
Retention of the road: the determining factors
Content
- Center of gravity
- Wheelbase / chassis
- Reinforcement of the chassis: anti-roll bars and a transverse bar
- Weight distribution
- Total weight / mass
- Shock absorbers
- Rigidity / flexibility
- Rigid / semi-rigid / multi-link axle
- Traction / Propulsion / Four-wheel drive
- Tires / Wheels
- Aerodynamics
- Brake
- Electronics: thanks to technology!

Undoubtedly, road holding is an essential element of safety and driving pleasure. We note the main factors that determine the quality of the behavior of the car.
Center of gravity
Each car has a more or less high center of gravity, depending on its height, as well as on the vertical distribution of mass. It makes sense that a sports car would have a much lower center of gravity than an SUV, since its height is much lower. However, two cars of the same size can have different centers of gravity ... Indeed, the more the masses are lowered (for example, some electric vehicles that put their flat batteries on the floor), the lower the center of gravity will be, and vice versa, the more weight, the higher the center gravity (which is why roof boxes can make your car more dangerous). A low center of gravity provides better stability, but also significantly reduces body mobility (and necessarily reduces suspension travel). The latter really causes an imbalance that also affects the traction of each train. The greater the movement of the body, the less uniform the distribution of pressure on each wheel. Some wheels will be crushed and others will be ecstatic (very little road contact, it may even happen that one of the wheels no longer touches the road on vehicles with a rudimentary rear axle: torsion bar axle).
You can change the center of gravity yourself a little by lowering the car, changing (or adjusting, but this is less common) the springs (which is why we put shorter ones). Note for amateurs that if you want to be on top, it is recommended to buy from KW or Bilstein.

Thanks to the dry sump engine, the Ferrari engine can be positioned even lower!

Beware of roof boxes that change the height of the center of gravity. The more it is filled, the more alert you will have to be.
Wheelbase / chassis
Of course, the very design of the chassis and undercarriage is important for good traction, but here we arrive at a technical and physical knowledge that is quite important, and on which I could not dwell in too much detail (however, some information here). ..
We can still talk about some of its components, such as the wheelbase (the distance between the front and rear wheels). When it is high, the car gains stability at high speed, but loses controllability a little in small turns (in extreme cases, a bus or limousine). Therefore, it must be large enough, but not too large, if we want a good balance between agility and stability (in addition, the ratio between track width and wheelbase length should not be too disproportionate). The long wheelbase contributes to understeer. Also, the more the wheels are at the ends of the chassis (short overhang), the better the road holding and the better body movement control (actually not that easy), but this remains a "relief" factor).

The 3 Series has a good compromise that allows both to maintain good low speed maneuverability while delivering over 200 km / h.

The 7 Series, like the Tasliman, offers erasing the understeer effect due to its very long wheelbase by offering steerable rear wheels.

If the Mini is amazingly efficient at moderate speeds, it takes a hard heart to try the 200 km / h peak ... Then stability will be compromised and the slightest bump in the steering wheel can be intimidating.
Reinforcement of the chassis: anti-roll bars and a transverse bar
These two bars affect the behavior of the car and, consequently, the quality of its handling. A strut brace (which can be located front and rear, or even in the middle of the cabin in competition) makes the chassis more rigid. We then feel that the car is very stiff, with the chassis feeling (more or less) disappearing (it 'rolls' less). You will be able to see it (if you have one) by opening the hood, it connects the two front shock absorber heads that run over the engine. So the purpose of the maneuver is to sum up, to strengthen the body structure by moving the elements to certain strategic places (those of the wheels are the points that take the most restrictions, which is logical since they carry the car)

Here is a two-piece spacer. The boom can also go straight from side to side in one block, unlike the photo above. In short, we are talking about the connection of the supports that hold the chassis.


here we are on the field of competition with a car prepared by Delage. The bar caliber speaks for itself ...
Also called anti-roll bar, anti-roll bar is found in almost all production cars, unlike the brace you find on the BMW 3 Series, but not actually in the Golf ... It thus allows you to limit roll without eliminating it. This is not the goal, because there should always be a minimum of roll (taking care not to be too important and therefore noticeable to the driver). It should be noted that, in general, the more efficient a car (such as a supercar), the more rigid the anti-roll bar will be (since it will be subjected to higher loads, it must be more resistant to deformation).

