Diesel injection systems. Design, advantages and disadvantages
 Unlike petrol engines, diesel engines had fuel injection from the start. Only the injection systems, fittings and the pressure of the fuel supplied to the cylinders changed.
Unlike petrol engines, diesel engines had fuel injection from the start. Only the injection systems, fittings and the pressure of the fuel supplied to the cylinders changed.
 The working principle of a diesel engine, commonly known as a diesel engine, is completely different from that of a gasoline engine. In fuel trucks, the fuel-air mixture enters the combustion chamber above the piston. After compression, the mixture is ignited due to the breakdown of an electrical spark at the electrodes of the spark plug. This is why gasoline engines are also called spark ignition (SI) engines.
The working principle of a diesel engine, commonly known as a diesel engine, is completely different from that of a gasoline engine. In fuel trucks, the fuel-air mixture enters the combustion chamber above the piston. After compression, the mixture is ignited due to the breakdown of an electrical spark at the electrodes of the spark plug. This is why gasoline engines are also called spark ignition (SI) engines.
In diesel engines, the piston in the combustion chamber compresses only air, which, under the influence of enormous pressure (at least 40 bar - hence the name "high pressure") is heated to a temperature of 600-800 ° C. Injection of fuel into such hot air results in immediate self-ignition of the fuel in the combustion chamber. For this reason, diesel powertrains are also referred to as compression ignition (CI) engines. From the beginning, they were supplied by injecting fuel into the combustion chamber, and not into the intake manifold, which only supplies air to the engine. Depending on whether the combustion chamber was divided or not, diesel engines were divided into power units with indirect or direct injection.
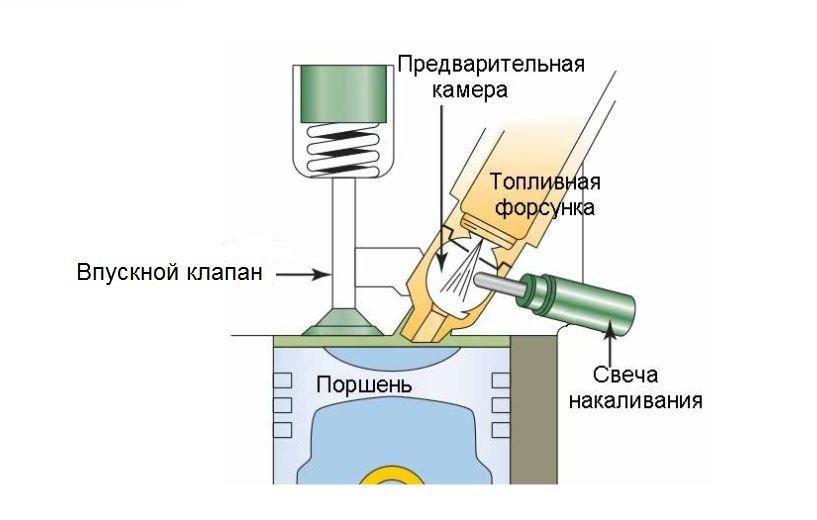
 Indirect injection
Indirect injection
Diesel, although it debuted with a direct injection system, was not used for long. This solution caused too many problems and in the automotive industry it was replaced by indirect injection patented in 1909. Direct injection remained in large stationary and marine engines, as well as in some trucks. Passenger car designers favored indirect-injection diesels, with smoother operation and less noise.
The term "indirect" in diesel engines means something completely different than in gasoline engines, where indirect injection is the injection of an air-fuel mixture into the intake manifold. In indirect injection diesel engines, as in direct injection designs, the fuel atomized by the injector also enters the combustion chamber. It's just that it is divided into two parts - an auxiliary part, into which fuel is injected, and the main part, i.e. the space directly above the piston in which the main process of fuel combustion takes place. The chambers are interconnected by a channel or channels. In terms of form and function, the chambers are divided into preliminary, vortex and air reservoirs.
