
Recovery of damages from the culprit of an accident without an OSAGO policy
Content
The introduction of OSAGO to a large extent freed victims of road accidents from the hardships associated with material compensation for harm. Even if you have to sue the insurance company about the amount of damage or in connection with a violation of the payment procedure, as a result, most often the funds will be collected or repairs will be made, and the offended car owner will receive tangible compensation in the form of a forfeit and a fine. But despite the obligation of insurance, from time to time there are car accidents with car owners who have not insured their liability. There are frequent situations when the invalidity of the policy comes as a surprise to the policyholder himself.
A participant in an accident without OSAGO insurance: causes and responsibility
According to the website of the State Statistics Committee, at the end of 2016, more than 45 million cars were registered in the Russian Federation. According to RIA Novosti with reference to the RSA, in 2017, about 6 million car owners did not insure their liability, and about 1 million are owners of fake policies. The main share of violations falls on the owners of cars, since bus and truck drivers are under special control not only from the traffic police, and they are unlikely to risk using a fake document or driving without OSAGO.

Thus, 15,5% of car drivers do not have insurance coverage. Assuming conditionally that an uninsured road user gets into car accidents on an equal basis with the insured, with equal probability can become both the culprit and the victim, we get 7–8% of accidents due to the fault of the driver without a policy. Even if, for the sake of objectivity, we reduce the resulting figure by 2 times, the probability of falling into such a situation significantly exceeds the value of the statistical error, and therefore is quite real.
Obligations of the insurer to pay compensation
The object of OSAGO are property interests associated with the risk of civil liability of the owner of the vehicle for obligations arising from causing harm to the life, health or property of victims when using the vehicle in the territory of the Russian Federation.
If there is a valid OSAGO contract, the insurer, instead of the culprit, makes a payment in the following cases:
- damage has been caused to the vehicle;
- damage was caused to property located in the vehicle of the victim and not being a part or constituent element of it (luggage, non-standard equipment, personal property of the driver and passengers, etc.);
- damage was caused to other property (buildings, structures, movable objects, personal belongings of pedestrians, etc.);
- harm was caused to the life and health of any other person (the second driver, passengers, including those who were in the car of the culprit, pedestrians, etc.).
More about concluding an insurance contract: https://bumper.guru/strahovanie/proverka-kbm-po-baze-rsa.html
If the driver has a valid policy, but he is not indicated as a person admitted to drive, or an accident occurred outside the period of use of the vehicle specified in the contract, the insurance company will pay out on a general basis. The right of the insurer to collect from such a guilty person the paid indemnity does not affect the interests of the victim.

The insurer's obligations under an invalid policy do not arise. The document will be invalid in the following cases:
- the term of the contract has expired;
- the policy is forged;
- the policy is issued on an original form, including with an original seal and signature, but the form is listed as stolen or lost;
- the electronic policy is issued not on the website of the insurer and is not an electronic document.
In the last three cases, the car owner may not suspect that the contract he has is invalid. Cases of theft of forms from insurers are not isolated. Policies issued on stolen forms are sold under the guise of valid ones. There are cases when scammers opened websites duplicating the websites of large insurance companies and collected money to their account or e-wallet. The first sign of the sale of invalid insurance is their undervalued value. A valid OSAGO policy cannot cost less than that of other insurers. Insurers have been given the right to determine the tariff within the range set by the Central Bank, but in practice maximum rates are used. No discounts, promotions or gifts when selling OSAGO are unacceptable (clauses 2.6–2.7 of the Rules for Professional Activities for the Promotion of Services on the OSAGO Market, approved by the post of the Presidium of the RAMI of August 31.08.2006, 3, pr. No. XNUMX).
There are also unscrupulous acting agents who appropriated the collected premium and told the insurer about the loss of the forms issued to him. All information about invalid forms must be posted on the websites of insurance companies and PCA. When drawing up an OSAGO agreement outside the office of the insurer, with an unfamiliar agent and in other similar cases, when from the situation it is impossible to be firmly convinced of the validity of the transaction, you should check its status in the appropriate section on the website of the PCA or a specific company 2–3 days after receiving the policy. The status of the form can be checked before signing the contract. Information about the invalidity of the form will be reflected on the PCA website, and stolen or lost forms will be included in the corresponding list on the insurer's website.

In case of bankruptcy of the insurer or revocation of its license, the obligation to compensate for material damage is transferred to the PCA. For damage to life and health caused as a result of an accident, the union will also pay compensation in cases where the responsibility of the perpetrator was not insured or he fled the scene and was not established (Article 18 of the Federal Law of April 25.04.2002, 40 No. XNUMX-FZ).
