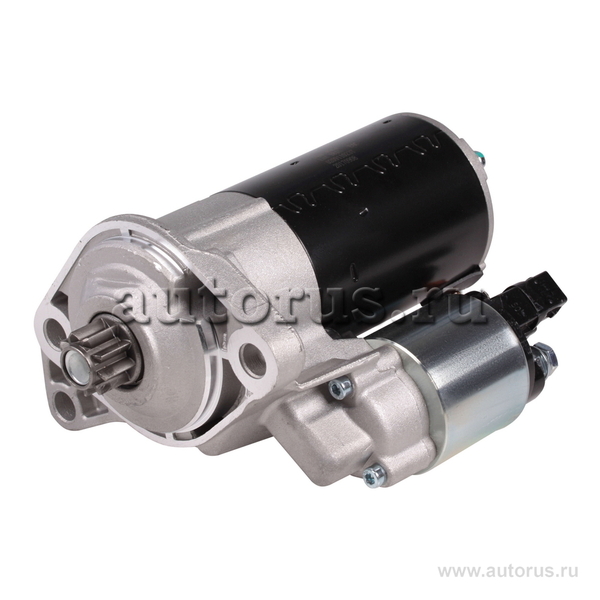
Starters to start!
Any type of motor requires the initiation of external energy. To accomplish this task, it is necessary to use an additional device that will reliably start even the largest drive unit every time. In cars, this function is performed by a starter, which is a DC motor. It is additionally equipped with gears and control systems.
How does it work?
The starter is a relatively small but ingenious device that overcomes the resistance of the shaft when it is started with a relatively low torque. The starting device is equipped with a small gear wheel (the so-called gear), which, when the engine is “started”, interacts with a special mesh around the circumference of the flywheel or torque converter. Thanks to the high starter speed converted into torque, the crankshaft can be rotated and the engine can be started.
Electrical to Mechanical
The most important element of the starter is a DC motor, which consists of a rotor and a stator with windings, as well as a commutator and carbon brushes. The stator windings create a magnetic field. After the windings are powered by direct current from the battery, the current is directed to the commutator through carbon brushes. Then the current flows to the rotor windings, creating a magnetic field. The opposite magnetic fields of the stator and rotor cause the latter to rotate. Starters differ from each other in terms of power and starting capabilities of drives of different sizes. Low-power devices designed for small cars and motorcycles use permanent magnets in the stator windings, and in the case of larger starters, electromagnets.
With single speed gearbox
So, the engine is already running. However, an important question remains to be solved: how now to protect the starter from constant acceleration by an already running drive? The above starting gear (gear) is driven by the so-called freewheel, colloquially known as a bendix. It performs a protective function against overspeed, allowing you to engage and disengage the starter gear with engagement along the flywheel circumference. How it works? After the ignition is turned on, the gear is moved by a special T-bar to engage around the circumference of the flywheel. In turn, after starting the engine, the power is turned off. The ring returns to its original position, releasing the gear from engagement.
Relay, i.e. electromagnetic switchhot
And finally, a few words about how to bring current to the starter, or rather to its most important windings. When it is turned on, the current flows to the relay, and then to two windings: retracting and holding. With the help of an electromagnet, a T-beam is actuated, which engages with a gear with engagement along the circumference of the flywheel. The core in the relay solenoid is pressed against the contacts and, consequently, the starter motor is started. The power supply to the pull-in winding is now off (the gear is already "connected" to mesh around the circumference of the flywheel), and current continues to flow through the holding winding until the car engine starts. At the moment of its operation and in this winding, the current stops flowing and the Taurus returns to its original position.