The latter can not be used, since their production has practically ceased. In the case of prechambers and swirl chambers, the nozzle is installed next to the auxiliary chamber and injects fuel into it. There, ignition occurs, then the partially burned fuel enters the main chamber and burns out there. Diesels with a prechamber or swirl chamber run smoothly and may have lightweight crank systems. They are not sensitive to fuel quality and may have nozzles of a simple design. However, they are less efficient than direct injection diesels, consume more fuel, and have trouble starting a cold engine. Today, indirect injection diesel engines in passenger cars are a thing of the past and are no longer produced. They are rarely found in modern cars on the market today. They can only be found in designs such as the Indian Hindustan and Tata, the Russian UAZ, the older generation Mitsubishi Pajero sold in Brazil, or the Volkswagen Polo offered in Argentina. They are used in much larger quantities in aftermarket vehicles.
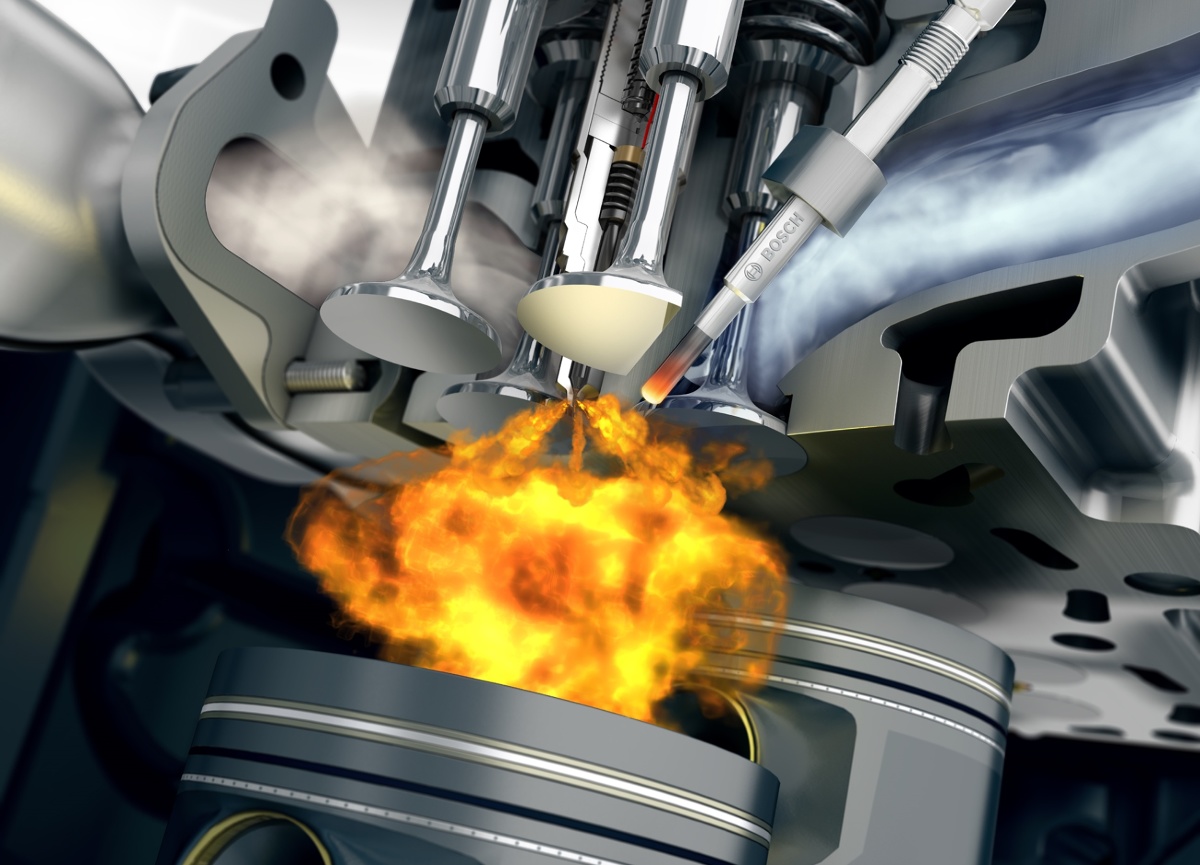
 Direct injection
Direct injection
It all started with him. However, the benefits of direct injection were not initially exploited. The importance of proper swirling of the fuel was not known and its combustion was not optimal. Fuel lumps formed, which contributed to the formation of soot. The processes on the piston went too fast, the engines worked hard, quickly destroying the crankshaft bearing. For this reason, direct injection was abandoned, preferring indirect injection.