In cases where the OSAGO policy is missing or invalid, the damage must be compensated by its causer in the general manner prescribed by civil law for such relations. There is nothing tragic or impossible about this. Such an order existed both in Soviet times and in modern Russia until 2003. But due to the fact that over the 15 years of OSAGO, car owners have already been spoiled by the relative simplicity and accessibility of the damage compensation procedure, fixed payment terms, in situations with an uninsured culprit, one has to remember aftercare practice.
Liability for lack of compulsory insurance
Failure to fulfill the obligation for compulsory civil liability insurance by the car owner, as well as driving a car, if there is obviously no insurance, forms an administrative offense under Part 2 of Art. 12.37 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation. The punishment in both cases is the same - a fine of 800 rubles. Knowing the actions of the car owner is important for the application of liability measures. The driver must be aware that his liability is not insured, and be aware of the wrongfulness of his behavior and the possible consequences. In case of conscientious acquisition of a fake policy, liability is excluded, but the car owner must prove that he did not know and could not know about the fake.
Driving a car by a driver not specified in the contract or outside the established driving period in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 12.37 will cost 500 rubles. The absence of a document from the insured driver is a violation of Part 2 of Art. 12.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation and is punishable by a fine of 500 rubles. or a warning.

Paragraph 2 of Art. 19 of the Federal Law of December 10.12.1995, 196 No. 2014-FZ “On Road Safety” establishes a ban on the operation of a vehicle by a driver whose liability is not insured under an OSAGO agreement. However, unlike in cases of driving while intoxicated, for example, there are no practical mechanisms for enforcing the ban. Until November XNUMX, in the absence of a valid insurance contract, the license plate was removed from the car, and the car owner had to issue a policy within XNUMX hours after that. Now such a security measure is not applied and the existing ban is declarative.
Currently, the State Duma is considering bill No. 365162-7, according to which it is planned to make a single fine in the amount of 5000 rubles. both for failure to fulfill the obligation of compulsory insurance, and for driving a car by an unregistered driver or outside the established period. As of May 2018, the draft has not yet passed the first reading, but the Committee of the State Duma on Transport and Construction appointed by the co-executor gave a negative conclusion. According to the Committee, the increase in the size of the fine will not only not encourage car owners to insure liability, but also "will contribute to a powerful impetus to the development and prosperity of corruption in the OSAGO market."
The traffic police inspector who arrived at the scene of the accident, among the first actions, checks the documents of the participants in the accident, including OSAGO policies. To check the validity of the contract, traffic inspectors are provided with mobile communication devices that allow them to quickly obtain information from the RSA database or a departmental database. The absence or invalidity of insurance when contacting the police for registration of a traffic accident will be established both in relation to the perpetrator and the victim. Even if this issue falls out of the attention of the traffic police, not a single insurer will make a payment under an invalid policy.
Consequences of not having a valid insurance contract
In addition to administrative sanctions, the culprit of a road accident is fully civilly liable for the harm caused. Moreover, the victim will not be bound by the methodology for determining the amount of damage used in determining the amount of damage, and the established procedure for paying compensation. The amount of damage determined in accordance with the Unified Methodology, approved. By Regulation of the Central Bank of September 19.09.2014, 432 No. 50-P, it is calculated from fixed prices for spare parts and materials, the average cost of a standard hour of work. The calculation takes into account wear up to XNUMX% of the actual cost of parts. In addition, the OSAGO rules imply an in-kind form of payment, and in case of compensation for harm by the culprit, the victim himself can determine the preferred option for compensation - to recover money or to oblige to carry out repairs.

In case of compensation for harm directly by the culprit, the damage will be determined based on other methods. At a minimum, the court will not take into account the wear and tear of parts. The cost of repairs will be determined by the actual costs without taking into account the discounts that insurers have from partners. As a result, the actual amount of damage to be compensated by the culprit turns out to be greater than that calculated by the insurance company.
In addition to the damage itself, the culprit may be charged additional costs:
- to conduct an independent evaluation;
- to a tow truck from the scene of an accident to the place of storage of the car, service station, if the vehicle cannot move;
- parking costs, if the car must be parked in a guarded parking lot after an accident in order to avoid additional damage (for example, the victim does not have a garage and the car is usually parked in the yard);
- postal (for sending telegrams about the inspection, etc.);
- other expenses related to the accident.
