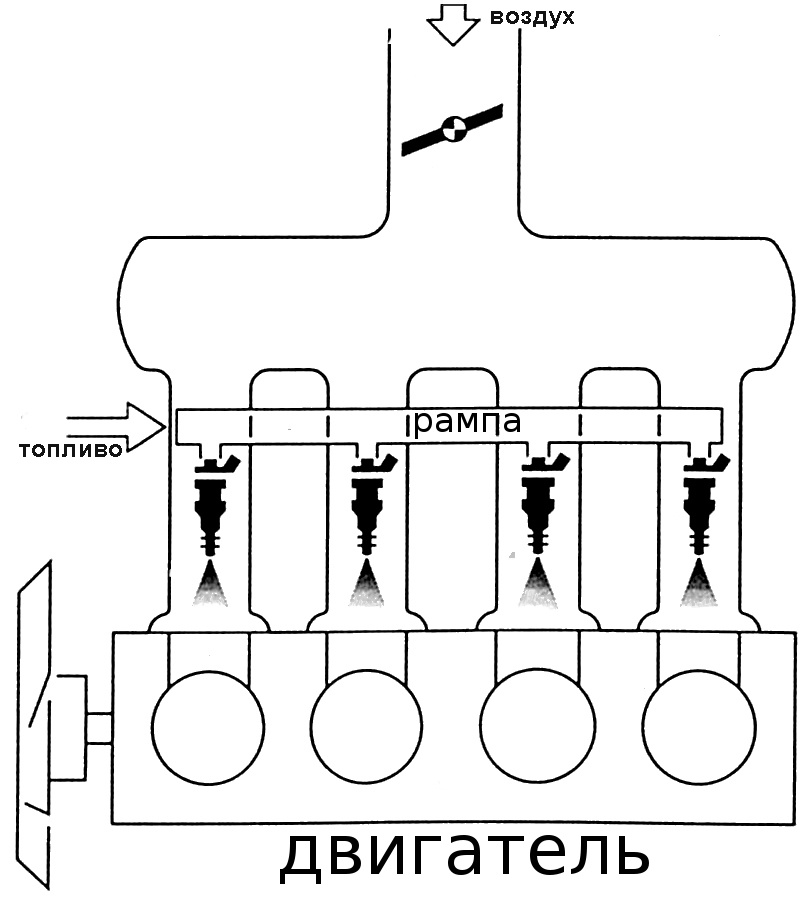
The device and principle of operation of multiport fuel injection MPI
Content
Pressurized fuel injection systems have evolved from simple mechanical devices to electronically controlled distributed systems that individually dose fuel into each engine cylinder. The abbreviation MPI (Multi Point Injection) is used to denote the principle of supplying gasoline by electromagnetic injectors to the intake manifold, as close as possible to the outside of the intake valve. Currently, this is the most common and massive way to organize the power supply of gasoline engines.
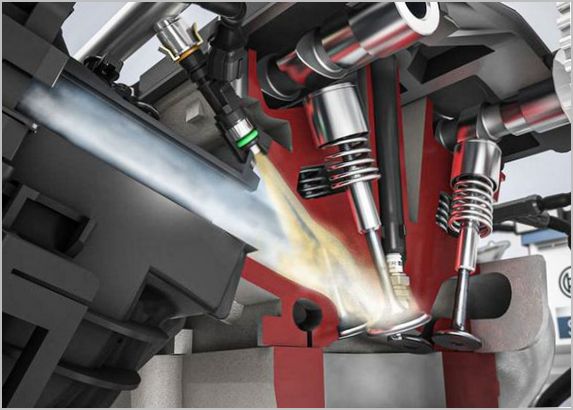

What is included in the system
The main goal of this construction was the accurate dosing of the cyclic fuel supply, that is, the calculation and cut-off of the required amount of gasoline, depending on the air mass supplied to the cylinders and other important current engine parameters. This is ensured by the presence of the main components:
- the fuel pump is usually located in the gas tank;
- pressure regulator and fuel line, can be single or double, with fuel return drain;
- ramp with injectors (injectors) controlled by electrical impulses;
- engine control unit (ECU), in fact, it is a microcomputer with advanced peripherals, permanent, rewritable and random access memory;
- numerous sensors that monitor engine operating modes, the position of controls and other vehicle systems;
- actuators and valves;
- software and hardware complex of ignition control, fully integrated into the ECM.
