EBD brake force distribution system - description and principle of operation
To combat the dynamic redistribution of the car's weight along the axles, primitive hydraulic devices were previously used to regulate the brake force on one or two axles depending on the suspension load. With the advent of high-speed multi-channel ABS systems and related equipment, this is no longer necessary. The component of the anti-lock braking system, which is responsible for regulating pressure when the center of gravity shifts along the axis of the car, is called EBD - Electronic Brake Distribution, that is, literally, electronic brake force distribution.

What is the role of EBD in a car
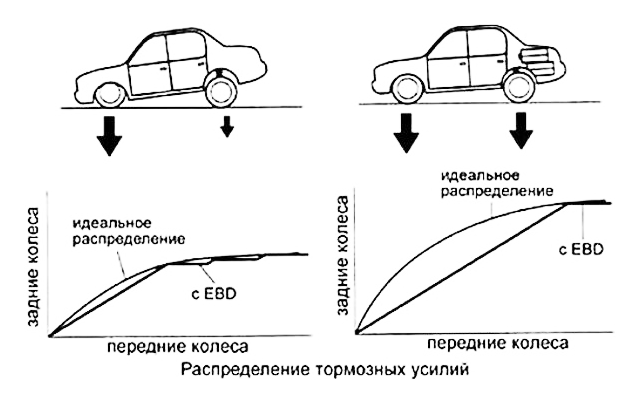
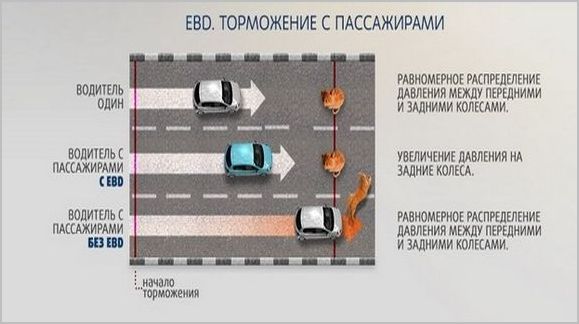
The distribution of the grip weight along the axles of the car is influenced by two factors - static and dynamic. The first is determined by the loading of the car, it is impossible to place the gas station, passengers and cargo in such a way that their center of mass coincides with that of an empty car. And in dynamics, a vector of negative acceleration is added to the vector of gravity during braking, directed perpendicular to the gravitational one. The result will shift the projection onto the road along the path. The front wheels will be additionally loaded, and part of the traction weight will be removed from the rear.
If this phenomenon is ignored in the brake system, then if the pressures in the brake cylinders of the front and rear axles are equal, the rear wheels can block much earlier than the front ones. This will lead to a number of unpleasant and dangerous phenomena:
- after the transition to the sliding of the rear axle, the car will lose stability, the resistance of the wheels to lateral displacement relative to the longitudinal one will be reset, the slightest impacts that always exist will lead to lateral slip of the axle, that is, skidding;
- the total braking force will decrease due to a decrease in the coefficient of friction of the rear wheels;
- the rate of wear of the rear tires will increase;
- the driver will be forced to ease the force on the pedals to avoid going into an uncontrolled slip, thereby relieving pressure from the front brakes, which will further reduce braking efficiency;
- the car will lose directional stability, resonance phenomena may occur that are very difficult to fend off even for an experienced driver.
Previously used regulators partially compensated for this effect, but did it inaccurately and unreliably. The appearance of the ABS system at first glance eliminates the problem, but in reality its action is not enough. The fact is that the anti-lock braking system simultaneously solves many other tasks, for example, it monitors the unevenness of the road surface under each wheel or the redistribution of weight due to centrifugal forces in corners. Complex work with the addition of a redistribution of weight may stumble upon a number of contradictions. Therefore, it is necessary to separate the fight against the change in grip weight into a separate electronic system using the same sensors and actuators as ABS.
However, the end result of the work of both systems will be the solution of the same tasks:
- fixing the beginning of the transition to slippage;
- pressure adjustment separately for wheel brakes;
- maintaining the stability of movement and controllability in all conditions along the trajectory and the condition of the road surface;
- maximum effective deceleration.
The set of equipment does not change.
Composition of nodes and elements
EBD uses:
- wheel speed sensors;
- ABS valve body, including a system of intake and unloading valves, a pump with a hydraulic accumulator and stabilizing receivers;
- an electronic control unit, part of the program of which contains the EBD operation algorithm.

The program selects from the general data flow those that directly depend on the weight distribution, and works with them, unloading the ABS virtual block.
The algorithm of action
The system sequentially evaluates the condition of the car according to the ABS data:
- the difference in the operation of the ABS program for the rear and front axles is being studied;
- the decisions made are formalized in the form of initial variables for controlling the unloading valves of the ABS channels;
- switching between pressure reduction or hold modes uses typical blocking prevention algorithms;
- if necessary, to compensate for the transfer of weight to the front axle, the system can use the pressure of the hydraulic pump to increase the force in the front brakes, which pure ABS does not.
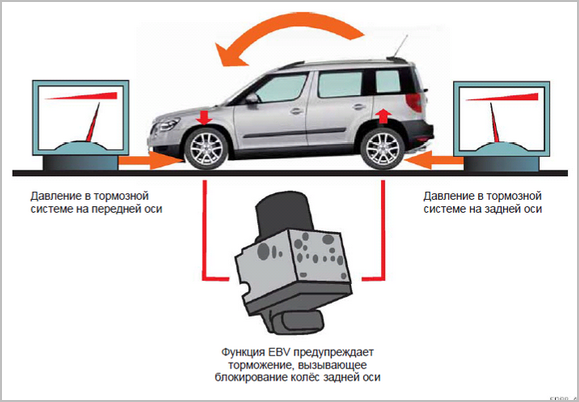
This parallel operation of the two systems allows precise response to longitudinal deceleration and shifting of the center of gravity as a result of vehicle loading. In any situation, the traction potential of all four wheels will be fully used.
The only drawback of the system can be considered its operation using the same algorithms and equipment as ABS, that is, some imperfection at the current level of development. There are shortcomings associated with the complexity and variety of road conditions, in particular slippery surfaces, loose and soft soils, profile fractures in combination with difficult road conditions. But with the advent of new versions, these issues are gradually being resolved.