And here is the anti-roll bar, indicated by the white arrows.
Weight distribution
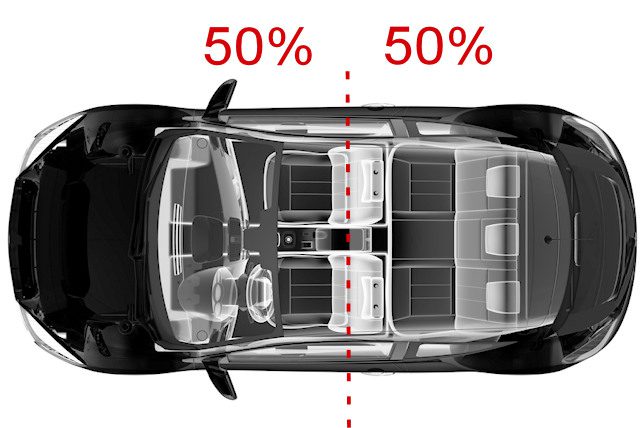
The ultimate goal of any car is to have a weight distribution on 50/50 or 50% of the weight in the front and the rest in the back (or in a pinch a little more in the back if it's a big propulsion to improve full load traction). And the easiest way to do this is to put the engine in the back, like any self-respecting super trainer. However, some front-engined sedans can also do this: it's usually a matter of the propulsion system, because the transmission going to the rear allows better mass distribution (traction, on the other hand, has all the weight in the front, since all the mechanicals designed to its thrusts are under the hood). When the engine is at the front, the goal will be to move it as far back as possible (hence towards the driver) using what is known as a longitudinal architecture.
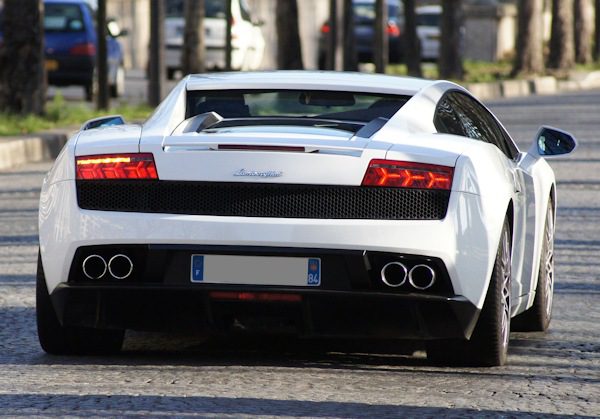

The Gallardo obviously has a center engine, in contrast to the diagram below, which shows a traditional front-engined car (more economical and practical. However, it is a longitudinal engine / powerplant version, so it is rather noble). Note in passing that this leads to certain behaviors that can be confusing to the less familiar. The rear wheels are also wider, as is often the case with high-performance powertrains (whether center / rear engine or not).
Total weight / mass
Overall weight is one of the most important components when handling it. That's why the racing stables are on the hunt for kilos, where carbon fiber is the star! It is really extremely durable and lightweight material at the same time. Unfortunately, its manufacturing method is very strange compared to other more traditional materials. This is really a fabric that needs to be shaped to the desired shape. When ready, it is placed in the oven and it hardens. As a result, it cannot be repaired and the cost of making/manufacturing it is prohibitive.

This is what carbon fiber looks like without paint.
But if weight seems to be the enemy, it is not always ... Indeed, at high speed it becomes a valuable ally! But this applies to aerodynamics, and in this case downforce.
Shock absorbers
Shock absorbers / suspensions almost as decisive than tires for handling. Their main function is to keep the tire in perfect contact with the road without bouncing (the more the tire stays stuck to the road, the more grip we have). Because indeed, if our suspension consisted only of banal springs, we would take up or lower speed bumps with a significant pumping effect (the car moves back and forth from bottom to top on every bump) to run over)… Thanks to the hydraulic system (shock absorber pistons) connected with a spring, the rebound effect is suppressed. Unfortunately, it can come back a bit when the shocks are worn out, so it's important to change them at the right time. This will depend on mileage, age, as well as the use of the vehicle (if you leave your car in the garage without moving, shock absorbers, like tires and some rubbers, tend to age).
Thus, the role of the shock absorber is to perfectly follow the road regardless of unevenness, and the goal is to keep the wheels in contact with the asphalt 100% of the time.

