TSI engine - advantages and disadvantages
Content
You often see cars with the TSI badge on the road and wonder what this means? Then this article is for you, we will consider the basics of the structure. TSI engine, working principle of internal combustion engine, Advantages and disadvantages.
Explanation of these abbreviations:
Oddly enough, TSI originally stood for Twincharged Stratified Injection. The following transcript looked a little differently Turbo Stratified Injection, i.e. the link to the number of compressors was removed from the name.

What is TSI engine
TSI is a modern development that appeared with the tightening of environmental standards for vehicles. A feature of such an engine is low fuel consumption, small liters of internal combustion engine and high performance. This combination is achieved thanks to the presence of dual turbocharging and direct fuel injection into the engine cylinders.
Twin turbocharging is provided by the combined operation of a mechanical compressor and a classic turbine. Such motors are installed in some models of Skoda, Seat, Audi, Volkswagen and other brands.
History of TSI motors
The development of a twin-turbocharged direct injection engine dates back to the first half of the 2000s. A fully working version entered the series in 2005. This line of motors received a significant update only in 2013, which indicates the success of the development.
If we talk about the modern TSI engine, then initially this abbreviation was used to designate a twin-turbocharged engine with direct injection (Twincharged Stratified Injection). Over time, this name was given to power units with a different device. So today, TSI also means a turbocharged unit (one turbine) with a layer-by-layer gasoline injection (Turbo Stratified Injection).
Features of the device and operation of TSI
As already noted, there are several modifications of TSI motors, therefore, we will consider the peculiarity of the device and the principle of operation using the example of one of the popular internal combustion engines. At 1.4 liters, such a unit is capable of developing up to 125 kW of power (almost 170 horsepower) and a torque of up to 249 Nm (available in the range of 1750-5000 rpm). With such excellent indicators per hundred, depending on the workload of the car, the engine consumes about 7.2 liters of gasoline.
This type of engine is the next generation of FSI engines (they also use direct injection technology). Gasoline is pumped by a high-pressure fuel pump (fuel is supplied under a pressure of 150 atmospheres) through injectors, the atomizer of which is located directly in each cylinder.
Depending on the desired operating mode of the unit, a fuel-air mixture of various enrichment degrees is prepared. This process is monitored by an electronic control unit. When the engine is idling up to the average rpm value. stratified injection of gasoline is provided.
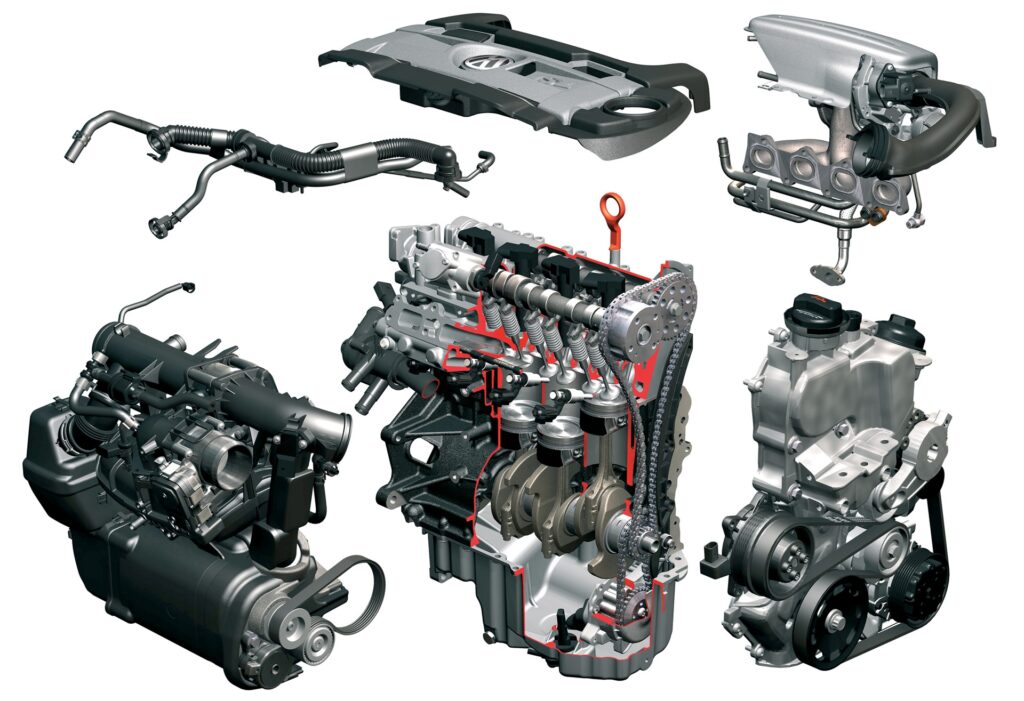
Fuel is pumped into the cylinders at the end of the compression stroke, which increases the compression ratio, although the powertrain uses two air blowers. Since such a design of the motor has a large amount of excess air, it acts as a heat insulator.
