Gasoline in engine oil
Content
Gasoline in oil leads to a decrease in the viscosity of the lubricant, as well as a loss of its performance. As a result of such a problem, the internal combustion engine starts to start poorly “hot”, its dynamics of work decreases and the fuel consumption of the car as a whole increases. There are many reasons why gasoline appears in the crankcase - a partial failure of the fuel pump (on carburetor ICEs), loss of gasket tightness, reduced compression, and some others. You can determine the exact reason why gasoline gets into the oil even in garage conditions. There are several proven methods for this.
How to understand if there is gasoline in the oil (signs)
There are ten basic signs that indicate that there is gasoline in the engine oil.
- The oil smells like gasoline. This is usually clearly felt when checking the level of lubricating fluid in the crankcase. You can smell both the dipstick and the filler hole. The smell is especially good when the internal combustion engine is warmed up. Often the smell is not gasoline, but acetone.
- The oil level gradually rises despite the fact that it was not added to the crankcase. Usually this does not happen suddenly, but gradually, as the car is used in the long term.
- Increase in fuel consumption (petrol) in parallel with an increase in the oil level.
- The oil becomes thinner. That is, it loses its viscosity. This can be determined simply by touch by tasting the composition with your fingers on the dipstick. Or just see that the oil has become easy to drain from the dipstick, although this has not been observed before.
- Reducing oil pressure. Moreover, this fact may be accompanied by a simultaneous increase in its level in the crankcase. This is due to its dilution (especially true for viscous oils).
- Difficulty starting the internal combustion engine "hot". This is due to the loss of oil viscosity.
- ICE power drop. This is expressed in a decrease in dynamic characteristics, as well as a loss of traction (the car accelerates poorly, does not pull uphill). Due to the increase in friction between the parts of the KShM.
- Spontaneous increase in engine speed at idle. Typical for injection engines.
- The occurrence of errors in the ECU memory. namely, they are associated with the formation of an enriched air-fuel mixture, misfiring, as well as malfunctions of the lambda probe (oxygen sensor).
- Exhaust gases acquire a sharper, fuel-like smell. Sometimes along with this they acquire a darker shade.
Please note that the last three signs may indicate other breakdowns in the car's internal combustion engine, so it is advisable to conduct a complete diagnosis, primarily using diagnostic scanners. The problem with fuel getting into the oil is also found in diesel power units, however, and it is determined by the same signs, but the reasons for these two types of internal combustion engines will be different.
Reasons why gasoline is in the oil
There are a lot of reasons why gasoline got into the oil, including they depend on the type of engine fuel system (carburetor, injection, direct injection). Let's consider them in order, and let's start with an injection gasoline engine:
- Use of low-quality fuel. It can damage the seals through which, over time, fuel will seep into the internal combustion engine. In addition, the combustible-air mixture created from it can damage the surfaces of cylinders, pistons, valves.
- Use of poor quality additives. Poor quality fuel additives can damage seals. Therefore, it is necessary to approach their use with an understanding of the matter and correctly make a choice of one or another means.
- Worn cylinder piston rings and poor compression. Usually this happens for natural reasons as a result of long-term operation of the car, or due to mechanical damage. For this reason, fuel enters the crankcase, where it mixes with engine oil.
- Faulty EGR system. Incorrect operation of the exhaust gas recirculation system can also cause gasoline to enter the oil.
- Missing nozzles. For ICEs with direct fuel injection (for example, TSI), if the injectors are leaking, then at the time the ICE is started, a small amount of gasoline from them will seep into the ICE oil. So, after parking with the ignition on (when the pump creates a pressure of up to 130 bar), the pressure in the fuel rail contributes to the fact that gasoline enters the combustion chamber, and through the gap in the rings into the oil. A similar problem (albeit to a lesser extent) can be in ordinary injection ICEs.
- Faulty vacuum fuel regulator. If it does not work correctly, part of the fuel returns to the internal combustion engine and mixes with oil through the gaps.
- Rich fuel-air mixture. The formation of a rich mixture can be caused by various reasons. On injection ICEs, this is due to a malfunction of sensors or nozzles, and for carburetor machines, the carburetor may simply be incorrectly configured.
- Faulty ignition coil/spark plug/high voltage wires. The result of this is the fact that the air-fuel mixture in a particular cylinder does not burn. The air naturally escapes, and the fuel vapors remain on the cylinder walls, from where they enter the crankcase.
Consider separately the reasons for carburetor ICEs:
- Fuel pump diaphragm damage. This can happen due to natural causes (aging and wear) or as a result of mechanical damage. The lower part of the diaphragm is designed to protect its upper part from harmful crankcase gases. Accordingly, if one or another layer is damaged, a situation may arise when gasoline seeps into the crankcase, mixing with the lubricant there.