And the suspension ...
Air suspension of the car is made on springs. In the case of an understated car, they will have to be changed to shorter and cooler versions. In such a case, behavior improves significantly, even if comfort is lost. Equipped in this way, even an average car can start offering amazing performance (this can be seen in amateur rallies, of which some small cars work wonders). Obviously, not putting a price on good tires will help little ...
Rigidity / flexibility
The basic rule is that the more damping is increased, the more effective the control (within certain limits, of course, as in any field ...). And it will be better for high speeds (which cause much more limiting downforce), but also for limiting parasitic body movements that throw the car out of balance.
Be careful, however ... On degraded roads, a softer suspension sometimes provides better handling (and therefore better traction) than a stiffer suspension, which can then cause some rebound effect.

This Subaru has a fairly flexible suspension, despite its athletic genes. This allows him to better "ride" on degraded roads. Rally cars are a good example of this. However, on a track in perfect condition, it will be more difficult for him to set a good lap due to excessive body movements.
Rigid / semi-rigid / multi-link axle
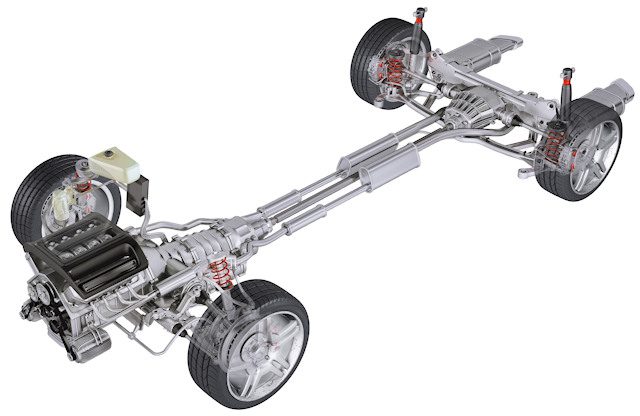

The quality of the axle design will also affect roadholding (but also the value of the vehicle ...). You should be aware that rigid and semi-rigid axles are more economical systems, but also less bulky for the rear axle (providing more living space). Therefore, their effectiveness is less important than the multi-channel process, which is much more technically advanced. For example, in the Volkswagen Golf 7 it is sold in a semi-rigid version (we are talking here only about the rear axle) with a TSI engine with 122 hp. and with a multi-link engine exceeding this power. Also note that the multi-link system provides slightly more comfort on poorly paved roads.
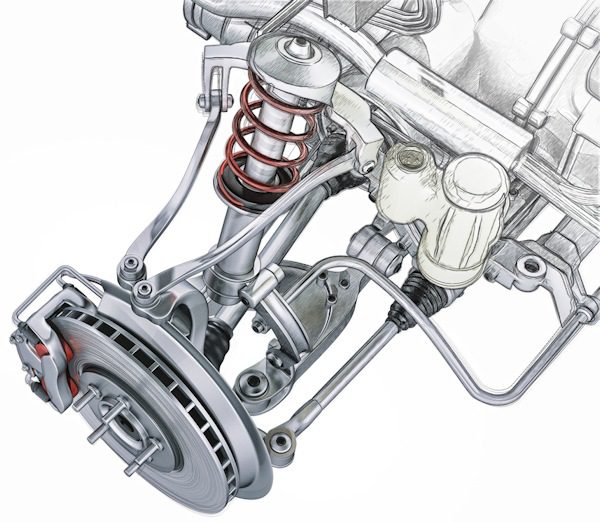
Rigid axles are no longer used for the front axles, nor for the rear axles for that matter. From now on, Macpherson axles are used primarily for the front axle, which allows space as the system is less cumbersome (there is also a double wishbone).
Therefore, the rear axle usually has a semi-rigid axle, which provides more comfort and flexibility in their kinematics than a completely rigid axle that can now be imagined. Note that a semi-rigid axle can only be used if it is a traction drive. Thus, it is the multi-link axle that remains the most efficient when it comes to premium vehicles. However, there is better, but this is rare (we see more in Ferrari), it is a double wishbone axle that further optimizes road stability and allows for more advanced settings (but takes up a lot of space). Note that the 2013 S-Class has double wishbones at the front and multi-link suspension at the rear. Ferrari has double wishbones front and rear.
If you're mixing brushes between different types of axes, take a quick tour here.
Traction / Propulsion / Four-wheel drive
For the less knowledgeable, let me remind you that traction means that the drive wheels are front. For propulsion, the rear wheels drive the machine.
If that doesn't make much of a difference for the modest horsepower, it should still be admitted that there will be better weight distribution to the rear wheel drive, since the elements (which weigh the weight) that make the rear wheels turn are located. at the rear, which is a bit against the weight of the front engine ...
And who says better weight distribution means better balance and therefore better handling. On the other hand, on very slippery ground such as snow, traffic can be annoying quickly (except for those looking to entertain the gallery with a skid, in which case it's perfect!).
Finally, know that thrust gets much better when it comes to inboard powerful engines. Indeed, in this configuration, power is transferred much better. The traction will lose traction and skid as soon as you accelerate too much (mostly the front end will deteriorate if overworked). This is why Audi usually offers its powerful models in a Quattro (4x4) version or because some powerful traction systems have a limited slip front differential. At the same time, we recall that the distribution of masses is necessarily worse in terms of adhesion (everything is located in the front).

