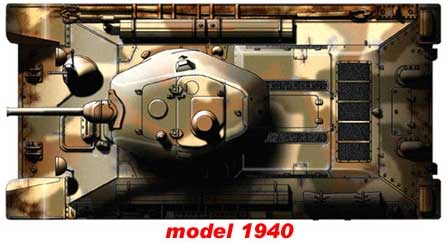
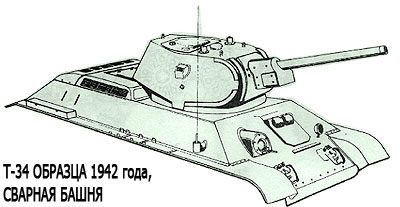
Medium Tank T-34
Medium Tank T-34
High mobility was provided by a powerful diesel engine and wide tracks. The high manufacturability of the design made it possible to set up serial production of the T-34 at seven machine-building plants of different equipment. During the Great Patriotic War, along with an increase in the number of tanks produced, the task of improving their design and simplifying the manufacturing technology was solved. The initial prototypes of the welded and cast turret, which were difficult to manufacture, were replaced by a simpler cast hexagonal turret. The increase in engine life was achieved by the creation of highly efficient air cleaners, improved lubrication systems and the introduction of an all-mode governor. Replacing the main clutch with a more advanced one and the introduction of a five-speed gearbox instead of a four-speed one contributed to an increase in the average speed. Stronger tracks and cast track rollers improve undercarriage reliability. Thus, the reliability of the tank as a whole was increased, while the complexity of manufacturing was reduced. In total, more than 52 thousand T-34 tanks were produced during the war years, which took part in all battles.
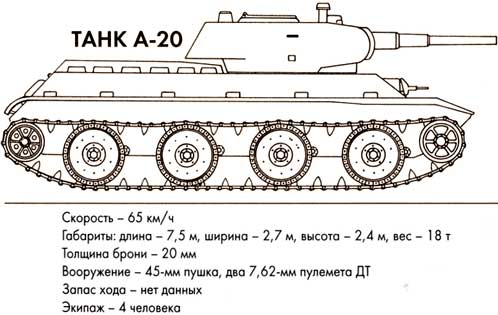
The history of the creation of the T-34 tankOn October 13, 1937, the Kharkov Steam Locomotive Plant named after the Comintern (plant number 183) was issued with tactical and technical requirements for the design and manufacture of a new wheeled-tracked tank BT-20. To accomplish this task, by the decision of the 8th Main Directorate of the People's Commissariat of the Defense Industry, a special design bureau was created at the plant, subordinate directly to the chief engineer. He received the factory designation A-20. In the course of its design, another tank was developed, almost identical to the A-20 in terms of weight and dimensions. Its main difference was the lack of a wheel drive.
As a result, on May 4, 1938, at a meeting of the USSR Defense Committee, two projects were presented: the A-20 wheeled-tracked tank and the A-32 tracked tank. In August, both of them were considered at a meeting of the Main Military Council, were approved and in the first half of the next year they were made in metal.
According to its technical data and appearance, the A-32 tank differed slightly from the A-20. It turned out to be 1 ton heavier (combat weight - 19 tons), had the same overall dimensions and shape of the hull and turret. The power plant was similar - diesel V-2. The main differences were the absence of a wheel drive, the thickness of the armor (30 mm instead of 25 mm for the A-20), the 76 mm cannon (45 mm was initially installed on the first sample), the presence of five road wheels on one side in the chassis.
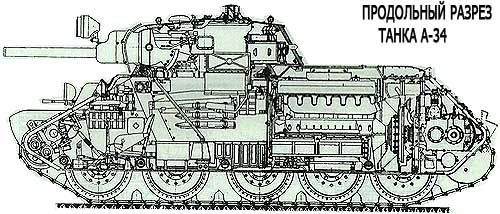
Joint tests of both machines were carried out in July - August 1939 at the training ground in Kharkov and revealed the similarity of their tactical and technical characteristics, primarily dynamic ones. The maximum speed of combat vehicles on tracks was the same - 65 km / h; the average speeds are also approximately equal, and the operational speeds of the A-20 tank on wheels and tracks did not differ significantly. Based on the test results, it was concluded that the A-32, which had a margin for increasing mass, should be protected with more powerful armor, respectively, increasing the strength of individual parts. The new tank received the designation A-34.
In October - November 1939, two A-32 machines were tested, loaded up to 6830 kg (up to the mass of A-34). On the basis of these tests, on December 19, the A-34 tank was adopted by the Red Army under the symbol T-34. Until the very beginning of the war, officials of the People's Commissariat of Defense did not have a firm opinion about the T-34 tank, which had already been put into service. The management of plant No. 183 did not agree with the opinion of the customer and appealed this decision to the central office and the people's commissariat, offering to continue production and give the army T-34 tanks with corrections and a warranty mileage reduced to 1000 km (from 3000). K. E. Voroshilov put an end to the dispute, agreeing with the opinion of the plant. However, the main drawback noted in the report of the specialists of the NIBT Polygon - the tightness has not been corrected.
