All about the engine oil pump
Content
No internal combustion engine will function without lubrication. The design of motors includes a large number of parts that work synchronously in different mechanisms on the basis of rotation, engagement and reciprocating movements. So that their contact surfaces do not wear out, it is necessary to create a stable oil film that prevents dry friction of the elements.
What is a car engine oil pump
The lubrication system of the components of the power unit can be of two types. The car is supplied with a wet sump by default. Some SUV and sports car models get a more complex dry sump system. Read more about the difference between them. in another review... Regardless of which system is used in the power unit, the oil pump will be an integral element in it. This is the most important mechanism, which ensures an uninterrupted supply of lubricant to all engine components, so that there is a protective film on its parts at all times, the unit is properly cleaned of metal waste and is properly cooled.

We will discuss the principle of its operation, what modifications exist, their malfunctions and how to diagnose these failures. It will also be helpful to consider a few tips for operating this mechanism.
Purpose of the oil pump
So that the frictional force between the parts of a running motor does not spoil them, engine oil is used. More details about the features of this material, and how to choose the right one for your car, is described separately... In short, the presence of a lubricant not only reduces friction between parts, but also provides additional cooling, since many ICE components are not sufficiently cooled without oil. Another function of engine oil is to wash off fine dust that forms as a result of the operation of the mechanisms of the power unit.
If the bearings have enough thick grease, which is in the cage throughout the entire service life of the product, then such a lubrication system cannot be used in the motor. The reason for this is too high mechanical and thermal loads. Because of this, the grease works out its resource much faster than the parts themselves.

So that the motorist does not have to completely sort out the motor every time the lubricant is replaced, in the most primitive engines, a lubrication system was used, in which an oil pump was necessarily installed.
In the classic version, it is a simple mechanism permanently connected to the motor. This can be a gearing directly through the crankshaft gear or a belt drive to which the gas distribution mechanism is connected, the generator drive and other mechanisms, depending on the layout of the car. In the simplest system, it is located in a pallet. Its task is to ensure a stable pressure of the lubricant so that it is constantly supplied to each cavity of the unit.
Principle of operation
The work of such a mechanism is as follows. When the crankshaft starts to rotate, the oil pump drive is activated. The gears begin to rotate, picking up the lubricant from the cavity. This is how the pump begins to suck oil from the reservoir. In classic engines with a wet sump, cooled lubricant flows directly through the filter through the corresponding channels to each part of the unit.
If the engine is equipped with a "dry sump", then it will have two pumps (sometimes there is a design with three oil pumps). One is suction and the other is discharge. The first mechanism simply collects oil from the sump and feeds it through a filter into a separate reservoir. The second supercharger already uses the lubricant from this tank, and supplies it under pressure through a channel made in the engine housing to the individual parts.

To relieve excess pressure, the system uses a pressure reducing valve. Usually there is a spring in his device that reacts to excessive pressure, and ensures that the oil is dumped back into the sump. The key task of the oil pump is the uninterrupted circulation of lubricant, which is of great importance for the performance of the power unit.
Oil pump device
If we consider a classic oil pump, then it has a hermetically sealed casing. It contains two gears. One of them is the leader and the other is the follower. The drive element is mounted on a shaft that is connected to the motor drive. A chamber is made in the body of the mechanism - lubricant is sucked into it, and then it enters the channels of the cylinder block.
An oil receiver with a mesh that cleans from large particles is connected to the body of the mechanism. This element must be located at the lowest point of the sump so that even if the oil level in it is minimal, the pump can continue to pump it into the line.
Types of oil pumps
The classic oil pump is driven by a gear train connected to the crankshaft, but there are also modifications that function from the rotation of the camshaft. The second type of blower is used very rarely due to the complexity of the design. The reason is that one revolution of the camshaft corresponds to two revolutions of the crankshaft, therefore it rotates more slowly, which means that to create the required pressure in the line, it is necessary to use a special torque transmission to the pump drive. Electric models are used even less often, and then mainly as an auxiliary element.