In conclusion, let's talk about all-wheel drive. If the latter could suggest that this is the best configuration, well, after all, it is not so obvious ... Without a doubt, on slippery surfaces, four-wheel drive will always be better. On the other hand, on a dry road, it will be punished by understeer ... And then four-wheel drive is always a little heavier, not very good.
For information, the brands that use powertrains almost systematically are BMW and Mercedes. Audi doesn't seem to be a fan (special engine layout that promotes traction) even with longitudinal engine cars and the major brands simply can't afford it or the average customer income would have to go up! In addition, from an interior design point of view, the propulsion system does not optimize the space that will be offered to passengers and luggage.
Tires / Wheels
You are far from the majority of those who place a high value on their tires, because often the goal is to pay as little as possible (and I understand that we don't all have the same purchasing power!). However, as you might expect, they play a vital role in circulation.
Sore gums

First of all, there are several types of tires that support either endurance (wear rate) or road holding, and you should know that depending on the season you have to adapt your tires, because temperature has a direct effect on the composition….
Therefore, if you fit softer tires, you will generally have better controllability, but your tires will wear out faster (when I rub a piece of wood on the asphalt, it wears out faster than when I rub a piece. Titanium ... An example is a little atypical, but has the advantage of making it clear that the softer the tire, the more it wears out on the pavement). Conversely, a stiff tire will resist longer but have less grip knowing that it is even worse in winter (rubber becomes hard like wood!).
However, as Einstein well knows, everything is relative! Therefore, softness should be selected depending on the outside temperature as well as the weight of the vehicle. A soft tire that looks good on a light car will ride much less on a heavier one, which will tend to distort them too much when driving dynamically. It is the same with temperature: a soft tire will become stiff below a certain threshold (hence the existence of winter tires, the softness of which is regulated according to very low temperatures: at normal temperatures they become too soft and wear out like snow in the sun).
Sculpture of erasers
Smooth tires are forbidden, but you should know that on dry there is nothing better (except when they are pulled on a rope and you are riding on braids ...), which is usually called a slick. In fact, the more ground contact, the better the road holding. This occurs when the ridges are removed from the tires. On the other hand, as soon as it rains, it is necessary to be able to pump water between the road and the tire, hence the paramount importance of these ridges at the present time (in the spots it is a guaranteed ice rink).

As far as individual tires are concerned, I suggest you see several different ranges here. If you are looking for efficiency and therefore safety, give preference to the so-called tires from directed.

Here's a directional tire
Inflation
Inflating your tires is critical. The less they are inflated, the smoother the contact of the undercarriage with the road will be, which will lead to rolling. Excessive inflation reduces the friction surface and therefore reduces roadholding.
A balance must therefore be found, as under-inflated tires cause significant rolling and twisting of the tires, while over-inflating lowers the friction surface. Plus, your gums won't necessarily work their best ...