Compensation for non-pecuniary damage will be a specific recovery from the culprit of the accident. In the absence of bodily injury, the amount of compensation for moral damage will be insignificant - no more than 1000–2000 rubles. Therefore, victims usually do not bother making such claims against the driver if the payment is made by the insurer. When recovering insurance compensation from the insurer in court, claims for compensation for moral damage are simultaneously made. But in this case, moral damage is caused by illegal actions of the insurance company, expressed in the delay in payment or refusal. The culprit causes moral harm to the victim in connection with the experiences and suffering caused by the accident and damage to the car. In the event of a judicial recovery of material damage from the culprit, compensation for moral damage will also be “attached”.
The culprit will also be liable to pay interest for late payment if compensation for damage is not made in a timely manner, court and enforcement costs in case of enforcement, etc. In addition to the material component, the participants in the incident will be forced to negotiate with each other, accept some compromises. In the presence of an OSAGO agreement, the parties do not have mutual financial claims (if the amount of damage does not exceed the sum insured) and, from a financial point of view, they are indifferent to each other’s attitude to the consequences that have occurred - the culprit does not care what damage he caused, and the victim is not interested in what he thinks about the amount of damage culprit. But when the obligation to compensate for harm is imposed on the culprit, the interests of the parties become directly opposite. The culprit wants to reduce the amount of damage and his guilt in the event, the victim intends to recover all the costs incurred.
The absence of an OSAGO policy for the victim entails only one negative consequence for the culprit - the inability to issue an accident without the participation of the traffic police in cases where this is provided for by OSAGO rules:
- the amount of damage does not exceed the established limit - from 01.06.2018/100/000 XNUMX rubles;
- two vehicles were involved in the accident and only the vehicles involved were damaged;
- the circumstances of the incident do not cause controversy among the participants (guilty is not disputed), and from 01.06.2018/100/000 with damage up to XNUMX rubles. without contacting the traffic police, it will be possible to register the event even if there are disagreements.

For the victim, the absence of an OSAGO policy from the culprit, in addition to the inability to file an accident without contacting the police, can result in material losses. The limited financial resources of the perpetrator make it much more difficult for the victim to obtain compensation. Even in the event of litigation with the insurer, the issue of payment is resolved within an acceptable time frame. The collection procedure from the moment a claim is submitted to the actual receipt of money usually does not take more than 4–5 months, and in many cases all issues are resolved at the pre-trial stage within a month. When recovering damages from an individual, a court decision often means only the beginning of a long and complex process of actually receiving money. It is possible that the victim will not be able to get anything from the tortfeasor, at least legally. From the position of the victim, we will further consider the possible situations that arise when harm is caused by an uninsured driver.
What to do in case of an accident if the culprit does not have a policy
The general duties of drivers in case of an accident are defined in paragraphs 2.5 - 2.6 of the SDA. Taking into account the requirements established by the legislation on OSAGO, and in relation to the topic under consideration, we will determine the procedure for the actions of participants in an accident. Under any circumstances, drivers involved in an accident must:
- immediately stop driving, turn on the emergency signaling and put up emergency stop signs in such a way that they notify drivers in advance of the presence of danger in the direction of their movement (in populated areas not less than 15 m from the location of the obstacle, outside populated areas - not less than 30 m);
- keep the location of the vehicles unchanged after the accident, and also do not move or remove (clean off) the scree formed as a result of the impact, signs of braking, keep broken off parts and parts of machines, cargo and any other objects in the place of the fall.
If people were injured as a result of the event, immediately provide them with first aid, if necessary, call an ambulance (single emergency number from a mobile phone 112). In emergency situations, participants in an accident are obliged to ensure the delivery of victims to a medical facility by passing transport, and if it is not possible, to deliver them on their own in their car. In such cases, the driver cannot be held liable for leaving the scene of the accident. The driver is obliged to provide the employees of the medical institution with his data, the license plate number of the car and present a passport (substitute document) or a driver's license and documents for the car. After delivering the victim, the driver must return to the scene of the accident.