When the engine is running smoothly, gasoline is injected into the cylinders when the intake stroke is performed. As a result, the air / fuel mixture burns better due to a more homogeneous mixture formation.
When the driver presses the gas pedal, the throttle valve opens to the maximum, which leads to a lean mixture. To ensure that the amount of air does not exceed the maximum volume for gasoline combustion, in this mode, up to 25 percent of the exhaust gases are supplied to the intake manifold. Gasoline is also injected at the intake stroke.
Thanks to the presence of two different turbochargers, the TSI engines provide excellent traction at different speeds. The maximum torque at low speeds is provided by a mechanical supercharger (thrust is present in the range from 200 to 2500 rpm). When the crankshaft spins up to 2500 rpm, the exhaust gases begin to rotate the turbine impeller, which increases the air pressure in the intake manifold to 2.5 atmospheres. This design makes it possible to practically eliminate turbocharges during acceleration.
The popularity of TSI engines of 1.2, 1.4, 1.8
TSI engines have gained their popularity for a number of undeniable advantages. Firstly, with a small volume, consumption decreased, while these cars did not lose power, since these motors are equipped with a mechanical compressor and a turbocharger (turbine). On the TSI engine, direct injection technology was used, which ensured the best combustion and increased compression, even at the moment when the mixture became “bottoms” (revs up to ~ 3 thousand) the compressor works, and at the top the compressor is no longer so efficient and therefore the turbine continues to support the torque. This layout technology avoids the so-called turbo lag effect.
Secondly, the motor has become smaller, therefore its weight has decreased, and after it the weight of the car has also decreased. Also, these engines have a lower percentage of CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. Engines with smaller displacement have less frictional losses, hence higher efficiency.
Summing up, we can say that the TSI engine is a reduced consumption with the achievement of maximum power.
The general structure has been described, now let's move on to specific modifications.
1.2 TSI engine

1.2 liter TSI engine
Despite the volume, the engine has enough thrust, for comparison, if we consider the Golf series, then the 1.2 with a turbocharger bypasses 1.6 atmospheres. In winter, it warms up longer, of course, but when you start driving, it warms up very quickly to operating temperature. With regard to reliability and resource, there are different situations. For some, the motor runs 61 km. and all flawlessly, but someone has 000 km. the valves are already burning out, but rather an exception than a rule, since the turbines are installed at low pressure and do not have a large effect on the engine resource.
Engine 1.4 TSI (1.8)

1.4 liter TSI engine
In general, these engines differ little in advantages and disadvantages from the 1.2 engine. The only thing to add is that all these engines use a timing chain, which can slightly increase the cost of operation and repair. One of the disadvantages of motors with a timing chain is that it is not advisable to leave it in gear while on a slope, as this can cause the chain to jump off.
2.0 TSI engine
On two liter engines, there is such a problem as chain stretching (typical for all TSIs, but more often for this modification). The chain is usually changed at 60-100 thousand mileage, but it needs to be monitored, critical stretching can happen earlier.
We bring to your attention a video about TSI engines
Advantages and disadvantages
Of course, this design is not just a tribute to environmental standards. The TSI engine has many advantages. These motors are different:
- High performance despite small volumes;
- Impressive traction (for gasoline engines) already at low and medium speeds;
- Excellent economy;
- The possibility of forcing and tuning;
- A high indicator of environmental friendliness.
Despite these obvious advantages, such motors (especially the EA111 and EA888 Gen2 models) have a number of significant disadvantages. These include:
- Increased oil consumption (more precisely, it develops its resource faster due to the operation of the turbine at extremely high temperatures).
- Due to the high torque, the timing chain stretches faster, and in some cases it simply breaks.
- The fuel should be of the best quality (the injectors work in a layered mode - a scanty part of gasoline is divided into two or three parts, the same can be said about the quality of the oil).
- Due to the operation of the mechanical supercharger, the motor will warm up more slowly.
