
What is a transformer? All you need to know
Content
You know what is a transformer? We got you!
A transformer is an electronic device translations electricity between two or more circuits. Transformers are used for to enlarge or reduction AC (alternating current) signal voltage.
But that is not all. Let's take a closer look at these amazing devices!

History of the transformer
The transformer was invented by an American engineer of Hungarian origin named Otto Blatti in 1884 year.
It is believed that he was inspired to create the device after seeing a failed experiment involving passing an electric current through a metal sheet.

The principle of operation of the transformer
The principle of operation of the transformer is based on the concept of induction. When power is applied to one coil, it creates an electromotive force in the other coil, which causes it to become magnetically polarized.
The end result is that currents are induced in one circuit which creates a voltage which then reverses its polarity.
What is the use of a transformer?
Transformers are commonly used for reduce voltage in the electrical circuit. This makes it safer for low voltage equipment that is in close proximity. sensitive electronic devices, and also prevents damage to household electrical wiring.
Transformers can also be used for distribution power that is overloaded or lacks stability by disconnecting the load from the supply line during periods of peak demand.
The transformer can be placed in different circuits depending on their needs which ensures that there are no overloads, even if one circuit has problems with voltage requirements.
This also allows you regulate how much power you need at any given time so that the electrical system doesn't work too hard and wear out prematurely, because there is always some load placed on all transformers.
Transformer parts
The transformer consists of a primary winding, a secondary winding and a magnetic circuit. When power is applied to the primary circuit, the magnetic flux from that phase acts on the secondary phase, diverting some of these currents back into it.
This creates a voltage that is induced in the second coil, which then reverses its polarity. This is due to the fact that the magnetic flux is cut off from one coil and applied to the other. The end result is an induced current in the secondary circuit as well as alternating voltage levels.
The primary and secondary coils can be connected either in series or in parallel with each other, which affects power transfer differently depending on the needs of that particular circuit.
This design allows us to use one circuit for multiple purposes. If there is no need for energy levels at a certain time, they can be transferred to another circuit that may have a greater need for them.
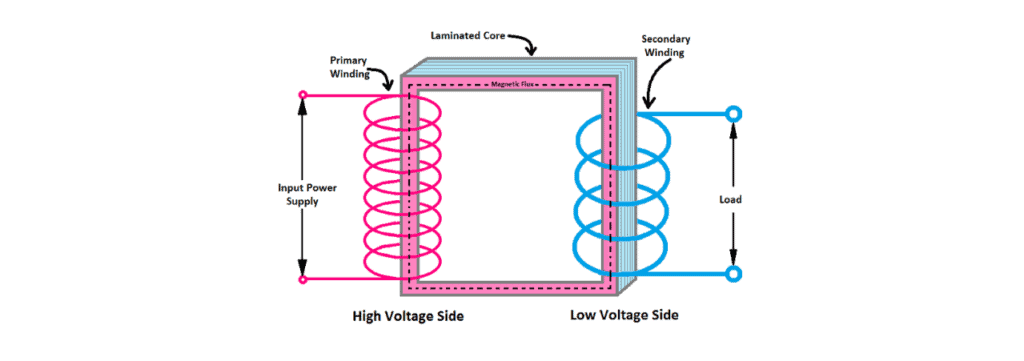
How does a transformer work?
The principle of a transformer is that electricity passes through one coil of wire, which creates a magnetic field, which then induces current in the others. This means that the primary winding supplies power to the secondary coil to cause it to produce voltage.
The process begins when an alternating current (AC) is present in the primary coil, which creates magnetism with polarity reversal back and forth between north and south. The magnetic field then moves outward towards the secondary coil and eventually enters the first coil of wire.
The magnetic field moves along the first wire and changes polarity or direction, which then induces an electric current. This process is repeated as many times as there are coils on the transformer. The voltage strength is affected by the number of turns in both the primary and secondary circuits.
The magnetic field continues to move through the secondary coil of wire until it reaches the end and then returns to the first coil of wire. This makes it so that most of the electricity goes in one direction rather than two different directions, which creates alternating current (AC).
Because the energy is stored in the transformer's magnetic field, there is no need for a second power supply.