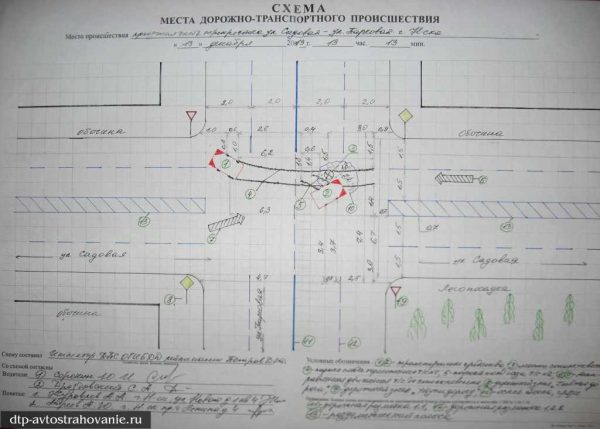
If the location of cars on the road after an accident prevents the passage of other vehicles, the participants in the accident are obliged to clear the carriageway. Before clearing the passage, drivers are required to record, including by photographing and video filming, the location of cars formed after the accident, scree, braking marks and fallen parts and objects with reference to the nearest stationary road object or other element (roadside, road signs, houses , poles, bus stops, etc.). In any case, you should draw up a diagram of the accident site on paper according to the rules of the traffic police, reflecting the relative position of the cars after the collision, tying to the terrain and indicating:
- distances between cars at extreme points;
- places of impact;
- direction of travel before the collision;
- brake wake length and trajectory;
- location, configuration and size of scree;
- locations of parts and objects that have broken off and fallen out of vehicles;
- distances from cars to the roadside, curb;
- the width of the carriageway and traffic lanes;
- distance to the anchored object (on a desert road, these can be kilometer posts, distant objects, characteristic bends in the road, geographical objects, etc.).
The scheme is compiled as a single document and signed by all drivers involved in the accident. If irreparable disagreements arise or one of the participants refuses to draw up the scheme, the document should be drawn up without his participation and with an indication of the refusal. Photographs and video recordings must confirm the information reflected in the diagram.
Learn more about the capabilities of the DVR: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/poleznoe/videoregistrator-s-radar-detektorom.html
It is permissible to change the location of vehicles after an accident in the presence of victims only if, while maintaining an unchanged position, the passage of other vehicles is impossible. Changing the arrangement due to the creation of obstacles to free movement, the formation of traffic jams and other circumstances that do not completely block the passage can be qualified as leaving the scene of an accident. If there are no victims, cars can be removed not only if it is impossible for other vehicles to pass, but also if it is difficult.
In case of an accident with victims, drivers are also required to identify witnesses of the event and take data from them (names, addresses, phone numbers). Witnesses can be passers-by waiting at stops, drivers and passengers of cars passing at the time of the accident (if the drivers stopped), people in adjacent buildings, etc. It is recommended to find witnesses in situations where the location of cars has changed in the absence of victims.
Find out how to prevent night crashes: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/poleznoe/kak-ne-usnut-za-rulem.html
The issue of whether drivers have insurance should be resolved immediately after the initial duties have been performed. If the culprit of the accident does not have an OSAGO policy, further events can develop in two directions:
- If the damage was caused only to the vehicles and property of the participants, there are no injured people, the culprit does not deny guilt and is ready to pay on the spot, calling the traffic police is not advisable. The traffic rules allow for the possibility of not filing an incident in any way, if none of the participants insists on this (the last paragraph of clause 2.6.1 of the traffic rules). Refusal to file an event deprives the victim of the opportunity to subsequently prove the circumstances of the incident or significantly complicates the procedure of proof, therefore, it is possible to agree to such a development of relations only if the settlement is immediate or quick (after withdrawing money from the nearest ATM, relatives or friends will be brought to the scene of the accident, etc.) .). Until the actual receipt of money, it is impossible to change the location of the cars and leave the scene of the incident. The transfer of money must be formalized in writing by an arbitrary receipt or act, which should reflect:
- time and place of the incident;
- personal data of participants (full name, passport or driver's license data, place of residence, telephone number);
- information about the cars involved in the accident (model, license plate);
- briefly the circumstances of the incident, the resulting damage;
- admission of guilt;
- paid amount.
- If the circumstances of the incident cause controversy, there is no unity in assessing the damage, there are victims or the culprit is not ready to pay immediately, contacting the traffic police is necessary. Promises to pay off in a few days should be treated critically. Even if the perpetrator admits his guilt in writing and assumes obligations to compensate for the damage, nothing will prevent him from subsequently retracting his words. A completed notice issued when applying for an OSAGO policy (sometimes called a European protocol), or a written obligation to pay for the court, at best, will only be evidence that after the accident the participant considered himself guilty. The driver will be able to explain the assumption of guilt by a state of shock, an incorrect assessment of circumstances, inexperience, or even psychological pressure from the victim.
