
What is a resistor? Symbol, Types, Block, Applications
Content
A resistor is a two-terminal passive electrical component that inventory electric resistance as a circuit element to limit the flow of electric current. It is used in electronic circuits for voltage separation, current reduction, noise suppression and filtering.
But the resistor a lot more than this. So if you are new to electronics or just want to learn more about what a resistor is, then this blog post is for you!

What does a resistor do in an electronics circuit?
A resistor is an electronic component control the flow of current in a circuit and resists the flow of electricity. Resistors prevent surges, surges and interference from reaching sensitive electronics such as digital electronic devices.
Resistor symbol and unit
The unit of resistance is Om (symbol Ω).
Resistor specifications
Resistors are electronic components restrict flow electric current to a given value. The simplest resistors have two terminals, one of which is called the "common terminal" or "ground terminal" and the other is called the "ground terminal". Resistors are wire-based components, but other geometries have also been used.
I hope now you have a better understanding of what a resistor is.
The two most common ones geometric figures are a block called a "chip resistor" and a button called a "carbon compound resistor".
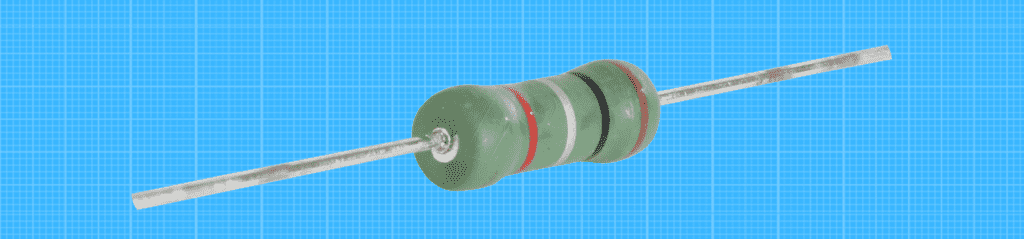
Resistors have colored stripes around their bodies to indicate their resistance values.
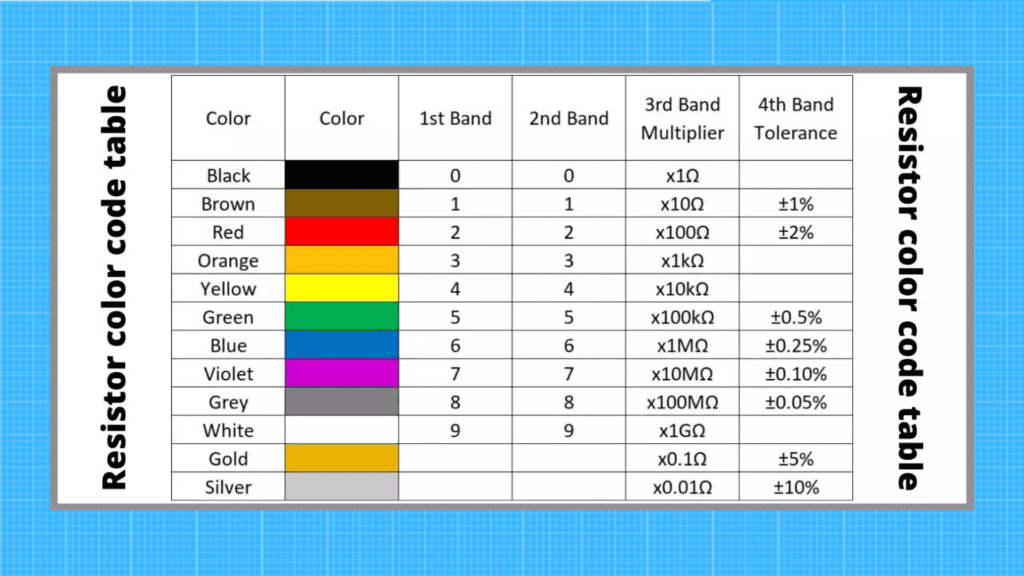
Resistor color code
Resistors will be color coded to represent them electrical quantity. It is based on a coding standard originally developed in the 1950s by the United Electronic Component Manufacturers Association. The code consists of three colored bars, which indicate from left to right the significant digits, the number of zeros and the tolerance range.
Here is a table of resistor color codes.

You can also use the resistor color code calculator.