Also note that the pressure in your tires increases when they are hot, this is due to the expansion of the oxygen present in the air. Therefore, it should be expected that the hot pressure will be higher. Then you can fill the tires with nitrogen to avoid this phenomenon (more details here).
Finally, the pressure must be adapted to your load. If you put on weight, the tire crush will increase, so you will have to compensate for this with more inflation. On the other hand, it is advisable to deflate the tires if the grip on the ground becomes unstable: this is the case, for example, when driving on sand or on very icy terrain. But in this case, you need to go further.
dimensions

The size of your tires, and therefore in this case the rims, will also have a direct impact on the behavior of your vehicle. Also knowing that a rim size can fit multiple tire sizes ... Remember a tire reads like this:
225
/
60 R15
so that
Width
/
Arrogance District
, knowing that the height is a percentage of the width (in the example it is 60% of 225 or 135).
This also means that a 15-inch rim can accommodate several tire sizes: 235/50 R15, 215/55 R15, etc. Basically, the width will be related (this is more than logical) to the width of the rim, but it can differ significantly as in example, just like the height of the tire, which can vary from 30 (%, I remember that) to 70 (rarely leave these dimensions). Regardless, we cannot completely select the tire sizes, there are restrictions that must be observed as indicated by the manufacturer. To find out which type of tire is right for you, contact any technical control center, they will tell you what options you have. If you do not follow this rule, you will fail and risk getting a less balanced car (these standards are not in vain).

Coming back to handling, we generally recognize that the wider the width, the more grip we will have. And it makes sense, because the more the surface of the tire is in contact with the road, the more grip you have! However, this increases aquaplaning and decreases productivity (more friction = less speed at a certain power). Otherwise, very thin wheels are better in the snow ... Otherwise, the wider, the better!
Finally, there is the tire sidewall height. The more it is reduced (we call them low profile tires), the less tire distortion (again logical), which reduces body roll.
Obviously, this all works in reasonable proportions. If you put 22 inches on a classic car, the handling may even be reduced. It is not enough to put as large a rim as possible, but as much as possible, depending on the chassis of the car. Some chassis will have better efficiency at 17 inches, others 19…. Therefore, you need to find the right shoe for your child's feet, and it won't necessarily be the biggest one you need to choose!
Depending on the weather


Therefore, when it rains, it is ideal to have tires with a tread pattern that allows maximum water drainage. Also, as I said, width can be a disadvantage here, as it promotes aquaplaning: the "underside" of the tires removes less water than it receives. There is accumulation under them, and therefore a layer of water forms between the undercarriage and the road ...
Finally, snow enhances this effect: the thinner the tires, the better. Ideally, you need to have very soft gums, and with nails this becomes very practical.
Rim weight

This is a factor we tend to forget about: too much wheel weights can cause some strange inertia in the car's behavior: the wheels seem to want to keep the car on course. Therefore, you should avoid installing large wheel rims on your vehicle, or you should ensure that their weight remains moderate. They are made lightweight by several materials, such as magnesium or aluminum.
Aerodynamics

The aerodynamics of a car can help keep the road better as speed increases. Indeed, the design of the car's profile can allow for greater aerodynamic support, meaning the car will be pressed to the ground due to the shape of the aircraft's inverted wing (roughly speaking). When hitting or colliding with the ground, the tires are all the more in contact with the road, which makes it possible to increase traction. Therefore, we are trying to make the car gain weight at high speed in order to achieve stability and not fly away. It also makes the very light F1 capable of handling extreme speeds. Without aerodynamics to hold it back, it would have to be ballasted with more weight to avoid takeoff. Also note that the same principle is used so that they can make tighter turns at high speed, they use different kinds of side fins to turn using the lift generated by the air. F1 cars are a mixture of car and aviation.

However, we have to admit that this remains anecdotal for the A7 ... The spoiler is mostly here to flatter its driver!