A return to the roots, but in a modern version, occurred only in 1987, when the Fiat Croma 1.9 TD entered mass production. Direct fuel injection requires efficient injection equipment, high injection pressure, good quality fuel, and a very strong (and therefore heavy) crankset. However, it provides high efficiency and easy start of a cold engine. Modern solutions for direct injection diesel engines are based mainly on completely flat heads and pistons with appropriately shaped chambers (cavities). The chambers are responsible for the correct turbulence of the fuel. Direct injection is widely used today in passenger car diesel engines.
 Direct Injection - Pump Injectors
Direct Injection - Pump Injectors
In traditional diesel engines, different types of pumps are responsible for supplying fuel. In pioneering times, fuel injection was done with compressed air; in the 20s, this was done with redesigned oil pumps. In the 300s, special pumps designed for diesel engines were already widely used. Initially, it was based on serial pumps that create low pressure (up to 60 bar). It was not until the 1000s that more efficient pumps with axial distributor (over 80 bar) appeared. In the mid-seventies they received mechanical injection control, and in the mid-eighties they received electronic control (BMW 524td, 1986).
Pump-injectors used in trucks already in the 30s were a slightly different way of fuel injection, they were widely used in passenger cars by the Volkswagen concern, for the first time in 1998 (Passat B5 1.9 TDI). In short, a pump injector is an injector with its own pump, which is driven by a camshaft. Thus, the entire process of pressurizing and injecting into the cylinder is limited to the cylinder head. The system is very compact, there are no fuel lines connecting the pump to the injectors. Therefore, there is no nozzle pulsation, which makes it difficult to regulate the dose of fuel and leaks. Since the fuel partially vaporizes in the unit injector chamber, the injection timing may be small (easy start). Most important, however, is the very high injection pressure of 2000-2200 bar. The dose of fuel in the cylinder mixes quickly with air and burns very efficiently.
In general, diesel with unit injectors is characterized by high efficiency, low fuel consumption, high speed and the possibility of obtaining high power density. But a unit injector engine is expensive to manufacture, mainly due to the complexity of the cylinder head. His work is hard and loud. When powered by unit injectors, there are also problems with exhaust toxicity, which largely contributed to VW's abandonment of this solution.
 Direct Injection - Common Rail
Direct Injection - Common Rail
The most important element of the Common Rail injection system is the "Common Rail", a type of tank also known as a "pressurized fuel accumulator", into which a pump pumps diesel fuel. It enters the nozzles not directly from the pump, but from the tank, while maintaining the same pressure for each cylinder.
Figuratively, we can say that each of the injectors does not wait for a portion of fuel from the pump, but still has fuel at a very high pressure. The electrical impulses that actuate the injectors are sufficient to supply fuel to the combustion chambers. Such a system allows you to create multi-phase injections (even 8 phases per injection), which leads to very precise combustion of fuel with a gradual increase in pressure. The very high injection pressure (1800 bar) allows the use of injectors with very small orifices that deliver fuel almost in the form of a mist.
All this is complemented by high engine efficiency, smooth running and low noise level (despite direct injection), good maneuverability and low exhaust emissions. However, common rail engines require the highest quality fuel and the best filters. Contaminants in the fuel can destroy injectors and cause damage that is extremely costly to repair.
