
What is a multi-link suspension, device and principle of operation
Content
The handling of cars in difficult conditions at high speeds began to be dealt with when engine power ceased to be a problem. It became clear that the ideal suspension from this point of view would be a two-lever parallelogram type. Well-chosen geometry of the levers made it possible to precisely maintain the constancy of the best contact of the wheel with the road.
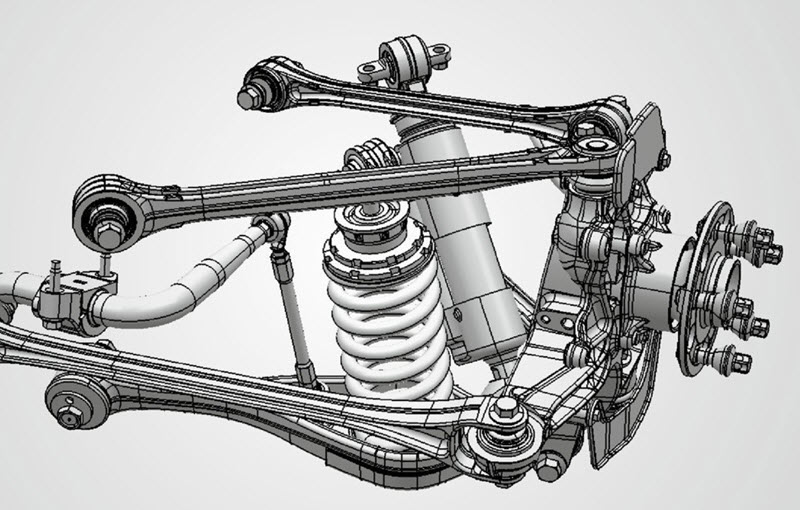
But there is no limit to perfection, and even the new scheme began to have inherent flaws, in particular, parasitic steering during wheel loading in corners. I had to go further.
Why is the suspension called multi-link
The improvement of the double wishbone suspension required the addition of additional forces acting on the wheel hubs in corners to the existing ones.
It is possible to create them by installing new levers in the suspension, with some change in the kinematics of the existing ones. The number of levers grew, and the suspension was called multi-link (Multilink).