Resistor types
Resistor types are available in many different dimensions, forms, rated power и voltage limits. Knowing the type of resistor is important when choosing a resistor for a circuit because you need to know how it will react under certain conditions.
carbon resistor
The carbon compound resistor is one of the most common types of resistors in use today. It has excellent temperature stability, low noise performance and can be used in a wide frequency range. Carbon compound resistors are not designed for high power dissipation applications.
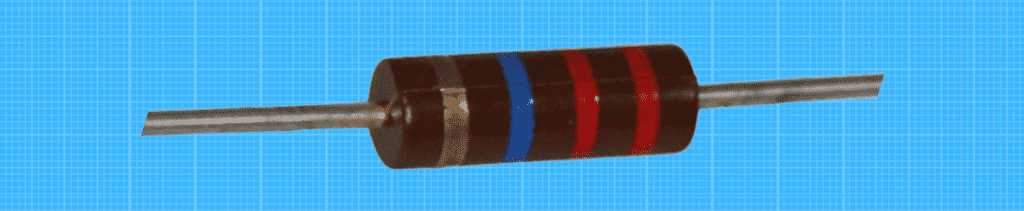
metal film resistor
A metal film resistor consists primarily of a sputtered coating on aluminum that acts as a resistive material, with additional layers to provide insulation protection from heat, and a conductive coating to complete the package. Depending on the type, a metal film resistor can be designed for high precision or high power applications.
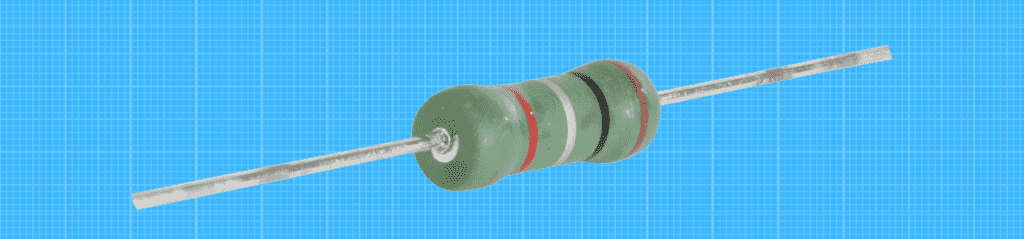
Carbon film resistor
This resistor is similar in design to the metal film resistor, except that it contains additional layers of insulating materials between the resistive element and the conductive coatings to provide additional protection against heat and current. Depending on the type, the carbon film resistor can be designed for high precision or high power applications.
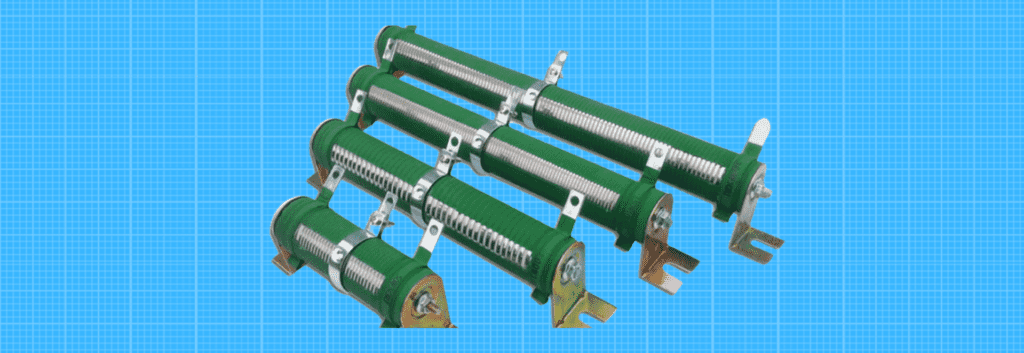
Wire wound resistor
This is a catch-all term for any resistor where the resistance element is made of wire rather than thin film as described above. Wirewound resistors are commonly used when the resistor must withstand or dissipate high power levels.

High voltage variable resistor
This resistor has a carbon rather than thin film resistive element and is used in applications requiring high voltage isolation and high stability at elevated temperatures.