If we conditionally divide all mechanisms into categories according to the principle of management, then there will be two of them:
- Unregulated... This means that the pressure correction in the line is performed by a special valve. The pump runs on a constant basis, so it creates a constant head, which sometimes exceeds the required parameter. In order to regulate pressure in such a scheme, the valve, when this parameter rises, releases the excess pressure through the crankcase into the sump.
- Adjustable... This modification independently regulates the pressure in the system by changing its performance.
If we divide these mechanisms according to the type of design, then there will be three of them: gear, rotary and vane oil pumps. Regardless of the type of lubricant flow control and the design of the mechanism, all blowers work in a similar way: they suck oil from the lowest part of the sump, feed it through a filter either directly into the engine line, or into a separate tank (a second blower is used to circulate the lubricant). Let's consider these modifications in more detail.
Gear pumps
Gear modifications are included in the category of unregulated types of blowers. A pressure reducing valve is used to adjust the line pressure. The shaft of the device is activated by rotating the crankshaft. In such an arrangement, the pressure force directly depends on the crankshaft rotational speed, so the line needs to dump the excess oil pressure.
The gear oil pump device consists of:
- Drive gear connected to the crankshaft;
- A driven secondary gear that engages with the first part;
- Hermetically sealed casing. It has two cavities. In one oil it is sucked in, and in the other it is already supplied under pressure, and goes into the main line;
- Overpressure relief valve (pressure reducing valve). Its operation resembles that of a plunger pair (read about this device separately). The valve assembly contains a spring that is compressed by excessive lubricant pressure. The piston in a pair moves until the channel opens to discharge excess lubricant;
- Seals that ensure the tightness of the mechanism.
If we talk about the drive of gear oil pumps, then there are two types of them:
- External gear... This is a design similar to most gear mechanisms such as a gearbox. In this case, the gears are engaged by the teeth located on their outer side. The advantage of such a mechanism is its simplicity of execution. The disadvantage of this modification is that when oil is captured between the teeth, a specific pressure zone is formed. To eliminate this effect, each gear tooth is equipped with a relief groove. On the other hand, additional clearance reduces pump performance at low engine speeds.
- Internal gearing... In this case, two gears are also used. One of them has internal, and the second - external teeth. The driving part is installed inside the driven one, and both rotate. Due to the displacement of the axis, the gears mesh with each other only on one side, and on the other there is sufficient for the intake and injection of lubricant. This design is more compact and differs from the previous modification in improved performance in any operating mode of the internal combustion engine.

The gear oil pump (external gearing principle) works according to the following principle. The oil flows through the suction channel to the gears. The rotating elements capture a small portion of the lubricant and compress it strongly. When the compressed medium enters the area of the delivery channel, it is pushed into the oil line.
Modifications that use the internal gearing principle can be equipped with a special baffle made in the shape of a sickle. This element is located in the area where the gear teeth are at the maximum distance from each other. The presence of such a baffle ensures a better oil seal, and at the same time a high-quality pressure in the line.
Rotary lobe pumps for transferring engine oil
This modification is similar in function to internal gear modifications. The difference lies in the fact that instead of movable gears, the mechanism has a fixed external element with internal teeth and a movable rotor (moves in the stator). The pressure in the oil line is provided due to the fact that the oil between the teeth is strongly compressed and is thrown under pressure into the pressure chamber.
As well as gear modifications, such blowers also regulate the pressure using a valve or by changing the internal space. In the second version, the circuit is equipped with a pressure reducing valve, and is driven by a rotating crankshaft. And its performance depends on it.

The first modification uses a movable stator. The associated control spring corrects the oil pressure. This function is performed by increasing / decreasing the distance between the rotating elements. The device will work according to the following principle.
With an increase in crankshaft speed, the pressure in the line decreases (the unit consumes more lubricant). This factor affects the compression ratio of the spring, and it, in turn, turns the stator slightly, thereby changing the position of this element relative to the rotor. This changes the volume of the chamber. As a result, the oil is compressed more and the head in the line increases. The advantage of this modification of oil pumps is not only in compact dimensions. In addition, it maintains performance in different operating modes of the power unit.
Vane or vane oil pumps
There is also a vane (or vane) type of oil pumps. In this modification, the pressure is maintained by changing the capacity, which depends on the speed of the internal combustion engine drive.
The device of such a pump includes the following elements:
- Casing;
- Rotor;
- Stator;
- Movable plates on the rotor.
The principle of operation of the mechanism is as follows. Due to the displacement of the rotor and stator axis, an increased crescent-shaped gap is formed in one part of the mechanism. When the speed of the crankshaft increases, plates are extended between the injection elements due to centrifugal force, thereby creating additional compression chambers. Due to the rotation of the rotor blades, the volume of these cavities changes.