Features
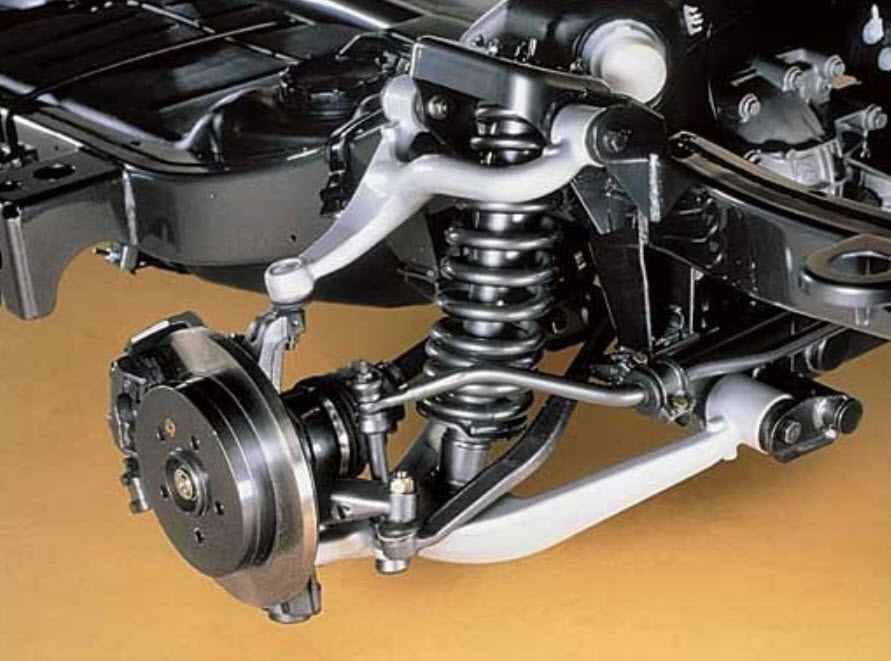
The new type of suspension has acquired fundamentally qualitative features:
- the upper and lower arms received a spaced design, each of them could be divided into separate rods, and the resulting undesirable degrees of freedom were compensated by additional rods and pushers;
- the independence of the suspension has been preserved, moreover, it has become possible to separately control the angles of the wheels, depending on their current position in the arches;
- the functions of providing longitudinal and transverse rigidity can be distributed over separate levers;
- by simply adding levers oriented in the desired plane, it became possible to program any trajectory of the wheel.
At the same time, all the positive qualities of double triangular levers were preserved, the new characteristics became an independent addition to the existing ones.
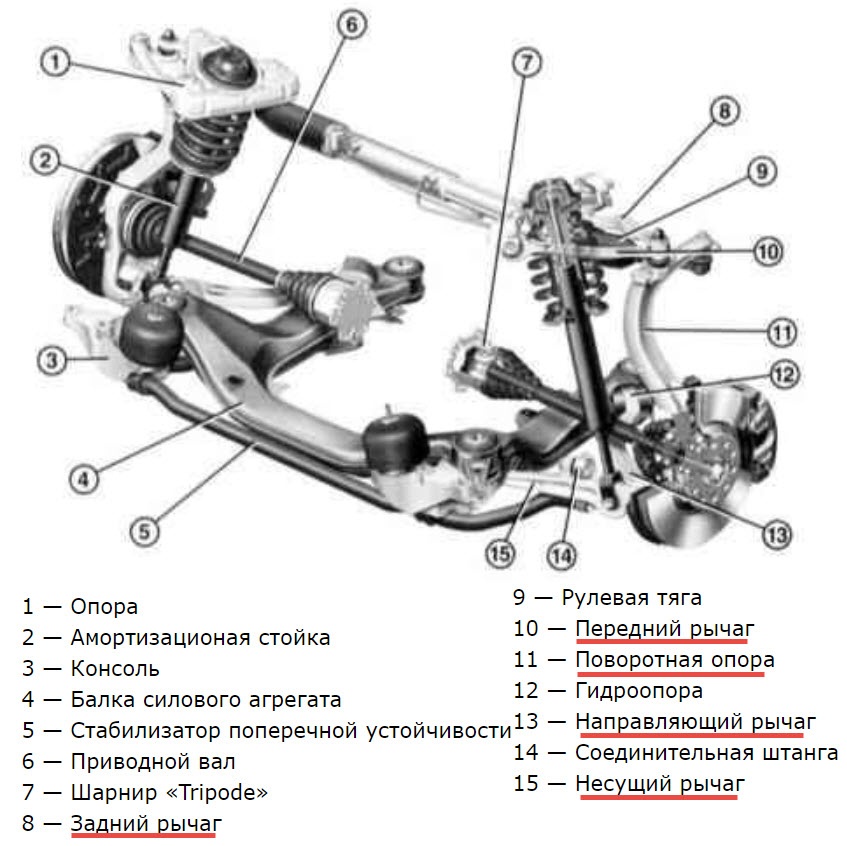
Scheme and device of the rear suspension
It all started with a change in the rear wheel suspension. Everything was fine with the front ones, because the driver himself could quickly influence their angles.
The first unpleasant feature of the classic independent suspension was the change in toe angles due to the natural kinematic compliance of triangular levers on silent blocks.
Naturally, in special racing cars, stiffer hinges were used, but this reduced comfort, and did not completely solve the problem. It was necessary to make very rigid subframes, bodies, which is unacceptable in civilian cars. It turned out to be easier to add another lever that compensated for the rotation of the wheel, creating the opposite torque.
The idea worked, after which the effect was further enhanced by turning parasitic oversteer into neutral, or even insufficient. This helped to stabilize the car in the turn, making it possible to screw it into the turn safely due to the steering effect.
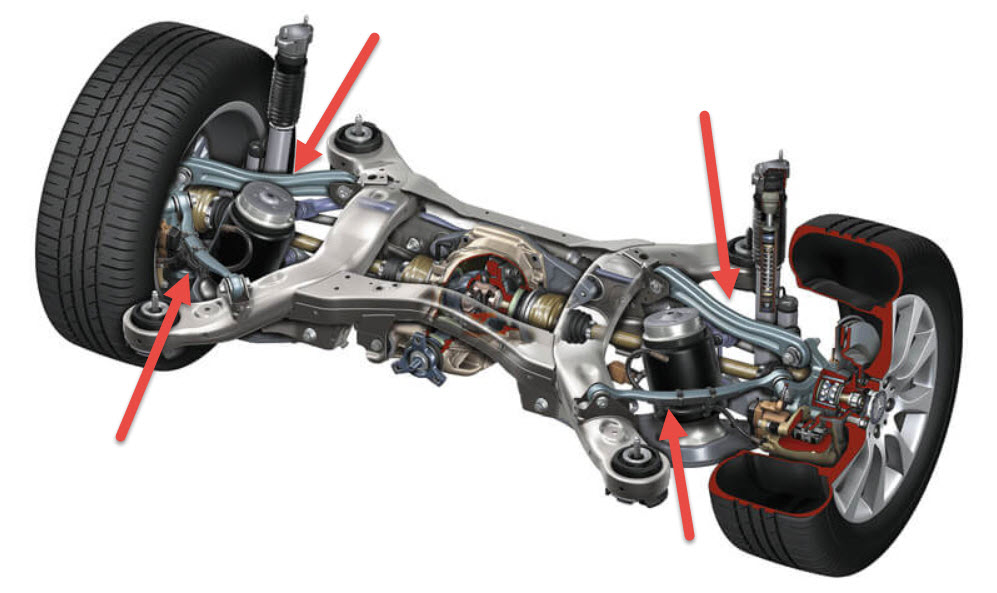