The rules of the road allow for the possibility of registering an accident in the presence of disagreements not at the scene of an accident, but at the nearest traffic police post or police unit. This is possible only on the basis of a direct instruction from the police officer who arrived or given by him by phone when reporting the event. In any case, the police must be informed that the perpetrator or the victim does not have an OSAGO policy. Upon receipt of instructions to issue documents not at the scene of an accident, drivers are required to record the scene of the accident in the manner indicated above and proceed to the designated place.
How to recover money for damage from the culprit if he does not have a policy
Compensation for harm can be carried out voluntarily or involuntarily. The absence of an OSAGO policy by the car owner does not unequivocally indicate the dishonesty of a person, but certain conclusions suggest themselves. Therefore, in any case, one should attend to the formation of the necessary evidence base.
Voluntary compensation
With significant damage, not every perpetrator has the opportunity to immediately or in a short time to pay off the victim. When resolving issues of compensation for harm, various options acceptable to both parties should be discussed:
- installment or deferment of payment;
- joint participation in the payment of repairs with subsequent reimbursement by the culprit of the costs of the victim;
- providing the perpetrator with the necessary time to apply for a loan, sell property for settlement with the victim, etc.;
- fulfillment of obligations in other ways (transfer of property, performance of work, etc.);
- fulfillment of an obligation by another person, etc.

The agreed procedure must be determined by a written agreement indicating the admission of guilt by the participant in the accident. Obligations to compensate for harm cannot arise from the contract, but a written document will be indirect evidence for the court in favor of the victim if the perpetrator subsequently violates the terms of the agreement or begins to dispute guilt. A basic sample agreement can be viewed here.
Determining the amount of damage
The most important step in resolving the issue of compensation for harm is to determine the amount of damage. No questions should arise either in court or in negotiations with the perpetrator about the amount due if the victim repairs the car at a workshop at his own expense in compliance with normal repair requirements (at a dealer station for a warranty car, at an official workshop for a non-warranty car with normal quality and deadlines). Excessive demands on the place, conditions, technology and terms of repair will not be satisfied by the court and should not be paid by the perpetrator voluntarily (for example, the victim will demand to replace the parts to be repaired, install more expensive items to replace the damaged ones, carry out repairs not at the nearest authorized dealer at the place of residence in Tula, and in Moscow, etc.).
Another way to record the damage received and establish the cost of repairs is to issue a preliminary order. To do this, the damaged car must be sent to the service station, where it will be disassembled, visible and hidden damage will be determined, and the estimated cost of the repair will be established. After disassembling the car, the service station must begin repairs. The technical station may require partial prepayment or payment of components and parts required for repair. In the absence of payment, repairs will not be carried out, and the car owner will be billed for storing the car. You can reimburse the costs of paying the bill from the culprit if the repair was delayed through his fault, but no one needs additional costs. Therefore, it is necessary to drive the car to the station and disassemble it after settling the issue of compensation for damage with the culprit or, if it is possible, to pay for the repairs yourself.

The universal and most reliable way for all parties is to conduct an independent examination. The appraiser's report will also be required to file a claim if the dispute goes to the judicial stage. The cost of the examination depends on the location, the volume and nature of the damage, the model of the car. For orientation, you can name the numbers 7000-10000 rubles. The initial examination will not identify hidden damage. After disassembling the machine at the workshop, it may be necessary to conduct an additional inspection and prepare an addendum to the conclusion. The issue of paying for the assessment should be decided upon the agreement of the participants in the accident, if they choose this method of determining the amount of damage. As a compromise, you can have the vehicle inspected by a technician or expert. Perhaps not every independent examination conducts inspections without compiling a report, but it is worth looking for such a company. In this case, the inspection report with the necessary photo table will cost 1000–3000 rubles, and on the basis of the inspection report, a repair cost report can be drawn up at any time. As a general rule, the amount of damage is determined by an expert on the date of the accident.
Enforced collection
If the culprit did not pay on the spot and no agreement was reached on the procedure for compensation and the amount of damage, or the culprit violated his obligations or the damage was not fully compensated, the only legal way is to recover. Events can develop in several directions:
- The traffic police documents are issued, but the culprit refuses to compensate for the damage. The victim must file a lawsuit to recover damages caused by the accident. In such situations, the perpetrator can often go to challenge his guilt. The issue of guilt will be resolved in the same process. Depending on the initiative and "creativity", the perpetrator may be the first to file a claim against the insurance company of the victim for damages, insisting on his guilt, file a counterclaim against the victim and his insurer, or state his objections to the culpability of causing damage when considering the claim of the victim. Previously, the perpetrator may try to appeal the decision (determination) of the traffic police. The participant in the accident should personally take part in such proceedings, since the representative will not be able to give exhaustive explanations about the circumstances of the event.
