Hard specialist with soft skills
Content
In the 1st century, the word "engineer" was used in some countries to refer to a builder of military equipment. The meaning of the word has changed over the centuries. Today, in the XNUMXth century, it is understood as never before in history (XNUMX).
By engineering achievements, we tend to understand a wide range of human creations, from the pyramids of ancient Egypt to the invention of the steam engine, to the expedition of man to the moon.
and society would cease to function if for some reason it was no longer used. More specifically, this is how we usually define the application of scientific knowledge, especially physical, chemical, and mathematical knowledge, to problem solving.
2. Freeman Dyson's book "Breaking the Universe".
Traditionally, the four major engineering disciplines are mechanical engineering, civil engineering, electrical engineering, and chemical engineering. Previously, an engineer specialized in only one discipline. Then he changed and is constantly changing. Today, even a traditional engineer (i.e. not a "software engineer" or "bioengineer") is often required to have knowledge of mechanical, electrical, and electronic systems, as well as software development and safety engineering.
Engineers work in a variety of sectors including automotive, defense, aerospace, energy including nuclear, oil and gas, and renewable energy such as wind and solar, as well as medical, packaging, chemical, space, food, electronic and steel industries. other metal products.
In his book Disrupting the Universe (2), published in 1981, physicist Freeman Dyson wrote: “A good scientist is a person with original ideas. A good engineer is a person who creates a design that works with as few original ideas as possible.” Engineers are not stars. They design, evaluate, develop, test, modify, install, verify and maintain a wide range of products and systems. They also recommend and define materials and processes, supervise production and construction, perform failure analysis, consult and guide.
From mechanics to environmental protection
The field of engineering is currently broken down into a wide range of specializations. Here are the most important ones:
Engineering - this is, for example, the design, production, control and maintenance of machines, devices and assemblies, as well as control systems and devices for monitoring their condition and operation. It deals, including vehicles, machinery, including construction and agricultural, industrial installations and a wide range of tools and fixtures.
Electrical engineering – covers the design, testing, production, construction, testing, control and verification of electrical and electronic devices, machines and systems. These systems vary in scale, from microscopic circuits to nationwide power generation and transmission systems.
– design, construction, maintenance and supervision of major infrastructure projects such as highways, railways, bridges, tunnels, dams and airports.
Aerospace engineering - design, manufacture and testing of aircraft and spacecraft, as well as parts and components such as airframes, power plants, control and guidance systems, electrical and electronic systems, communication and navigation systems.
Nuclear engineering – design, manufacture, construction, operation and testing of equipment, systems and processes for the production, control and detection of nuclear radiation. These systems include particle accelerators and nuclear reactors for power plants and ships, and the production and research of radioisotopes.
construction machinery is the design, construction and supervision of load-bearing structures such as buildings, bridges and industrial infrastructure.
– the practice of designing systems, equipment and devices for use in medical practice.
chemical engineering is the practice of designing equipment, systems and processes for purifying raw materials and mixing, combining and processing chemicals to produce valuable products.
Computer engineering – the practice of designing components of computer hardware, computer systems, networks and computer software.
Industrial engineering – the practice of designing and optimizing devices, equipment, systems and processes for manufacturing, material handling and any other work environment.
environmental engineering – the practice of preventing, reducing and eliminating sources of pollution that affect air, water and land. It also detects and measures pollution levels, pinpoints sources of pollution, cleans and remediates contaminated sites, and enforces local and national regulations.
It often happens that individual specialties overlap significantly. For this reason, engineers must have a general knowledge of several fields of engineering in addition to their specialty. For example, a civil engineer must understand structural design concepts, an aerospace engineer must apply mechanical engineering principles, and a nuclear engineer must have a working knowledge of electrical engineering.
All engineers, regardless of specialization, need a thorough knowledge of mathematics, physics and computer technologies such as computer modeling and design. Therefore, today most engineering research programs contain solid elements of knowledge in the creation and use of both computer software and hardware.
