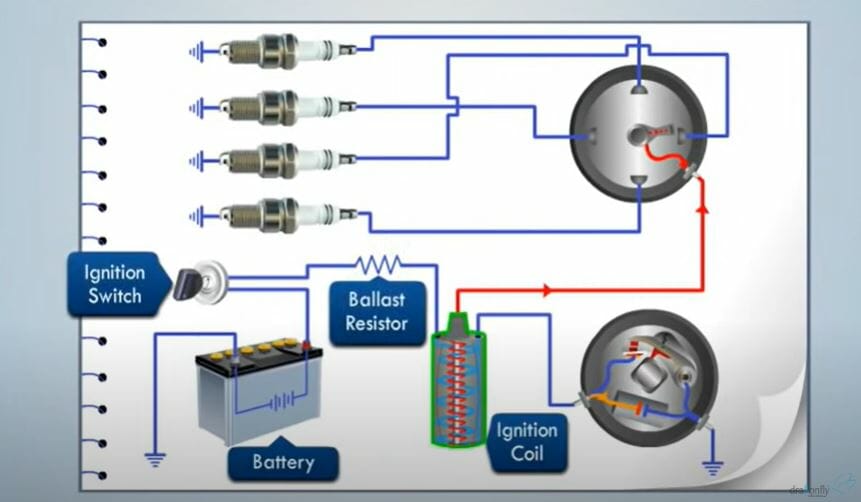
First, a 4-wire ignition coil has four pins. Study the image above for the wiring diagram of the coil pack.
- contact 12 V
- Pin 5V IGT (reference voltage)
- pin IGF
- Ground contact
The 12V contact comes from the ignition switch. The battery sends a 12V signal to the ignition coil through the ignition switch.
The 5V IGT pin acts as a reference voltage for the 4-wire ignition coil. This pin connects to the ECU and the ECU sends a 5V trigger signal to the ignition coil through this pin. When the ignition coil receives this trigger signal, it fires the coil.
Quick-Tip: This 5V reference voltage is useful for testing ignition coils.
The IGF output sends a signal to the ECU. This signal is a confirmation of the health of the ignition coil. The ECU continues to work only after receiving this signal. When the ECU does not detect an IGF signal, it sends code 14 and stops the engine.
The ground pin connects to any ground point in your vehicle.
How a 4-wire ignition coil works
The 4-wire ignition coil consists of three main parts; iron core, primary winding and secondary winding.
Primary winding
The primary winding is made of thick copper wire with 200 to 300 turns.
Secondary winding
The secondary winding is also made of thick copper wire, about 21000 turns.
iron core
It is made of a laminated iron core and is able to store energy in the form of a magnetic field.
And this is how these three parts generate about 50000 volts.
- When current passes through the primary, it creates a magnetic field around the iron core.
- Due to the process described above, the contact breaker connection is disconnected. And destroy the magnetic field too.
- This sudden disconnection creates a very high voltage (about 50000 V) in the secondary winding.
- Finally, this high voltage is transmitted to the spark plugs through the ignition distributor.
How do you know if your car has a bad ignition coil?
A bad ignition coil will cause all sorts of problems for your car. For example, the engine may start to stall when the vehicle accelerates. And the car can suddenly stall due to this misfire.
Quick-Tip: Misfires can occur when one or more cylinders ignite incorrectly. Sometimes the cylinders may not work at all. You may need to test the ignition coil module when this happens.
In addition to engine misfires, there are several other signs of a bad ignition coil.
- Check if the engine light is on
- Sudden loss of power
- Poor fuel economy
- Difficulty starting the car
- Hissing and coughing sounds
Take a look at some of our articles below.
- How to connect ignition coil circuit
- How to check the ignition coil with a multimeter
- How to check the ignition control unit with a multimeter
Video links


Watch this video on YouTube


Watch this video on YouTube

