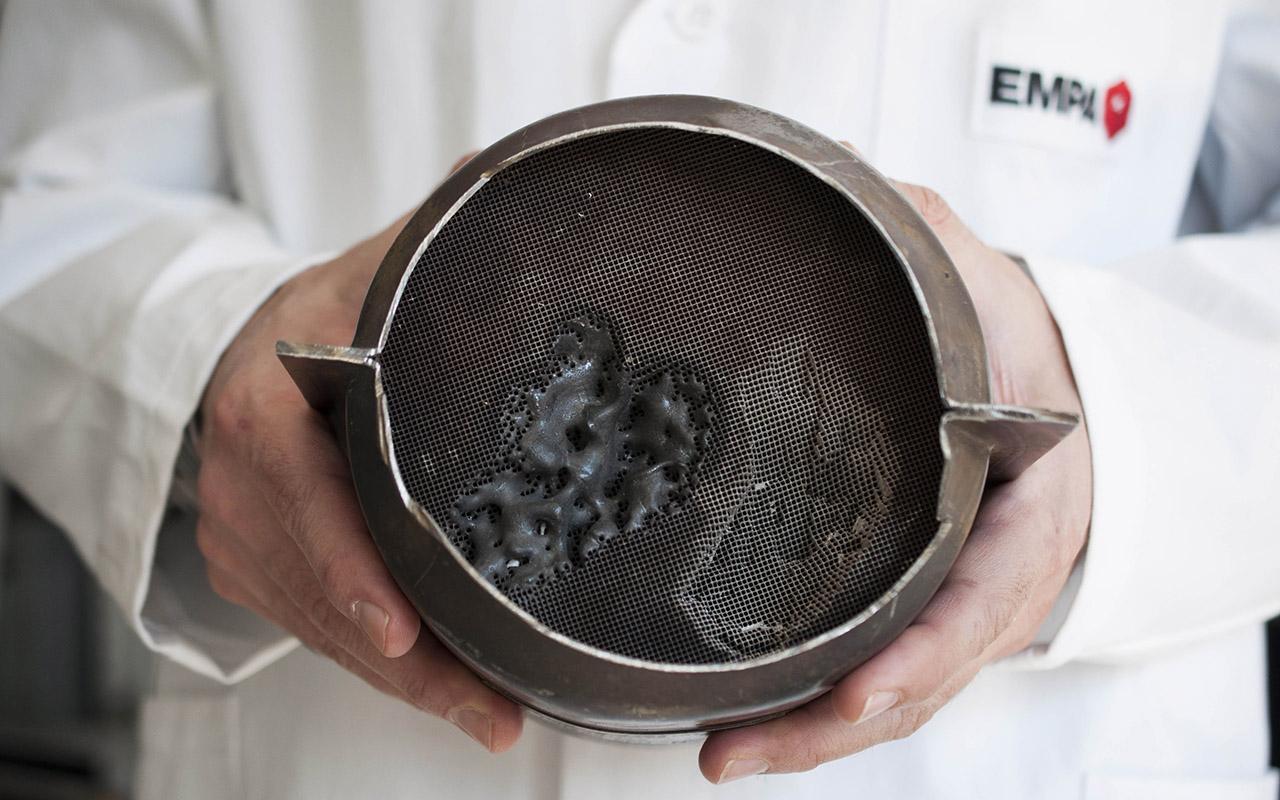
Clogged catalytic converter
 Loss of engine power, poor acceleration, vibration at idle, and erratic engine operation can occur if the catalytic converter is clogged.
Loss of engine power, poor acceleration, vibration at idle, and erratic engine operation can occur if the catalytic converter is clogged.
Loss of engine power, poor acceleration, vibration at idle, and engine roughness are clear signs that an engine is nearing the end of its life and a costly overhaul is imminent. But such symptoms can also appear on a running engine, due to a clogged catalytic converter.
It happens that the driver complains about a significant deterioration in engine performance, and if it is a car with high mileage, the mechanic exaggerates a little in the diagnosis that the engine, injection system or turbocharger needs to be repaired. Unfortunately, this is not always an accurate diagnosis. Problems begin when an engine overhaul fails to restore engine power. Then, a little in the dark, through trial and error, you try to find the cause, and finally  Suspicions fall on a clogged exhaust system. Most often this is a clogged catalytic converter, although it can also happen that the muffler may become clogged.
Suspicions fall on a clogged exhaust system. Most often this is a clogged catalytic converter, although it can also happen that the muffler may become clogged.
Correct diagnosis
A clogged catalytic converter effectively prevents exhaust gases from escaping and acts as an engine brake. When it is partially blocked, the driver usually does not feel it, while when blocking most of it, the weakening is clearly noticeable. In extreme cases, the flow of exhaust gases can be completely blocked, and the engine will not start. Then the cause is sought in the ignition or power system. Suspicions fall on the fuel pump, injectors and fuel filter.
When it is a diesel, the low power is due to a damaged compressor or drain valve. These parts are expensive, and replacing them does not help. Then the injection pump and injectors are suspected. Another unnecessary expense that will not bring improvement. Meanwhile, a clogged catalyst is to blame for all the troubles.
In gasoline engines, the insert may melt as a result of a power failure or too lean mixture (this often happens with LPG installations). Catalysts have also been used in diesels for several years now and if a car has around 200 km it is very likely that this is what is causing the problems. Older designs don't have electronics, so particle buildup doesn't burn off and, as a result, exhaust gas flow decreases. In new engines filled with electronics, the computer takes care of the patency of the catalyst and, in case of clogging, the driver receives information about the need to visit the service station.
Worth mentioning
When it turns out that the defect is a damaged catalyst, unfortunately, in most cases, the repair consists in removing the catalyst liner. This is happening at the expense of the environment. In this case, older car models will work properly because their control system does not control the composition of the exhaust gases after the catalytic converter. In new designs, driving without a catalytic converter is not possible, since the composition of the exhaust gases is also checked behind the catalyst and, if it does not meet the standards, the computer signals a malfunction.
Buying a new catalytic converter shouldn't ruin your home budget. Factory catalysts are actually very expensive - prices reach several thousand. PLN, but you can successfully use the universal one, the cost of which is from 300 to 600 PLN plus about 100 PLN for the exchange.