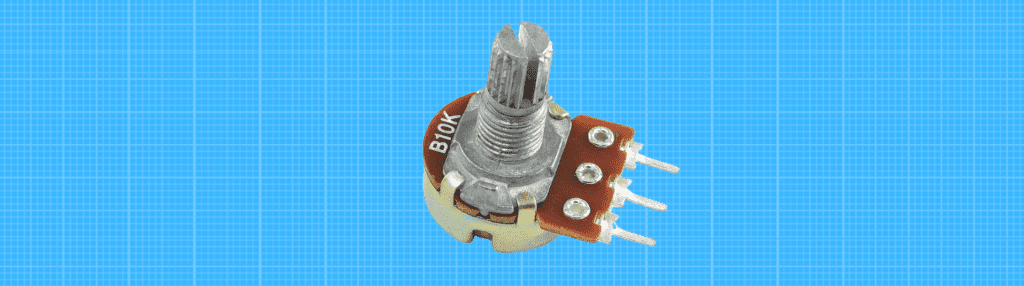
Potentiometer
A potentiometer can be thought of as two variable resistors connected in anti-parallel. The resistance between the two outer leads will change as the wiper moves along the guide until the maximum and minimum limits are reached.
thermistor
This resistor has a positive temperature coefficient, which causes its resistance to increase with increasing temperature. In most cases, it is used because of its negative temperature coefficient of resistance, where its resistance decreases with increasing temperature.

varistor
This resistor is designed to protect circuits from high voltage transients by first providing a very high resistance and then reducing it to a lower value at higher voltages. The varistor will continue to dissipate the applied electrical energy as heat until it breaks down.

SMD resistors
They small, do not require mounting surfaces for installation and can be used in very high density mesh. The disadvantage of SMD resistors is that they have less heat dissipating surface area than through-hole resistors, so their power is reduced.
SMD resistors are usually made from ceramic materials.
SMD resistors are usually much smaller than through-hole resistors because they don't require mounting plates or PCB holes to install. They also take up less PCB space, resulting in higher circuit density.
Company flaw The use of SMD resistors is that they have much less heat dissipation surface area than through-holes, so their power is reduced. They also more difficult to manufacture and solder than through resistors due to their very thin lead wires.
SMD resistors were first introduced at the end 1980s. Since then, smaller, more precise resistor technologies have been developed, such as Metal Glazed Resistor Networks (MoGL) and Chip Resistor Arrays (CRA), which have led to further downsizing of SMD resistors.
Today, SMD Resistor technology is the most widely used resistor technology; it's getting fast dominant technology. Through-hole resistors are fast becoming history as they are now reserved exclusively for niche applications such as car audio, stage lighting and "classic" instruments.
The use of resistors
Resistors are used in the circuit boards of radios, televisions, telephones, calculators, tools, and batteries.
There are many different types of resistors, each with their own set of applications. Some examples of using resistors:
- Device protection: Can be used to protect devices from damage by limiting the current flowing through them.
- Voltage regulation: Can be used to regulate the voltage in a circuit.
- Temperature control: Can be used to control the temperature of the device by dissipating heat.
- Signal attenuation: Can be used to attenuate or reduce signal strength.
Resistors are also used in many common household items. Some examples of home devices:
- Light bulbs: A resistor is used in a light bulb to regulate the current and create a constant brightness.
- Ovens: A resistor is used in the oven to limit the amount of current through the heating element. This helps prevent the element from overheating and damaging the oven.
- Toasters: A resistor is used in the toaster to limit the amount of current passing through the heating element. This helps prevent the element from overheating and damaging the toaster.
- Coffeemakers: A resistor is used in the coffee maker to limit the amount of current through the heating element. This helps prevent the element from overheating and damaging the coffee maker.
Resistors are an important component of digital electronics and are used in a variety of applications. They are available in a wide range of tolerance levels, wattages and resistance values.
How to use resistors in a circuit
There are two ways to use them in an electrical circuit.
