Cars with a rotary engine - what are their advantages?
Content
Usually the "heart" of the machine is a cylinder-piston system, that is, based on reciprocating motion, but there is another option - rotary engine vehicles.
Cars with a rotary engine - the main difference
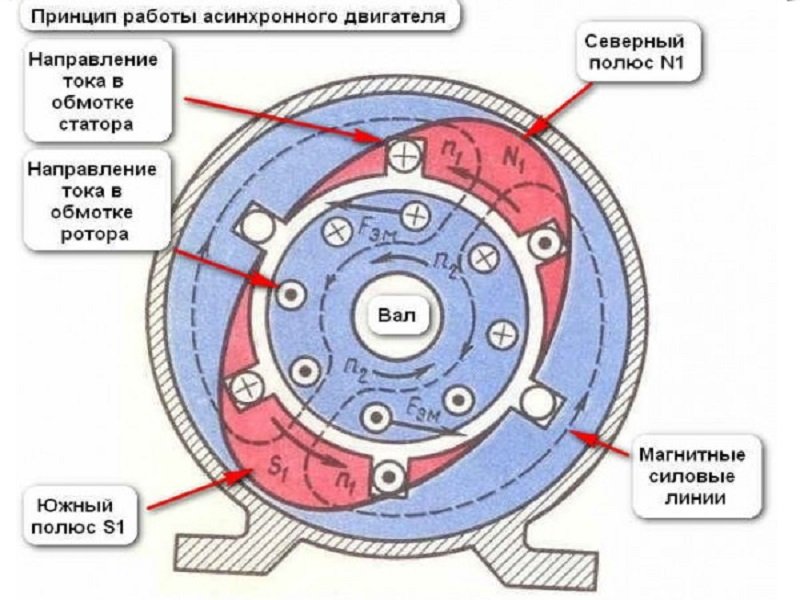
The main difficulty in the operation of internal combustion engines with classic cylinders is the conversion of the reciprocating motion of the pistons into torque, without which the wheels will not rotate.. That is why, from the moment the first internal combustion engine was created, scientists and self-taught mechanics puzzled over how to make an engine with exclusively rotating components. The German nugget technician Wankel succeeded in this.
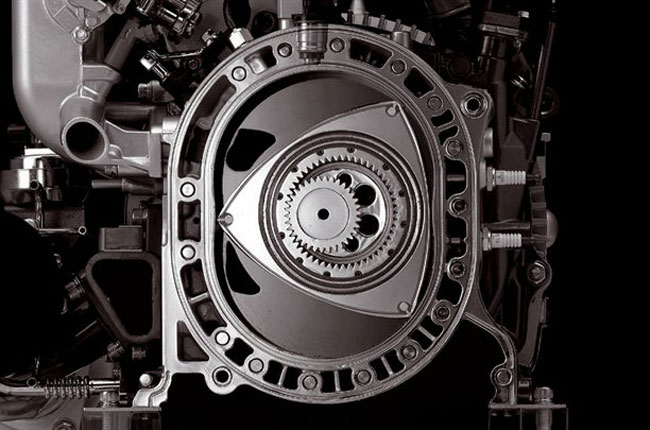
The first sketches were developed by him in 1927, after graduating from high school. In the future, the mechanic bought a small workshop and came to grips with his idea. The result of many years of work was a working model of a rotary internal combustion engine, created jointly with engineer Walter Freude. The mechanism turned out to be similar to an electric motor, that is, it was based on a shaft with a trihedral rotor, very similar to the Reuleaux triangle, which was enclosed in an oval-shaped chamber. The corners rest against the walls, creating a hermetic movable contact with them.
The cavity of the stator (case) is divided by the core into the number of chambers corresponding to the number of its sides, and three main cycles are worked out for one revolution of the rotor: fuel injection, ignition, exhaust gas emission. In fact, of course, there are 5 of them, but two intermediate ones, fuel compression and gas expansion, can be ignored. In one complete cycle, 3 revolutions of the shaft occur, and given that two rotors are usually installed in antiphase, cars with a rotary engine have 3 times more power than classic cylinder-piston systems.
How popular is a rotary diesel engine?