- additional means of reducing toxicity.

The equipment is distributed throughout the interior of the car from the trunk to the engine compartment, the nodes are connected by electrical wiring, computer data buses, fuel, air and vacuum lines.
Functioning of individual units and equipment as a whole
Gasoline is supplied from a pressurized tank by an electric pump located there. The electric motor and the pump part work in the environment of gasoline, they are also cooled and lubricated with it. Fire safety is ensured by the lack of oxygen necessary for ignition; a mixture with air enriched with gasoline is not ignited by an electric spark.
After two-stage filtration, gasoline enters the fuel rail. The pressure in it is maintained stable with the help of a regulator built into the pump or rail. Excess is drained back into the tank.
At the right time, the electromagnets of the injectors, fixed between the ramp and the intake manifold, receive an electrical signal from the ECM drivers to open. The pressurized fuel is actually injected into the intake valve, simultaneously spraying and evaporating. Since the pressure drop across the injector is kept stable, the amount of gasoline supplied is determined by the opening time of the injector valve. The change in vacuum in the collector is taken into account by the controller program.
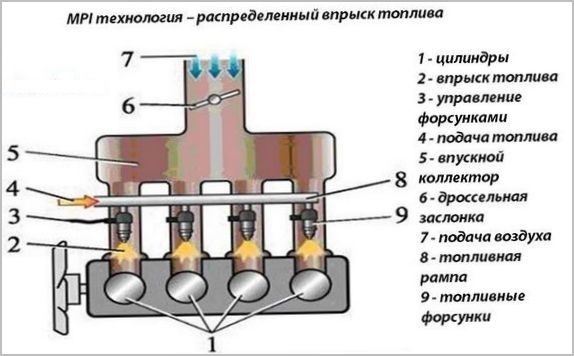
The nozzle opening time is a calculated value calculated on the basis of data received from sensors:
- mass air flow or manifold absolute pressure;
- suction gas temperature;
- throttle opening degree;
- presence of signs of detonation combustion;
- engine temperature;
- frequency of rotation and phases of the position of the crankshaft and camshafts;
- the presence of oxygen in the exhaust gases before and after the catalytic converter.
In addition, the ECM receives information from other vehicle systems via the data bus, providing engine response in various situations. The block program continuously maintains the torque mathematical model of the engine. All its constants are written in multidimensional mode maps.
In addition to direct injection control, the system provides the operation of other devices, coils and spark plugs, tank ventilation, thermal stabilization and many other functions. The ECM has hardware and software to perform self-diagnosis and provide the driver with information about the occurrence of errors and malfunctions.
Currently, only individual phased injection for each cylinder is used. In the past, the injectors worked simultaneously or in pairs, but this did not optimize the processes in the engine. After the introduction of camshaft position sensors, each cylinder received separate control and even diagnostics.
Characteristic features, advantages and disadvantages
You can distinguish MPI from other injection systems by the presence of individual nozzles with a common ramp directed into the manifold. Single-point injection had a single injector that took the place of the carburetor and was similar in appearance to it. Direct injection into the combustion chambers has nozzles resembling diesel fuel equipment with a high pressure pump installed in the head of the block. Although sometimes, to compensate for the shortcomings of direct injection, it is supplied with a parallel operating ramp to supply part of the fuel to the manifold.
The need to organize more efficient combustion in cylinders led to the development of the MPI equipment. The fuel enters the mixture as close as possible to the combustion chamber, effectively sprays and evaporates. This allows you to work on the most lean mixtures, ensuring efficiency.
Precise computerized feed control makes it possible to meet ever-increasing toxicity standards. At the same time, hardware costs are relatively low, machines with MPI are cheaper to manufacture than with direct injection systems. Higher and durability, and repairs cost less. All this explains the overwhelming predominance of MPI in modern cars, especially budget classes.