- The documents of the traffic police are executed, the culprit does not dispute the guilt, does not refuse to compensate for the damage, but does not pay voluntarily. This is the most typical situation. The culprit has no means to redress the harm and simply goes with the flow. Litigation in such cases is usually not difficult.
- The documents of the traffic police are executed, the culprit partially paid for the damage and believes that the amount paid is sufficient. There is a dispute about the amount of damage. Recovery is also made in a lawsuit, but a forensic examination may be required to confirm the amount of damage. The court is likely to appoint an examination at the request of the defendant, even if he does not provide sufficient evidence that the stated requirements do not correspond to the actual damage.
- The traffic police documents are not executed, there is a written consent of the culprit to compensate for the damage (letter of guarantee, notice of an accident, etc.) or nothing is available. If the perpetrator decides to challenge the guilt of causing damage, the nature and extent of the damage, it will be extremely difficult for the victim to prove his position. "Experienced" perpetrators can go exactly this way. Due to the lack of an OSAGO policy, they ask the victim not to call the traffic police, promising to pay within 1-2 days. In support of the words, a receipt is issued indicating the amount, but without a list of damages and a description of the circumstances. After that, the payment terms are constantly postponed. As a result, the victim, at best, has an appraiser’s report or work order drawn up much later than the date of the accident, which does not confirm the time and circumstances of the damage, and an insignificant receipt. It is difficult to count on a positive decision of the court in such a situation.
Pre-trial claim
The claim procedure is not mandatory in relations between individuals and is not applied in practice. If the uninsured culprit turned out to be a legal entity, a preliminary claim may be useful in fixing the timing of obligations. Organizations are unlikely to sign an agreement on admission of guilt and voluntary compensation for harm, since such a document is not flawless from a legal point of view.
The claim must state (example here):
- addressee name;
- data of the victim;
- name "Claim for compensation for damage caused as a result of an accident";
- a description of the event, indicating the participants and vehicles;
- requirements;
- deadlines for voluntary satisfaction of claims.
Documents that the culprit does not have must be attached to the claim:
- appraiser's report on the amount of damage, work order, invoice for repairs;
- receipts confirming associated expenses (payment for the services of an appraiser, expenses for a tow truck if the vehicle cannot move, etc.;
- PTS or SR TS.
Traffic police documents can not be attached, since the culprit has the right to get them himself. From the expiration of the period for voluntary satisfaction of claims, interest can be charged for each day of delay in payment in accordance with Art. 395 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation based on the key rate of the Central Bank. The current rate is 7,25% per annum. The total amount of interest will be insignificant, but an increased penalty and a fine can only be applied to the insurer. In case of delay in payment by the culprit - an individual, interest is accrued from the date established by the agreement for the voluntary payment of compensation.
Judicial recovery
The claim is filed with the Magistrate's Court with the amount of the claim up to 50 rubles. (damage plus all other claims, except compensation for non-pecuniary damage) or to the district court for large amounts. You can prepare a claim and conduct proceedings on your own, if the perpetrator does not object to the guilt and the amount of damage. A sample claim with attached documents is available here. When recovering damages from the culprit, a state duty is paid in the amounts established by paragraphs. 000) paragraph 1 of Art. 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In other cases, it is recommended to seek legal advice. Bringing the perpetrator to justice for violating traffic rules is not sufficient evidence for the court to prove his guilt in causing harm. The court in certain cases can establish the mutual guilt of the participants and even the absence of a connection between the violation of traffic rules and the infliction of harm.

After the entry into force of the court decision that satisfied the requirements of the victim, you should receive a writ of execution and transfer it to the FSSP at the place of residence of the perpetrator. If the debtor does not have sufficient funds on accounts and cards to execute the decision, the bailiff will most likely begin to withhold the amount collected from the salary in the amount of up to 50%. If the culprit's car was seized, the decision can be enforced through the sale of the car. At the execution stage, numerous problems can arise related to the lack of money or the unofficial salary of the culprit.
Video: what to do to the victim if the culprit does not have a valid OSAGO policy
The absence of an OSAGO policy is disadvantageous not only to the culprit who caused harm as a result of an accident, but also to the victim, who, instead of promptly resolving the situation in the insurance company, is forced to engage in additional negotiations, litigation and enforcement proceedings. The conscientious fulfillment of the responsibility for liability insurance reflects the worthy attitude of the car owner towards others and himself.