An engineer does not work alone
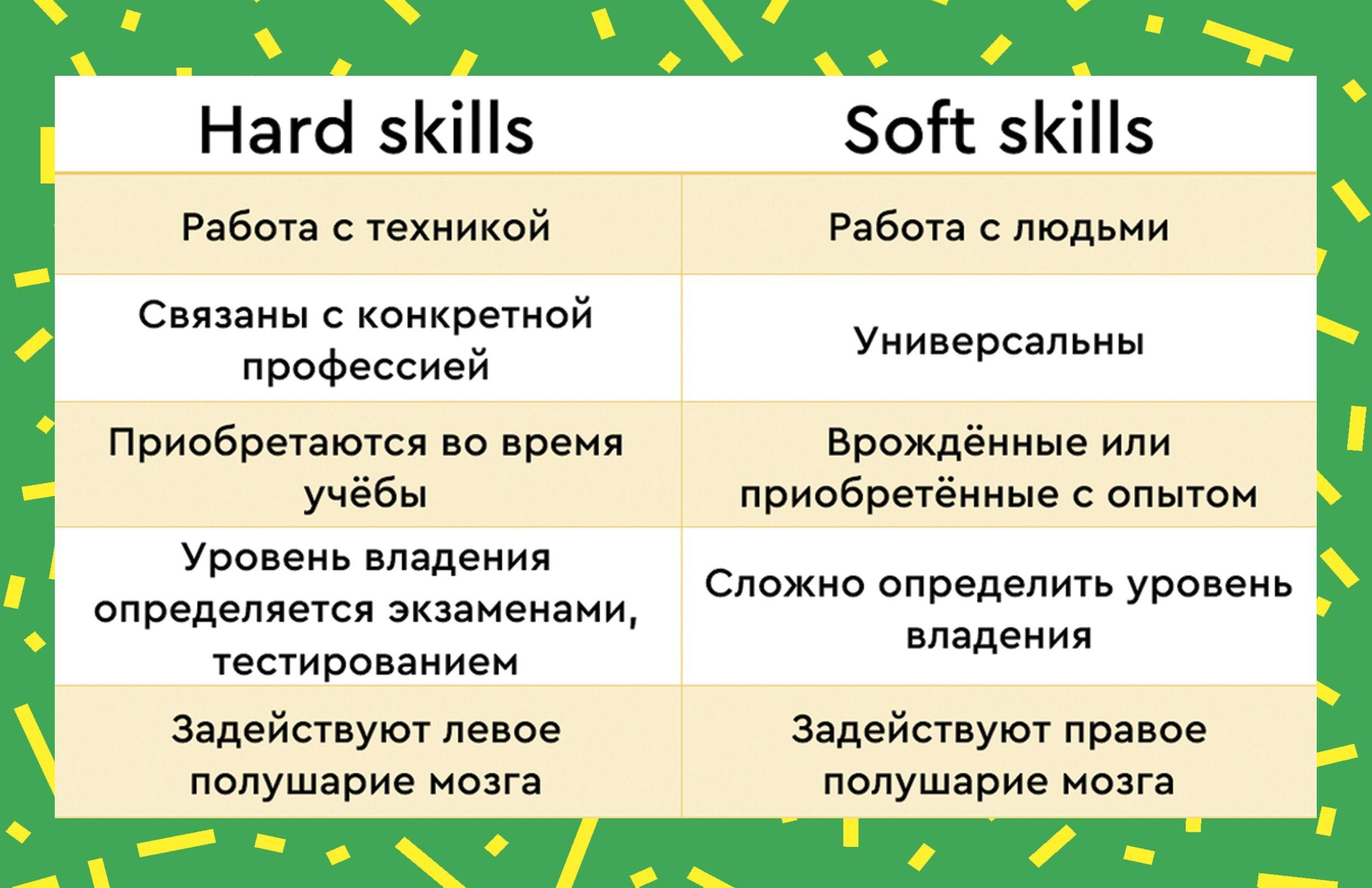
In addition to the relevant education, knowledge and, as a rule, technical skills, modern engineers must possess a range of so-called "soft" skills. Generally speaking, these skills are about adapting to the work environment and dealing with groups of people, in the face of new problems and emerging "non-technical" situations.
For example, leadership qualities and the ability to form appropriate relationships come in handy when an engineer manages groups of employees. Formalized methods of reaching an agreement with people with a technical background are not enough. Very often, you also have to communicate with people outside the industry, such as customers, and sometimes with the general public, people who do not have a technical background. It is important that you can translate your experience into terms that people in and outside of your department can understand.
Due to the high technical requirements, communication is often one of the most sought-after soft skills. Engineers almost never work alone. They work with a wide range of employees, both fellow engineers and people outside their department, to complete their projects. And these “soft” skills also include such traits as the so-called “Emotional Intelligence”, presentation and teaching skills, the ability to explain complex problems, the ability to motivate, the ability to negotiate, stress tolerance, risk management, strategic planning and knowledge of project management techniques. .
This is a set of "soft" competencies that goes beyond many other "more complex" areas of knowledge, but also goes beyond the strictly understood specialization of an engineer. The latter includes a wide range, ranging from programming languages, statistical knowledge, data processing, the ability to design models, structures, systems, and process control.
Like other professionals who need project management skills, some engineers apply for a project management certificate, for example, according to the well-known PMI methodology.
Nowadays, engineering is mostly about problem solving and multitasking.and that means finding new ways to apply existing knowledge—a truly creative process. Engineering can include a creative element.
The days of narrow specializations are long gone.
Daniel Cooley (3), vice president and chief strategy officer of Silicon Labs, points out in a press release that an engineer entering the third decade of the XNUMXth century should "beware" of a few more things that have grown rapidly in recent years.
The first is machine learning and its implications for various fields of technology (4). The second point that Cooley points out is information security practices, which modern engineers simply cannot take lightly. Other issues to keep in mind are context and links to other areas of technology. Engineering should forget about sweet isolation and think of its specialization as separate from everything else.
The report of the American National Academy of Engineering (NAE), entitled "Engineer of the Year 2020" describes the world of mechanical engineering in a rapidly changing environment where technological progress is rapid and constant. We read in it, among other things, the assumption that areas such as nanotechnology, biotechnology and high performance computing will contribute to economic growth in the future, which means that the role of engineers with experience in these areas will increase. As the world becomes more and more interconnected and webbed of countless dependencies, engineers will need to take an increasingly multidisciplinary approach. Some engineering professions will also have additional responsibilities. For example, civil engineers will be partly responsible for creating a sustainable environment while improving the quality of life. The days of narrow specializations are over, and this trend will only deepen - this is evident from the report.