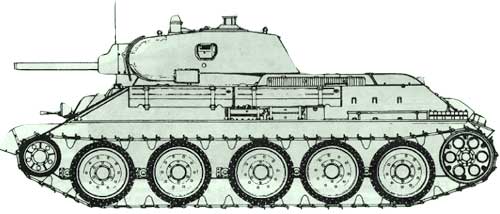
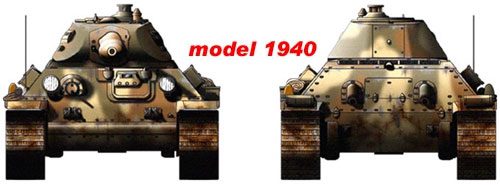
In its original form, the T-34 tank produced in 1940 was distinguished by a very high quality of processing of armor surfaces. In wartime, they had to sacrifice for the sake of mass production of a combat vehicle. The original production plan for 1940 provided for the production of 150 serial T-34s, but in June this number had increased to 600. Moreover, production was supposed to be deployed both at Plant No. 183 and at the Stalingrad Tractor Plant (STZ), which was supposed to produce 100 vehicles. However, this plan turned out to be far from reality: by September 15, 1940, only 3 serial tanks were produced at the KhPZ, and the Stalingrad T-34 tanks left the factory workshops only in 1941.
The first three production vehicles in November-December 1940 underwent intensive shooting and mileage tests on the Kharkov-Kubinka-Smolensk-Kiev-Kharkov route. The tests were carried out by officers of the NIBT Polygon. They identified so many design flaws that they questioned the combat effectiveness of the machines being tested. GABTU submitted a negative report. In addition to the fact that the armor plates were installed at large angles of inclination, the thickness of the armor of the 34 T-1940 tank surpassed most of the average vehicles of that time. One of the main drawbacks was the L-11 short-barreled cannon.
The second prototype A-34
Initially, a 76-mm L-11 cannon with a barrel length of 30,5 calibers was installed in the tank, and starting from February 1941, along with the L-11, they began to install a 76-mm F-34 cannon with a barrel length of 41 calibers. At the same time, the changes affected only the armor mask of the swinging part of the gun. By the end of the summer of 1941, T-34 tanks were produced only with the F-34 gun, which was produced at plant No. 92 in Gorky. After the start of the Great Patriotic War, by GKO decree No. 1, the Krasnoye Sormovo plant (Plant No. 34 of the People's Commissariat of Industry) was connected to the production of T-112 tanks. At the same time, the Sormovites were allowed to install aircraft parts brought from Kharkov on tanks.
Thus, in the fall of 1941, STZ remained the only major manufacturer of T-34 tanks. At the same time, they tried to deploy the release of the maximum possible number of components in Stalingrad. Armored steel came from the Krasny Oktyabr plant, armored hulls were welded at the Stalingrad shipyard (plant No. 264), guns were supplied by the Barrikady plant. Thus, almost a complete production cycle was organized in the city. The same was true in Gorky and Nizhny Tagil. It should be noted that each manufacturer made some changes and additions to the design of the vehicle in accordance with its technological capabilities, therefore, T-34 tanks from different plants had their own characteristic appearance.
In total, 35312 T-34 tanks were manufactured during this time, including 1170 flamethrower ones. There is a T-34 production table, which differs somewhat in the number of tanks produced: 1940
1941
1942
1943
1944
Total
Back – Forward >> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


 The T-34 tank was created on the basis of an experienced medium A-32 and entered service in December 1939. The design of the thirty-four marks a quantum leap in the domestic and world tank building. For the first time, the vehicle organically combines anti-cannon armor, powerful armament and a reliable chassis. Projectile armor is provided not only by the use of rolled armor plates of great thickness, but also by their rational inclination. At the same time, the joining of the sheets was carried out by the method of manual welding, which in the course of production was replaced by automatic welding. The tank was armed with the 76,2 mm L-11 cannon, which was soon replaced by the more powerful F-32 cannon, and then the F-34. Thus, in terms of armament, it matched the KV-1 heavy tank.
The T-34 tank was created on the basis of an experienced medium A-32 and entered service in December 1939. The design of the thirty-four marks a quantum leap in the domestic and world tank building. For the first time, the vehicle organically combines anti-cannon armor, powerful armament and a reliable chassis. Projectile armor is provided not only by the use of rolled armor plates of great thickness, but also by their rational inclination. At the same time, the joining of the sheets was carried out by the method of manual welding, which in the course of production was replaced by automatic welding. The tank was armed with the 76,2 mm L-11 cannon, which was soon replaced by the more powerful F-32 cannon, and then the F-34. Thus, in terms of armament, it matched the KV-1 heavy tank.