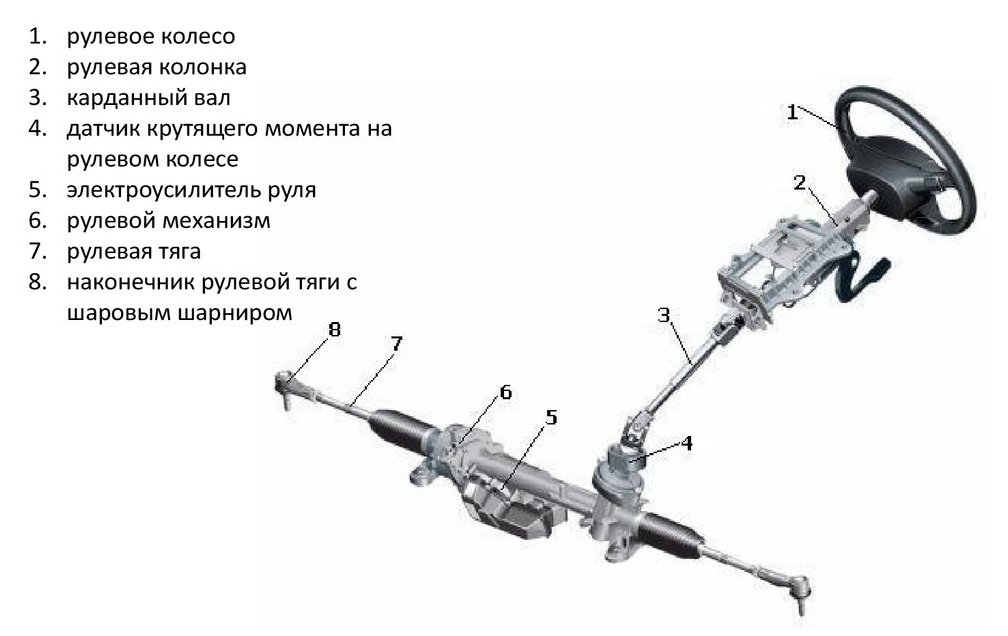
Types, design and principle of operation of the steering mechanism
Content
Changing the direction of the car is done by turning the steered wheels using the steering wheel. However, between him and the wheels there is a device that converts the effort of the driver's hands and his direction to directly apply force to the swing arms. It is called the steering mechanism.

What is the steering gear for?
In the general steering scheme, the mechanism performs the following tasks:
- converts the rotation of the input shaft, to which the steering column is connected, into translational rotation for the steering trapezium rods;
- coordinates the force that the driver can create with the necessary force on the levers connected to the steering knuckles of the undercarriage, using the mechanical transmission available in the design with a certain gear ratio;
- in most cases, provides joint work with power steering;
- protects the driver's hands from kickbacks from road bumps.
With a certain degree of accuracy, this device can be considered a gearbox, as it is often called.
Varieties of steering mechanisms
There are three most popular gear schemes:
- worm-roller;
- rack-and-pinion;
- ball screw type.
Each of them has its own advantages and areas of use.
Worm-roller mechanism
This type was widely used in the past on all cars, but now has limited use due to many disadvantages compared to other schemes.
The principle of operation of the worm gear is to run a sector toothed roller with a spiral worm wheel on the steering column shaft. The input shaft of the reducer is made as a single piece with a worm knurling of variable radius, and is equipped with a slotted or wedge connector for connection with the column shaft. The toothed sector of the roller is located on the bipod output shaft, with the help of which the gearbox is connected to the steering linkage rods.

The whole structure is placed in a rigid housing, also called a crankcase due to the presence of lubrication in it. This is usually a transmission type liquid oil. The shaft exits from the crankcase are sealed with glands. The crankcase is bolted to the frame or engine bulkhead of the body.
The rotation of the input shaft in the gearbox is converted into a rotational-translational bipod ball tip. Rods are attached to it to the wheels and additional trapezoid levers.
The mechanism is capable of transmitting significant forces and is quite compact with large gear ratios. But at the same time, it is difficult to organize control with minimal backlash and low friction in it. Hence the scope - trucks and SUVs, mostly of a conservative design.
Steering racks
The most widely used mechanism for passenger cars. The rack and pinion is much more precise, provides good feedback and fits well in the car.
The rack mechanism consists of:
- hulls with fastening to the bulkhead of the body;
- toothed rack lying on the journal bearings;
- drive gear connected to the input shaft;
- thrust mechanism, providing a minimum clearance between the gear and the rack.
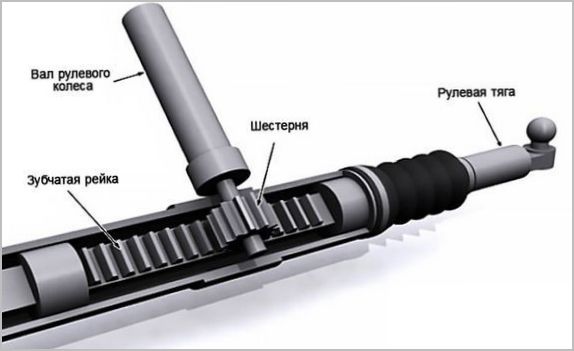
The output mechanical connectors of the rack are connected to the ball joints of the steering rods, which work through the tips directly with the swing arms. This design is lighter and more compact than the worm gear steering linkage. This is where the high control accuracy comes from. In addition, the clearance of the drive gear is much more accurate and stable than that of the complex shape of the roller and worm. And the increased return to the steering wheel is compensated by modern amplifiers and dampers.
Screw with ball nut
Such a gearbox is similar to a worm gearbox, but important elements are introduced in it in the form of a segment of a rack with a gear sector moving along the input shaft screw through circulating metal balls. The rack sector is connected to the teeth on the bipod shaft.
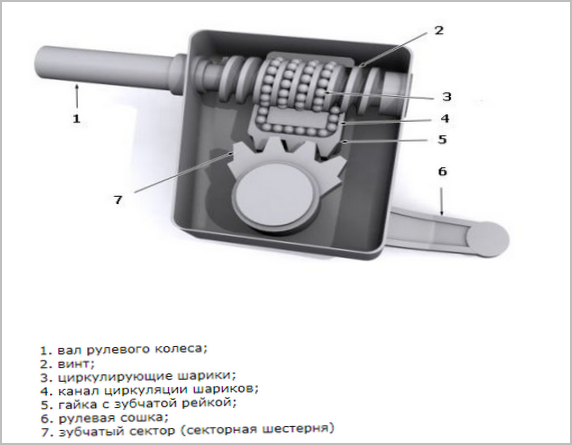
Due to the use of a short rail, which is actually a nut with balls along the thread, friction is significantly reduced under high loads. Namely, this was the determining factor when using the mechanism on heavy trucks and other similar vehicles. At the same time, accuracy and minimum clearances are observed, due to which these same gearboxes have found application in large premium passenger cars.
Clearances and friction in steering mechanisms
All gearboxes need periodic adjustments to varying degrees. Due to wear, the gaps in the gear joints change, a play appears at the steering wheel, within which the car is uncontrollable.
Worm gears are controlled by moving the gear sector in a direction perpendicular to the input shaft. Maintaining clearance at all steering angles is difficult to ensure, since wear occurs at different rates in the frequently used direction of travel straight and more rarely in turns at various angles. This is a common problem in all mechanisms, the rails also wear out unevenly. With severe wear, parts have to be replaced, otherwise, when the steering wheel is rotated, the gap will turn into an interference with increased friction, which is no less dangerous.