- Needle valve problems. Over time, it can also get damaged and work incorrectly, skipping gasoline.
- Incorrect carburetor setting. As a result, gasoline may overflow into the carburetor, including the formation of an enriched air-fuel mixture. And in case of damage to the diaphragm, the situation only gets worse.
How to determine gasoline in oil
Any car enthusiast can determine if there is gasoline in the oil during a standard procedure in the morning before starting the internal combustion engine. You can do this using one of the methods below.
Check smell
The simplest test method that will allow you to find out gasoline in oil is smell the oil while checking the level with the dipstick or by unscrewing the oil filler cap. If the engine oil smells like gasoline, this should alert you and force you to do a few other checks. Notice that the oil may smell not of gasoline, but of acetone. It depends on the quality of the gasoline and oil used, the condition of the lubricant and other reasons.
Drip test
Often, with a change in the smell of oil, it becomes more liquid, that is, it begins to easily drain from the dipstick. This also needs to be paid attention to, especially if the oil was filled in a long time ago, for example, the mileage on it is already more than the middle of the service life. Therefore, in addition to lubrication for smell, conduct a drop test to determine the quality of the oil.
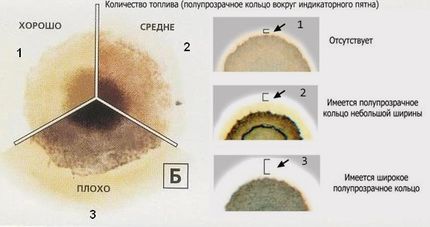
So, to perform it, you just need to drop a few grams of the lubricant being tested on plain paper. You will not get an instant answer, because you need to leave it in a warm place for at least a couple of hours (preferably 12). But, having analyzed the spreading zones (there will be a sector with a yellowish or reddish tint along the edges of the circle), then with a high degree of probability gasoline gets into the oil or not.
And in order to reduce the erroneous suspicion to zero, it is worth taking a closer look at the signs considered above and checking for combustion.
Burning engine oil
Many experienced drivers, in order to find out if there is gasoline in the oil, offer to simply set fire to the lubricant. Inexperienced drivers who have never encountered such a problem often mistakenly try to simply set fire to the oil directly on the dipstick. This approach will not work, except that the oil already contains a critical part of gasoline, but this rarely happens, and this will be seen from other, obvious, signs.
In fact you need to set fire to the oil heated in a test tube. So, for this you need to take a glass test tube with a narrow neck and pour a small amount of oil into it. If the test tube has a flat bottom, then it is better to heat it on an electric stove. If the test tube has a rounded bottom, then you can take it in laboratory tongs and heat it on an open fire source (stove, candle, dry alcohol, etc.). Please note that during the heating process, the neck (upper part) of the test tube must be hermetically sealed with some kind of lid so that the gasoline does not evaporate during the heating process.
The ignition temperature of engine oil vapors is much higher than that of gasoline vapors, so in the normal state, oil vapors will not burn. further, after a certain amount of time has passed, when the test samples have warmed up sufficiently, you need to open the lid of the test tube and quickly bring a source of open flame (a lighter, a match). If the outgoing vapors do not ignite, then most likely there is no gasoline in the oil or its amount is negligible. Accordingly, if the presence of gasoline is serious, then a tongue of flame will appear on the neck of the test tube. In this case, it will be the result of the combustion of gasoline vapors emanating from the lubricating fluid in the test tube.
What to do when gasoline gets into oil
If you find that there is fuel in the engine oil, then the first thing to think about is diagnostics to determine the cause and change the oil itself. It is impossible to operate the machine for a long time in this mode!
The search for a fuel leak in the engine oil begins with a compression test, injector seals and their performance. Injector diagnostics can be performed with or without dismantling. On carbureted vehicles, it is required to check the carburetor setting, less often, its needle mechanism and seat assembly are replaced.
In parallel with checking the operation of the fuel system of the system, it is worth unscrewing and checking the candles. The color of soot and their condition will allow you to judge the operation of the ignition system.
What are the consequences of operating a car with gasoline in oil
But what happens if gasoline gets into the oil and it is not detected in time? Can the machine be operated under such conditions? We will answer right away - you can operate, but not for long.
This is due to the fact that the fuel, entering the crankcase, significantly dilutes the lubricating fluid, thereby violating its performance. A decrease in viscosity leads to poor-quality lubrication of individual parts of the motor, this is especially true when it operates at high temperatures and at high loads. In addition, gasoline neutralizes the effect of additives in it.
In the most critical situations, the oil in the internal combustion engine can simply ignite with all the ensuing consequences!
Therefore, in order not to lead to the occurrence of such situations and to preserve the resource of the internal combustion engine as much as possible, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics and appropriate repair measures as soon as possible.