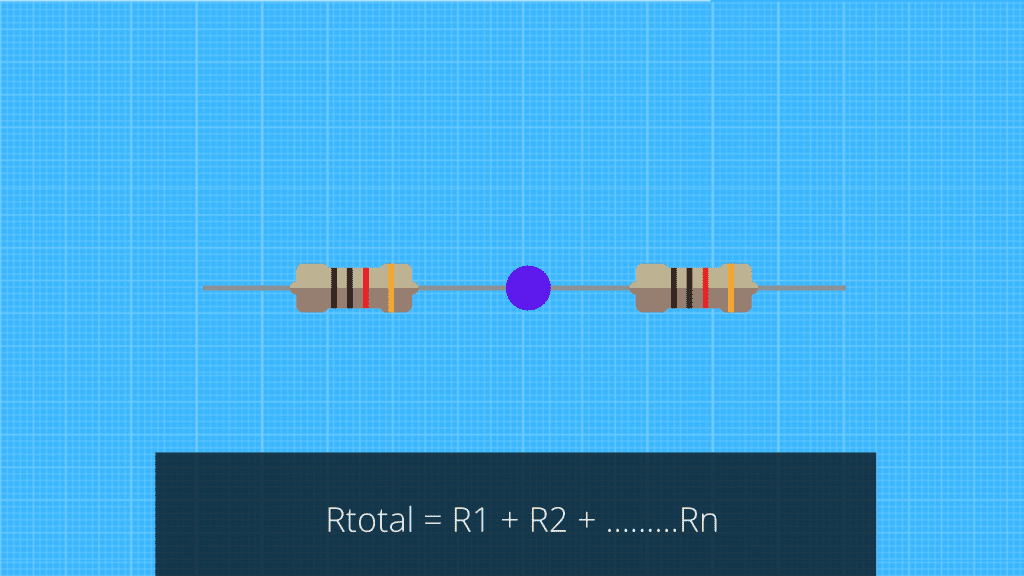
- Resistors in series are resistors in which circuit current must flow through each resistor. They are connected in series, with one resistor next to the other. When two or more resistors are connected in series, the total resistance of the circuit increases according to the rule:
Robsch = R1 + R2 + ………Rн
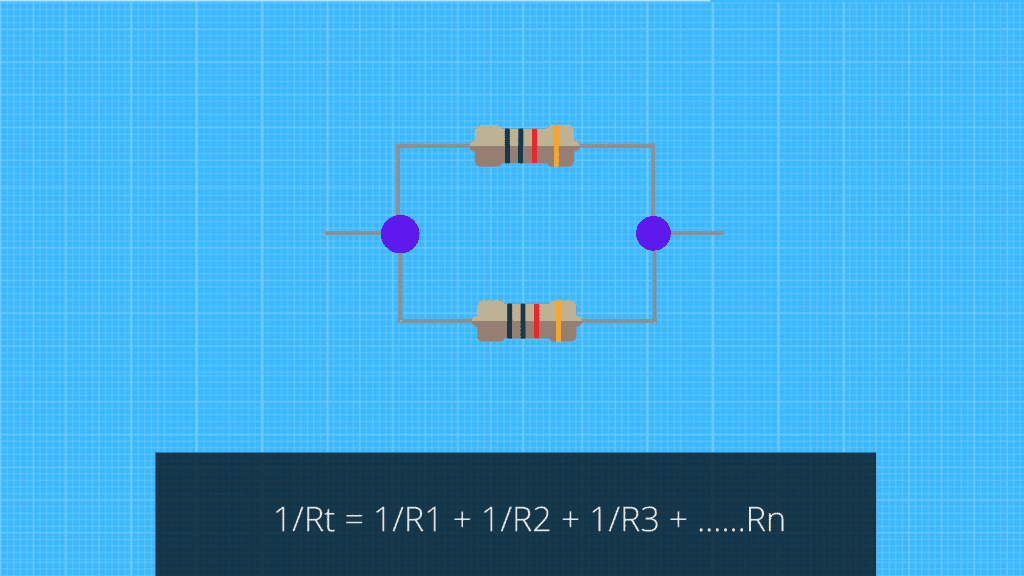
- Resistors in parallel resistors that are connected to different branches of the electrical circuit. They are also known as parallel connected resistors. When two or more resistors are connected in parallel, they share the total current flowing through the circuit without changing its voltage.