As the volume of the chamber increases, a vacuum is created so that the lubricant is sucked into the pump. As the blades move, this chamber is reduced and the lubricant is compressed. When the cavity filled with oil moves to the delivery channel, the working medium is pushed into the line.
Operation and maintenance of the oil pump
Despite the fact that the oil pump mechanism is made of strong and durable materials, and it works in conditions of abundant lubrication, if the operating conditions are violated, the device may not complete its working life. To eliminate this, consider the common issues related to the operation, maintenance and repair of oil pumps.
Oil pump malfunctions
As mentioned earlier, there are two types of engine lubrication systems - dry and wet sump. In the first case, the oil pump is located between the filter and the oil storage tank. Some modifications of such systems receive a pump installed near the cooling radiator of the engine lubrication system. To understand where the oil pump is located in a separate car model, you should pay attention to which mechanisms are connected to the motor drive (belt or chain drive).
In other lubrication systems, the oil pump is located in front of the power unit, at its lowest point. The oil receiver must always be immersed in oil. Further, the lubricant is fed to the filter, in which it is cleaned of small metal particles.
Since the proper operation of the power unit depends on the lubrication system, the oil pump is manufactured so that it has a large working resource (in most car models, this interval is calculated in hundreds of thousands of kilometers). Despite this, these mechanisms periodically fail. The main breakdowns include:
- Worn gears, rotor or stator teeth;
- Increased clearances between gears or moving parts and pump casing;
- Damage to parts of the mechanism by corrosion (most often this happens when the machine is idle for a long time);
- Failure of the overpressure relief valve (this is mainly a wedge due to the use of low-quality oil or ignoring the oil change regulations). When the valve does not work on time or does not open at all, a red oil can lights up on the dashboard;
- Destruction of the gasket between the elements of the device body;
- Clogged oil receiver or dirty oil filter;
- Breakdown of the mechanism drive (most often due to natural wear of the gears);
- Additional malfunctions of the oil pump can also include a breakdown of the oil pressure sensor.

A malfunction of the oil pump is mainly associated with the use of low-quality oil, a violation of the lubrication change schedule (read more about how often to change the engine oil) or increased loads.
When the oil pump fails, the oil supply to the parts is disrupted in the lubrication system line. Because of this, the engine may experience oil starvation, which leads to various damage to the power unit. Also, the negative effect is on the motor and excessive pressure in the system. In the event of a breakdown of the oil pump, it is changed to a new one - most of the new modifications cannot be repaired.
Diagnostics and adjustment of the oil pump
The very first sign that problems have appeared with the oil pump in the engine is an oil can lit on the dashboard. When diagnosing the on-board system, you can identify an error code that can indicate a failure of the pressure sensor. Basically, the pressure in the system is reduced. It is impossible to find out a specific breakdown in the system without a thorough check of the mechanism and related devices.
The sequence in which the pump is checked is as follows:
- First, it is dismantled;
- A visual inspection of the case is carried out to identify possible visible damage, such as cracks or deformations;
- The housing cover is removed and the integrity of the gasket is checked;
- An inspection of the gears of the mechanism is carried out. If their teeth are chipped, in the presence of replaceable parts, they are replaced with new ones;
- If there are no visual defects, it is necessary to measure the clearances between the gear teeth. A special probe is used for this procedure. In a working pump, the distance between the elements to be engaged should be from 0.1 to 0.35 millimeters;
- Also, the gap between the outer gear (if the model is with internal gearing) and the housing wall is measured (should be in the range from 0.12 to 0.25mm);
- Also, too large a clearance between the shaft and the pump casing affects the performance of the mechanism. This parameter should be between 0.05-0.15mm.
- If there is an opportunity to purchase replacement parts, then they are installed instead of worn out ones. Otherwise, the device is replaced with a new one.
- After checking and repairing, the device is assembled in the reverse order, installed in its place. The engine is started and the system is checked for leaks. If the oil can light on the dashboard does not light up, then the job is done correctly.
It should also be noted that each type of pump has its own parameters, which are most often indicated in the technical documentation of the car.
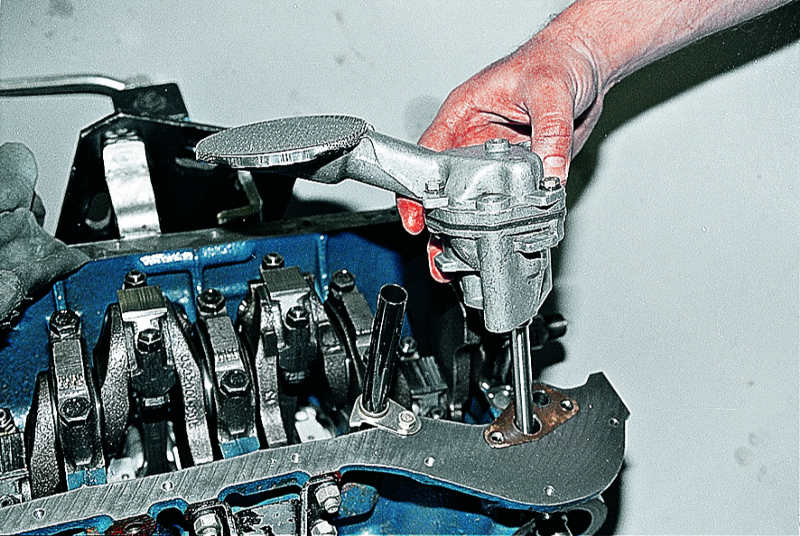
Replacing the oil pump
If the engine lubrication system requires replacing the oil pump, then in almost all cars this work is accompanied by a partial disassembly of the power unit. However, in most cases, installing a new pump is not difficult. To do this professionally, the machine must be put on an overpass or driven into a pit. This will facilitate the dismantling and assembly of the mechanism.
Before starting work, you need to take care of safety. To do this, the car must be stationary (there must be stops under the wheels), and the battery must be disconnected.
After that, the timing drive is removed (chain or belt, depending on the car model). This is a rather complex system, so the procedure must be performed exclusively in accordance with the instructions for repair and maintenance of the car. After that, the pulley and gears are dismantled, blocking access to the pump shaft.