The same positive effect is given by changing the camber of the wheel during the working stroke of the suspension in the right direction. Engineers got a good tool with which it became possible to fine-tune the suspension.
At present, the best option is the use of five levers on each side of the axle with computer-calculated trajectories of wheel movement between the extreme points of forward and reverse suspension travel. Although in order to simplify and reduce the cost, the number of levers may decrease.
Scheme and device of the front suspension
The front multi-link is used much less frequently. This is not particularly necessary, but some manufacturers are working in this direction.

Mainly to improve the smoothness of the ride, making the suspension more elastic, while maintaining controllability. As a rule, it all comes down to the complication of the design of the circuit with two triangular levers.
Theoretically, this is an ordinary parallelogram, but practically a system of autonomous levers with its own hinges and functional purpose. There is no single approach here. Rather, we can talk about limiting the use of such complex guide vanes to premium machines.


Watch this video on YouTube
How Multilink works
During the working stroke of the suspension, the wheel can be affected not only by the loading forces that compress the spring, external to the rotation of the wheel, but also by longitudinal forces during braking or acceleration in turns.
The wheel begins to deviate forward or backward depending on the sign of acceleration. In any case, the toe angle of the rear axle wheels begins to change.
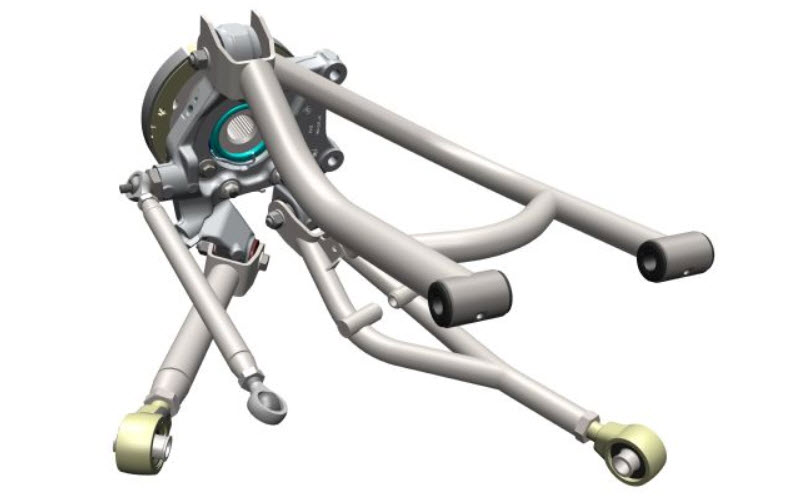