The first cars on which the Wankel ICE was installed were the NSU Spider cars of 1964, with a power of 54 hp, which made it possible to accelerate vehicles up to 150 km / h. Further, in 1967, a bench version of the NSU Ro-80 sedan was created, beautiful and even elegant, with a narrowed hood and a slightly higher trunk. It never went into mass production. However, it was this car that prompted many companies to buy licenses for a rotary diesel engine. These included Toyota, Citroen, GM, Mazda. Nowhere did the novelty catch on. Why? The reason for this was its serious shortcomings.
The chamber formed by the walls of the stator and rotor significantly exceeds the volume of a classic cylinder, the fuel-air mixture is uneven. Because of this, even with the use of a synchronous discharge of two candles, complete combustion of the fuel is not ensured. As a result, the internal combustion engine is uneconomical and non-environmental. That is why, when the fuel crisis broke out, NSU, which made a bet on rotary engines, was forced to merge with Volkswagen, where the discredited Wankels were abandoned.
Mercedes-Benz produced only two cars with a rotor - C111 of the first (280 hp, 257.5 km / h, 100 km / h in 5 seconds) and the second (350 hp, 300 km / h, 100 km /h for 4.8 sec) generations. Chevrolet also released two test Corvette cars, with a two-section 266 hp engine. and with a four-section 390 hp, but everything was limited to their demonstration. For 2 years, starting in 1974, Citroen produced 874 Citroen GS Birotor cars with a capacity of 107 hp from the assembly line, then they were recalled for liquidation, but about 200 remained with motorists. So, there is a chance to meet them today on the roads of Germany, Denmark or Switzerland, unless, of course, their owners were given a major overhaul of the rotary engine.
Mazda was able to establish the most stable production, from 1967 to 1972 1519 Cosmo cars were produced, embodied in two series of 343 and 1176 cars. During the same period, the Luce R130 coupe was mass-produced. Wankels began to be installed on all Mazda models without exception since 1970, including the Parkway Rotary 26 bus, which develops speeds of up to 120 km / h with a mass of 2835 kg. Around the same time, the production of rotary engines began in the USSR, however, without a license, and, therefore, they came up with their own minds using the example of a disassembled Wankel with NSU Ro-80.


Watch this video on YouTube
The development was carried out at the VAZ plant. In 1976, the VAZ-311 engine was qualitatively changed, and six years later the VAZ-21018 brand with a 70 hp rotor began to be mass-produced. True, a piston internal combustion engine was soon installed on the entire series, since all the “wankels” broke during the run-in, and a replacement rotary engine was required. Since 1983, the VAZ-411 and VAZ-413 models for 120 and 140 hp began to roll off the assembly line. respectively. They were equipped with units of the traffic police, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and the KGB. Rotors are now exclusively handled by Mazda.
Is it possible to repair a rotary engine with your own hands?
It is quite difficult to do anything on your own with the Wankel ICE. The most accessible action is the replacement of candles. On the first models, they were mounted directly into a fixed shaft, around which not only the rotor rotated, but also the body itself. Later, on the contrary, the stator was made immobile by installing 2 candles in its wall opposite the fuel injection and exhaust valves. Any other repair work, if you are used to classic piston internal combustion engines, is almost impossible.
In the Wankel engine, there are 40% fewer parts than in a standard ICE, the operation of which is based on a CPG (cylinder-piston group).
The shaft bearing liners are changed if the copper begins to show through, for this we remove the gears, replace them and press the gears again. Then we inspect the seals and, if necessary, change them too. When repairing a rotary engine with your own hands, be careful when removing and installing oil scraper ring springs, the front and rear ones differ in shape. The end plates are also replaced if necessary, and they must be installed according to the letter marking.
Corner seals are primarily mounted on the front side of the rotor, it is advisable to put them on green Castrol grease to fix them during assembly of the mechanism. After installing the shaft, rear corner seals are installed. When laying gaskets on the stator, lubricate them with sealant. Apexes with springs are inserted into the corner seals after the rotor is placed in the stator housing. Lastly, the front and rear section gaskets are lubricated with sealant before the covers are fastened.


Watch this video on YouTube