Compression ratio and octane number of gasoline
Content
Compression ratio - self-ignition resistance
The physical ratio of the total volume of the cylinder at the time the piston is in the dead center to the working volume of the internal combustion chamber is characterized by the compression ratio (CL). The indicator is described by a dimensionless quantity. For gasoline drives it is 8–12, for diesel drives it is 14–18. Increasing the parameter increases power, engine efficiency, and also reduces fuel consumption. However, high CV values increase the risk of self-ignition of the combustible mixture at high pressure. For this reason, gasoline with a high coolant index must also have high knock resistance - octane number (OC).


Octane rating - knock resistance
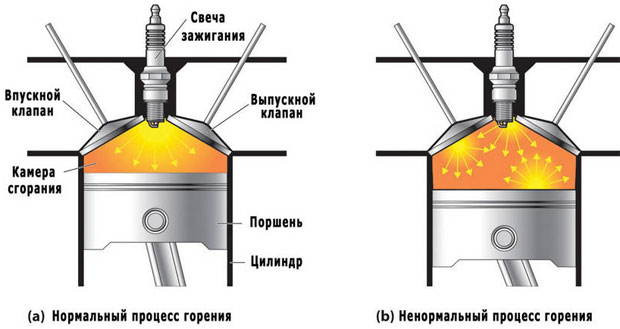
Premature combustion of gasoline is accompanied by a characteristic knock caused by detonation waves inside the cylinder. A similar effect is due to the low resistance of liquid fuel to self-ignition at the time of compression. Knock resistance is characterized by an octane number, and a mixture of n-heptane and isooctane was chosen as a reference. Commercial grades of gasoline have an octane value in the region of 70–98, which corresponds to the percentage of isooctane in the blend. To increase this parameter, special octane-correcting additives are introduced into the mixture - esters, alcohols, and less often heavy metal ethylates. There is a relationship between the compression ratio and the brand of gasoline:
- In the case of CV less than 10, AI-92 is used.
- AI-10 is required for SJ 12–95.
- If CV is 12–14 - AI-98.
- With CV equal to 14, you will need AI-98.

For a standard carbureted engine, the CV is approximately 11,1. In this case, the optimal OC is 95. However, methanol is used in some racing types of cars. The SD in this example reaches 15, and the OC varies from 109 to 140.
Use of low octane gasoline
The car manual indicates the type of engine and the recommended fuel. The use of a combustible mixture with a low OC leads to premature burnout of the fuel and sometimes the destruction of the structural elements of the motor.
It is also important to understand which fuel supply system is used. For a mechanical (carburetor) type, compliance with the requirements for OC and SJ is mandatory. In the case of an automatic or injection system, the air-fuel mixture is adjusted electronically. The gasoline mixture is saturated or depleted to the required OCH values, and the engine is running normally.


High octane fuel
AI-92 and AI-95 are the most used brands. If you fill the tank, for example, with the 95th instead of the recommended 92nd, there will be no serious damage. Only the power will increase within 2-3%. If you fill the car with 92 instead of 95 or 98, then fuel consumption will increase, and power will decrease. Modern cars with electronic injection control the supply of a combustible mixture and oxygen and thereby protect the engine from undesirable effects.
Table of compression ratio and octane number
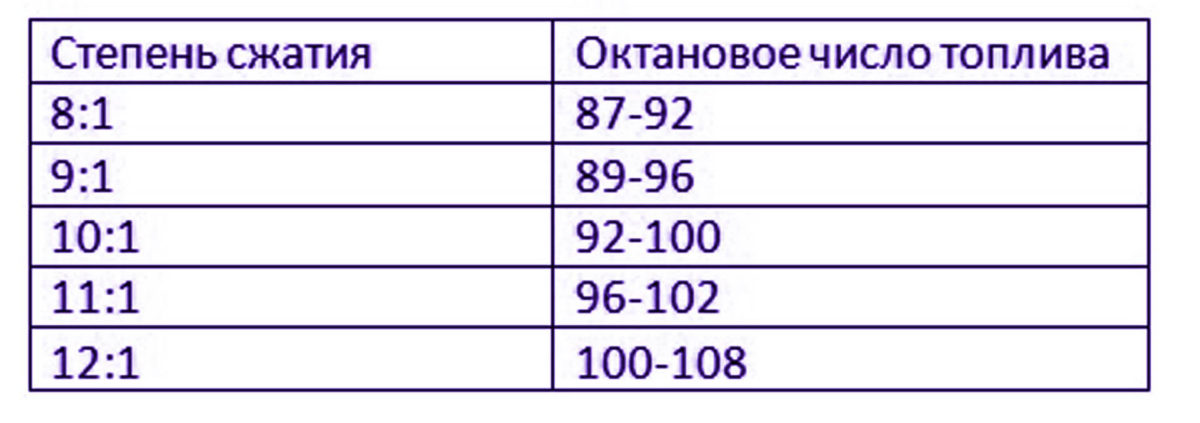
The knock resistance of automotive fuel has a direct relationship with the compression ratio, which is presented in the table below.
| Och | SJ |
| 72 | 6,8 – 7,0 Feet |
| 76 | 7,2 – 7,5 Feet |
| 80 | 8,0 – 9,0 Feet |
| 91 | 9,0 |
| 92 | 9,1 – 9,2 Feet |
| 93 | 9,3 |
| 95 | 10,5 – 12 Feet |
| 98 | 12 – 14 Feet |
| 100 | More 14 |
Conclusion
Motor gasolines are characterized by two main characteristics - knock resistance and compression ratio. The higher the SO, the more OC is required. The use of fuel with a lower or higher value of knock resistance in modern cars will not harm the engine, but will affect the power and fuel consumption.


Watch this video on YouTube