Depending on the ICE model, the pump is attached to the cylinder block with several bolts. After the device is removed from the engine, it is necessary to check the operation of the pressure reducing valve. The oil receiver is cleaned, worn parts are changed or the pump is completely driven.
Installation of the device is carried out in the reverse order. The only caveat is that the tightening torque of the fastening bolts is required for tightness. Thanks to the torque wrench, the threads of the bolts will not be torn off or too weak during the tightening process, due to which, during the operation of the pump, the fastening will loosen and the pressure in the system will drop.
Car tuning and its effect on the oil pump
Many motorists modernize their cars to make them more attractive or dynamic. here). If, to increase the efficiency of the engine, its parameters are changed, for example, the cylinders are bored or a different cylinder head, sports camshaft, etc. are installed, you should also think about buying another model of an oil pump. The reason is that the standard mechanism may not be able to withstand the load.

During technical tuning, to improve the engine lubrication system, some install an additional pump. At the same time, it is important to correctly calculate what the performance of the mechanism should be, and how to correctly connect it to the general system.
How to extend pump life
Compared to the overhaul of the power unit, the cost of a new oil pump is not so high, but no one wants the new device to fail quickly. In order to avoid additional costs, a motorist needs to take into account a few simple tips:
- Do not allow the oil level to fall below the permissible level (a corresponding dipstick is used for this);
- Use a lubricant designed for this power unit;
- Observe the engine oil change procedure. The reason is that the old grease gradually thickens and loses its lubricating properties;
- In the process of changing the lubricant, also dismantle the old oil filter and install a new one;
- Replacing the oil pump should always be accompanied by fresh oil filling and sump cleaning;
- Always pay attention to the oil pressure indicator in the system;
- Periodically check the condition of the pressure relief valve, if any, and clean the oil intake.
If you adhere to these simple rules, the mechanism that pumps lubricant to all components of the power unit will serve the entire period due to it. In addition, we suggest watching a detailed video on how the diagnostics and repair of an oil pump is carried out on the classic:
Questions and answers:
What is an oil pump for? It creates pressure in the engine lubrication system. This allows the oil to reach all corners of the power unit, ensuring proper lubrication of all its parts.
Where is the main engine oil pump located? Wet sump - between the oil receiver (located in the oil pan) and the oil filter. Dry sump - two pumps (one between the oil receiver in the sump and the filter, and the other between the filter and the additional oil tank).
How is the oil pump regulated? Most classic oil pumps are unregulated. If the model is adjustable, the pump will have a dedicated regulator (see manufacturer's instructions).