This sometimes happens under a car with a diffuser designed to create downforce (reverse lift). The car then falls to the ground due to the ground effect.
Brake

Braking plays an important role in the behavior of the vehicle. The larger the discs and pads, the more friction there will be: the better the braking will be. In addition, ventilated discs and ideally drilled discs should be preferred (holes accelerate cooling). Braking consists in converting kinetic energy (inertia of a running car) into heat due to friction between the pads and the discs. The better you know how to cool the system, the more efficient it is ... The carbon / ceramic versions don't allow you to brake shorter, but they are more resistant to wear and heat. In the end, it may be more economical because the circuit eats up metal discs very quickly!
More information here.
The most economical cars sit on barrels. They are less efficient and sharp, but are suitable for small, low-powered vehicles (like the Captur).
Electronics: thanks to technology!
Those who are not too fond of electronics will be unhappy, but we have to admit that it improves the behavior of our cars, and not in an anecdotal way! Each wheel is electronically controlled, which can then brake each wheel independently, see here. Thus, the loss of control occurs much less frequently than before.

ABS: irreplaceable!
ABS helps prevent the wheels from locking when the driver brakes too much (usually reflexively), more on this operation here. It is so useful that it never turns off on modern cars, unlike ESP. In any case, removing it will not work.
Emergency Brake Assist (AFU)
What is this beast? We just talked about the ABS, what might this bug correspond to? Well, those studying accidents have found that many drivers refrain from pressing the brake pedal hard in an emergency for fear of locking the wheels (like your brain's ABS!). To remedy this, they programmed a small program that detects if the driver has an urgent need for braking (by observing the movements of the brake pedals). If the computer detects the need, it will slow down the car as much as possible, instead of allowing the driver to "bump" into an obstacle in front. The wheels are not locked, because in this case everything works with the ABS. More explanation here.
ESP

ESP is a bit like the fusion of a Gran Turismo (video game) and your car. Now that the engineers have been able to simulate the physics of objects on computers (and therefore create super-realistic car games, among other things, of course ...), they thought it could be used to help people with disabilities. Data processing field. Indeed, when the chip detects (using sensors) the movement of each wheel, position, speed, grip, etc., the Human will only feel a small fraction of all these elements.
As a result, when people make a mistake or want to make a turn at high speed (also a mistake), the machine interprets this and ensures that everything ends for the best. To do this, he will control the brakes wheel by wheel, having the ability to brake them independently, which a person can never do (except for 4 brake pedals ...). For more information about this system, I invite you to read this article.
Thus, it improves behavior by reducing the effect of oversteer and understeer, which is important! Plus, if a brutal flywheel 130 used to send you to the cabbage, now it's over! You will get to where you point the car and you will no longer be in uncontrolled rotation.
Since then, we have made further progress in the area of torque vectoring (see last paragraph).
Active suspension: top!
So, here we achieve the best of what has been made in the automotive world! If DS invented the principle, it has since been linked to electronics to achieve an impressive level of sophistication.
First, it allows you to adjust the damping of the shock absorbers depending on whether you want comfort or sportiness (and therefore roadholding). In addition, it allows, thanks to the leveling corrector, to avoid excessive body movements (leaning too much in turns), which significantly increases stability and stability on the road. In addition, the 2013 S-Class reads the road and detects bumps to soften the damping on the fly ... Better!
More information here.
Of course, a distinction should be made here between adjustable shock absorbers and air suspension. Therefore, the main active suspensions are based only on adjustable shock absorbers: the electronics can change the calibration of the shock absorbers, allowing oil to pass more or less quickly between the chambers (there are several methods for this).
The air suspension goes further, it includes adjustable dampers (a must, otherwise it doesn't make sense), and it also adds airbags instead of coil springs.
Torque vector?
Having become very fashionable, it is about using an independent wheel braking system to improve cornering speed. Indeed, the goal here is to slow down the inside wheel when cornering so that the outside wheel gets a bit more torque. Those who know how a differential works will understand that by doing this we are also increasing the torque transmitted to the outer wheel (the differential sends power to the axle that has the least resistance).
All comments and reactions
Dernier comment posted:
JLUC (Date: 2021, 08:14:09)
I admit that I have a certain fondness for half-slickers. They have less tenderness ... and they wear out less quickly.
Tenderness or tenderness? That is the question :)
(Your post will be visible under the comment after verification)
Write a comment