For the transfer of power from the primary coil to the secondary to work, they must be connected together in a closed circuit. This means that there is a continuous path, so electricity can pass through both of them.
The efficiency of a transformer depends on the number of turns on each side, as well as what metal they are made of.
The iron core increases the strength of the magnetic field, so it's easier for the magnetic field to pass through each wire instead of pushing against it and getting stuck.
Also, transformers can be made to increase voltage while decreasing current. For example, an ammeter is used to measure the number of amperes flowing through a wire.
A voltmeter is used to measure how much voltage is present in an electrical circuit. For this reason, they must be made together in order to work correctly.
Like any other electronic device, transformers can sometimes fail or short out due to overload. When this happens, a spark may form and burn the device.
It is important to make sure that electricity does not pass through the transformer if you are doing any kind of maintenance. This means that the power supply must be turned off, for example by a circuit breaker, to ensure the safety of everyone.
Types of transformers
- step up and step down transformer
- Power transformer
- Distribution transformer
- Distribution transformer use
- Instrument transformer
- Current transformer
- Potential transformer
- Single phase transformer
- Three phase transformer
step up and step down transformer
A step-up transformer is designed to produce an output voltage that is higher than the electrical input voltage. They are used when you need a large amount of effective power for a short time, but not all the time.
One example of this would be people traveling on an airplane or working with electronic devices that use a lot of current. These transformers are also used to power homes that have wind turbines or solar panels.
Step-down transformers are designed to reduce the voltage at an electrical input so that it can provide power at a lower output voltage.
This type of transformer is often used in households or computers where energy or simple machinery such as lamps or lanterns is used all the time.
Power transformer
A power transformer transmits power, usually in large quantities. They are mainly used to transmit electricity over long distances through the electrical grid. A power transformer consumes low voltage electricity and converts it into high voltage electricity so that it can travel long distances.
The transformer then switches back to low voltage near the person or business that needs power.
Distribution transformer
The distribution transformer is designed to create a safe electric current distribution system. They are mainly used for homes, offices, factories and other facilities where energy needs are at different levels, requiring a uniform power flow.
They reduce power surges by regulating the flow of electricity to homes and buildings.
A distribution transformer is not really a transformer in the sense that it delivers a higher voltage than the input, however it provides a safer and more efficient distribution of electricity.
This is made possible by its primary function of converting energy from the electrical grid to a lower voltage so that it can be used safely in homes and businesses.
Instrument transformer
An instrument transformer is considered a special type of transformer device. It has the same functions as a distribution transformer, but is designed for an even smaller load.
They are smaller and less expensive than other types of transformers, making them ideal for use with small appliances such as handheld power tools or microwave ovens.
Current transformer
A current transformer is a device that allows you to measure high voltage. It is called a current transformer because it injects AC current into the device and measures the amount of DC output as a result.
Current transformers measure currents that are 10-100 times lower than voltage power, making them ideal tools for measuring certain electrical equipment or devices.
Potential transformer
A voltage transformer is a device that converts electrical voltage to a more convenient level for measurement. The device injects high voltage electricity and as a result measures the amount of lower voltage electricity.
Like current transformers, voltage transformers allow measurements to be made at voltage levels 10 to 100 times lower than those used by distribution transformers.
Single phase transformer
A single-phase transformer is a type of distribution transformer that distributes 120 volts of power. They are found in residential areas, commercial buildings and giant power plants.
Single-phase transformers operate on three-phase circuits where the input voltage is distributed over two or more conductors 120 degrees apart to reach the customer's premises. The input voltage that goes into a kite is typically between 120 and 240 volts in North America.
Three phase transformer
A three-phase transformer is a type of transmission or distribution transformer that distributes 240 volts of power. In North America, the input voltage ranges from 208 to 230 volts.
Transformers are used to serve large areas where many consumers need electricity. An area served by a three-phase transformer will have three sets of wires radiating from it that are 120 degrees apart, and each set supplies a different voltage.
A three-phase transformer has six secondary windings. They are used in various combinations to obtain the desired voltage for each client's specific area.
The six secondary windings are divided into two types: high and low voltage. An example of this would be if there were three consumers in a zone fed by a three-phase distribution transformer.
Conclusion
We believe that now you understand what is a transformer and why we can't live without them.