An additional Multilink lever, set at a certain angle, is able to change the toe. The loaded wheel turns in such a way as to compensate for the parasitic withdrawal of the plane of rotation. The machine restores its original handling characteristics.
All other functions of the suspension units are similar to any other independent type design. An elastic element in the form of a spring, a telescopic hydraulic shock absorber and an anti-roll bar work in exactly the same way.
Advantages and disadvantages
Like any complicated mechanism, a multi-link suspension performs all the functions for which it was created:
- cars with Multilink have excellent handling, the contact patch with the road is always as large as possible, the influence of unwanted lateral forces is minimized, and positive forces appear in time and are well regulated when fine-tuning the suspension;
- the suspension provides the comfort inherent in any independent scheme, minimizing not only the vertical acceleration of the body, but also lateral shocks when it hits bumps in corners, numerous elastic elements work out small vibrations well;
- the design has good maintainability, all levers and hinges are self-contained and can be independently dismantled for replacement;
- the suspension is usually combined with a subframe, which allows it to be further isolated from the body;
- spacing in space of all levers and their arbitrary configuration (only the relative position of the end hinges is important) make it easy to assemble the rear-wheel drive units.
The disadvantage, in fact, is one - high complexity, and hence the price. Both in production and in repair, since a large number of wearable hinges are subject to replacement.
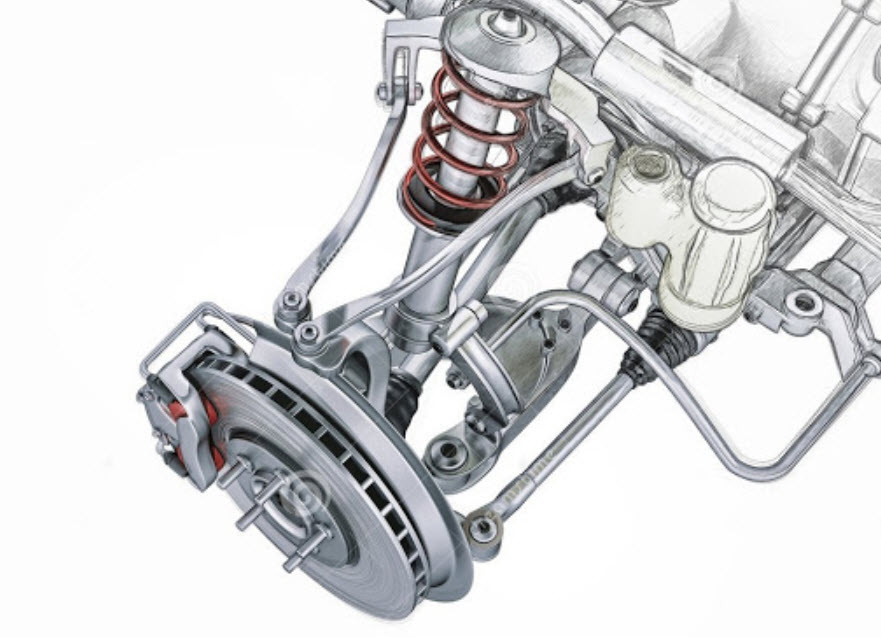

It is unprofitable to lay in them an increased margin of safety, the addition of unsprung masses is multiplied by the number of levers.
Which is better, Torsion beam, MacPherson strut or Multi-link
There is no absolute scale of values for different types of suspensions; each has its own limited application in certain classes and categories of cars. And the mood of manufacturers often change over time.
The suspension is simple, durable, cheap and ideal for the most inexpensive cars. At the same time, it will not provide perfect controllability, as well as high comfort.
In addition, it is very desirable to use a subframe, which the torsion beam does not need.
Recently, there has been a return to simpler suspensions, even in those models where a multi-link was previously used. Manufacturers find it redundant to cater to the desires of sophisticated auto journalists, which are not always clear to ordinary car buyers.
Possible malfunctions of the multi-link suspension
Despite the apparent complexity, the operation of the multi-link does not require anything special from the owner. It all comes down to the usual replacement of worn hinges, only a large number of them cause inconvenience.
But there is a special, only this suspension inherent problem. Numerous levers due to the desire to reduce their total mass are not strong enough. Especially when they are made of aluminum alloys to facilitate them.
Bumps from bumps in the road can accidentally fall in the wrong direction, when they are perceived by only one light and fragile lever.
The metal is deformed, the car begins to actively wear out the rubber and sharply loses controllability. This needs to be watched especially. Stronger beams and double levers are much less likely to do this.


Watch this video on YouTube
The rest of the suspension care is similar to all other types. Leaking shock absorbers, weakened or broken springs, worn struts and stabilizer bushings are subject to replacement.
After any intervention in the suspension, it is necessary to check and restore the initial wheel alignment angles, for which adjusting clutches or eccentric bolts are made in the levers.