To find the equivalent resistance of parallel resistors, use this formula:
1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + ……..1/rn
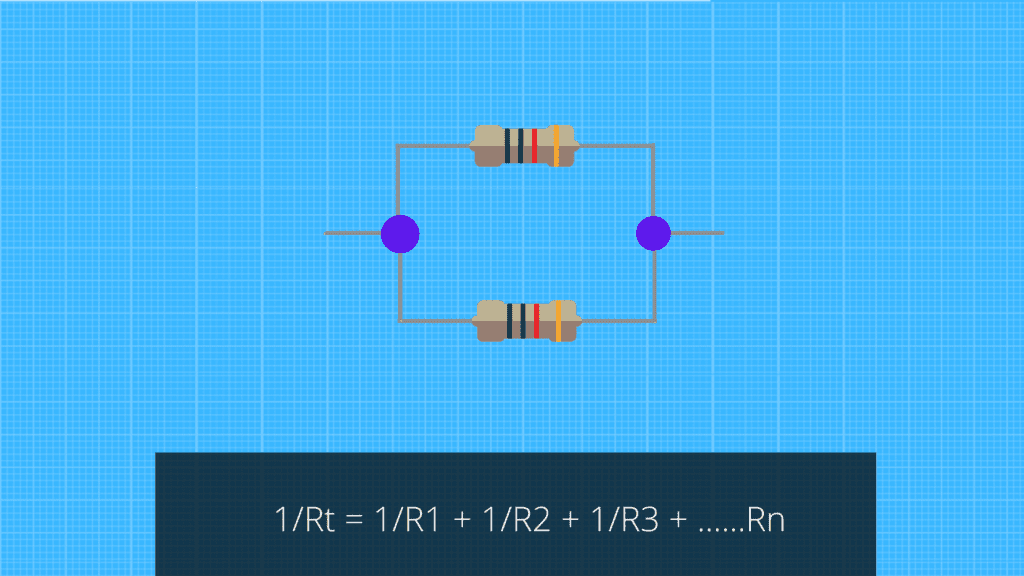
The voltage across each resistor must be the same. For example, if four 100 ohm resistors are connected in parallel, then all four will have an equivalent resistance of 25 ohms.
The current passing through the circuit will remain the same as if a single resistor were used. The voltage across each 100 ohm resistor is halved, so instead of 400 volts, each resistor now has only 25 volts.
Ohm's law
Ohm's law is simplest all the laws of electrical circuits. It states that "the current that passes through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage difference between the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance between them."
V = I x R or V/I = R
Where,
V = voltage (volts)
I = current (amps)
R = resistance (ohm)
There are 3 versions of Ohm's law with several applications. The first option can be used to calculate the voltage drop across a known resistance.
The second option can be used to calculate the resistance of a known voltage drop.
And in the third option, you can calculate the current.
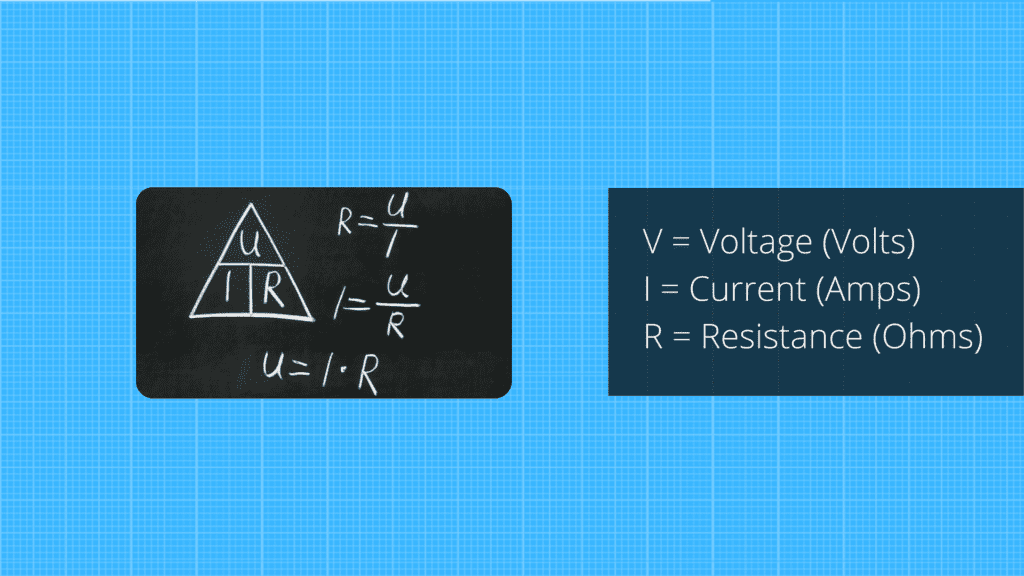
Video tutorial about what a resistor is
More about resistors.
Conclusion
Thanks for reading! I hope you learned what a resistor is and how it controls the flow of current. If you find it difficult to learn electronics, don't worry. We have many other blog posts and videos to teach you the basics of electronics.

One comment
Yat Dara
Good