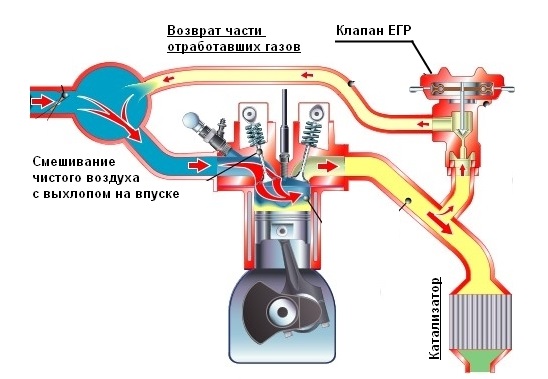
EGR system
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system was developed to improve the environmental rating of a car engine. Its use can reduce the concentration of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases. The latter are not sufficiently well removed by catalytic converters and, since they are the most toxic components in the composition of exhaust gases, the use of additional solutions and technologies is required.

How the system works
EGR is an abbreviation of the English term "Exhaust Gas Recirculation", which translates as "exhaust gas recirculation". The main task of such a system is to divert part of the gases from the exhaust manifold to the intake manifold. The formation of nitrogen oxides is directly proportional to the temperature in the combustion chamber of the engine. When exhaust gases from the exhaust system enter the intake system, the concentration of oxygen, which acts as a catalyst during the combustion process, decreases. As a result, the temperature in the combustion chamber decreases and the percentage of nitrogen oxide formation decreases.
The EGR system is used for diesel and gasoline engines. The only exceptions are turbocharged gasoline vehicles, where the use of recirculation technology is inefficient due to the specifics of the engine operation mode. In general, EGR technology can reduce nitrogen oxide concentrations by up to 50%. In addition, the probability of detonation is reduced, fuel consumption becomes more economical (by almost 3%), and diesel cars are characterized by a decrease in the amount of soot in exhaust gases.
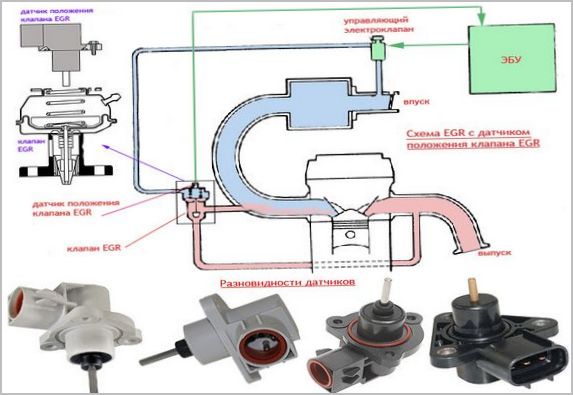
The heart of the EGR system is the recirculation valve, which controls the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. It operates at high temperatures and is subjected to high loads. Forced temperature reduction can be created, which requires a radiator (cooler) that is installed between the exhaust system and the valve. It is part of the car's overall cooling system.
In diesel engines, the EGR valve opens at idle. In this case, exhaust gases make up 50% of the air entering the combustion chambers. As the load increases, the valve gradually closes. For a gasoline engine, the circulation system usually operates only at medium and low engine speeds and delivers up to 10% of the exhaust gases in the total air volume.
What are EGR valves
Currently, there are three types of exhaust recirculation valves, which differ in the type of actuator:
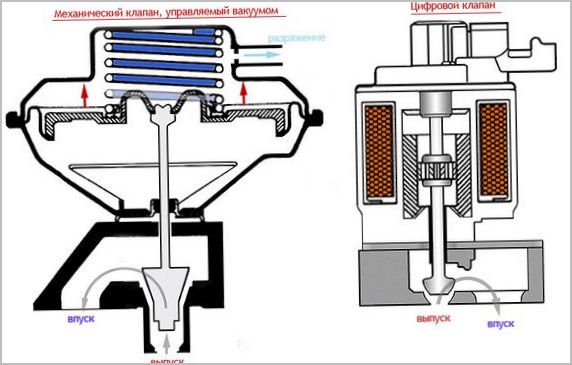
- Pneumatic. The simplest, but already outdated actuator of the exhaust gas recirculation system. In fact, the effect on the valve is carried out by a vacuum in the intake manifold of the car.
- Electropneumatic. The pneumatic EGR valve is controlled by a solenoid valve, which operates from signals from the engine ECU based on data from several sensors (exhaust gas pressure and temperature, valve position, intake pressure and coolant temperature). It connects and disconnects the vacuum source and creates only two positions of the EGR valve. In turn, the vacuum in such a system can be created by a separate vacuum pump.
- Electronic. This type of recirculation valve is directly controlled by the vehicle's engine ECU. It has three positions for smoother exhaust flow control. The position of the electronic EGR valve is switched by magnets that open and close it in various combinations. This system does not use a vacuum.
Types of EGR in a diesel engine
The diesel engine uses various types of exhaust gas recirculation systems, the coverage of which is determined by the vehicle's environmental standards. There are currently three of them:
- High pressure (corresponds to Euro 4). The recirculation valve connects the exhaust port, which is installed in front of the turbocharger, directly to the intake manifold. This circuit uses an electro-pneumatic drive. When the throttle is closed, the pressure in the intake manifold decreases, resulting in a higher vacuum. This creates an increase in the flow of exhaust gases. On the other hand, boost intensity is reduced because less exhaust gases are fed into the turbine. At wide open throttle, the exhaust gas recirculation system does not work.
- Low pressure (corresponds to Euro 5). In this scheme, the valve is connected to the exhaust system in the area between the particulate filter and the muffler, and in the intake system before the turbocharger. Thanks to this compound, the temperature of the exhaust gases is reduced, and they are also cleaned of soot impurities. In this case, compared to the high-pressure scheme, the pressurization is carried out at full capacity, since the entire gas flow passes through the turbine.
- Combined (corresponds to Euro 6). It is a combination of high and low pressure circuits, each with its own recirculation valves. In normal mode, this circuit operates on the low pressure channel, and the high pressure recirculation channel is connected when the load increases.
On average, the exhaust gas recirculation valve lasts up to 100 km, after which it can clog and fail. In most cases, drivers who do not know what recirculation systems are for simply remove them completely.