Major faults
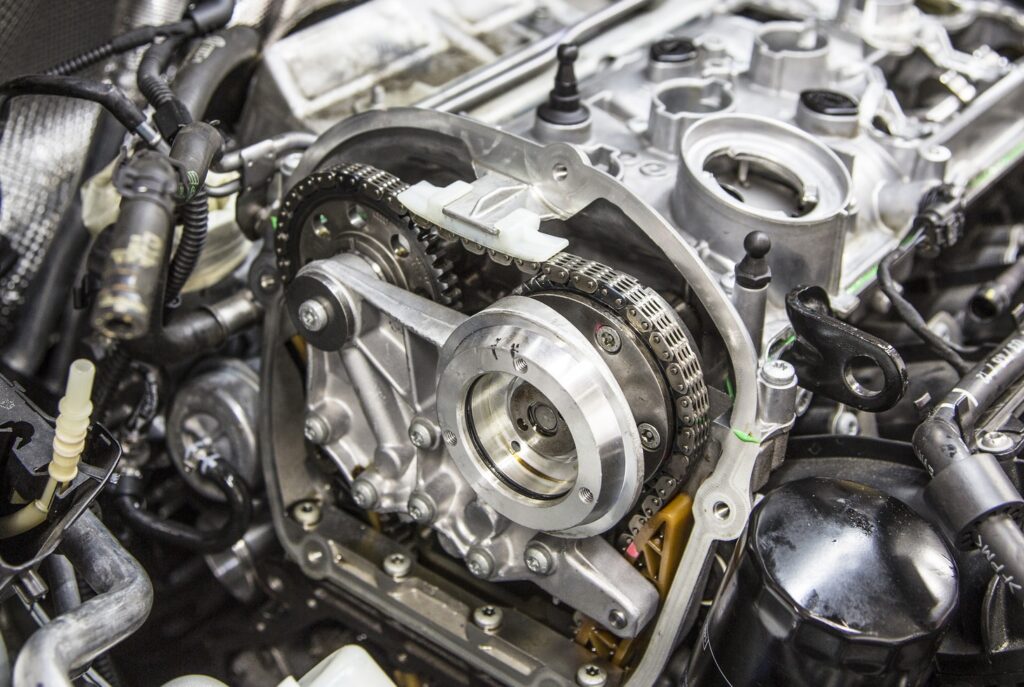
The real headache for TSI engines is a stretched or torn timing chain. as already indicated, this problem is a consequence of high torque at low crankshaft rpm. In such internal combustion engines, it is recommended to check the chain tension every 50-70 thousand kilometers.
In addition to the chain itself, both the damper and the chain tensioner suffer from high torque and heavy load. Even if a circuit break is prevented in time, the procedure for replacing it is quite expensive. But in the event of a circuit break, the motor will have to be repaired and tuned, which entails even more material costs.
Due to the heating of the turbine, hot air is already entering the intake manifold. Also, due to the operation of the exhaust gas recirculation system, particles of unburned fuel or oil mist enter the intake manifold. This leads to carbonization of the throttle valve, oil scraper rings and intake valves.
In order for the engine to always be in good condition, the car owner needs to follow the oil change regulations and buy high quality lubricant. Moreover, oil consumption in turbocharged engines is a natural effect created by a red-hot turbine, special piston design and high torque.


For proper engine operation, it is recommended to use gasoline with an octane rating of at least 95 as fuel (the knock sensor will not work). Another feature of the twin turbo engine is a slow warm-up, although this is also its natural state, and not a breakdown. The reason is that during operation, the internal combustion engine heats up a lot, which requires a complex cooling system. And it prevents the engine from reaching operating temperature faster.
Some of the listed problems have been eliminated in the third generation of TSI EA211, EA888 GEN3 motors. First of all, this affected the procedure for replacing the timing chain. Despite the previous resource (from 50 to 70 thousand kilometers), replacing the chain has become a little easier and cheaper. More precisely, the chain in such modifications is replaced by a belt.
Recommendations for use
Most of the TSI engine maintenance recommendations are the same as for classic powertrains:
- Use high quality lubricants and consumables;
- Undergo maintenance on time;
- Monitor the condition of the timing chain (or belt, as in the case of the third generation of twin turbo engines) and its tensioner;
- Fill in high-quality gasoline;
- Use sports riding less often;
- Do not attempt to quickly pick up speed on short sections of the road, increasing the torque to the maximum at low revs.
If a long warm-up of the engine is annoying, then to speed up this process, you can buy a pre-heater. This device is especially effective for those who often use the car for short trips, and winters in the region are long and cold.
Buy a car with TSI or not?
If a motorist is looking for a car for dynamic driving with high engine output and low consumption, then a car with a TSI engine is what you need. Such a car has excellent dynamics, will give a lot of positive emotions from high-speed driving. In addition to the aforementioned advantages, such a power unit does not consume gasoline at the speed of light, as is inherent in many powerful engines with a classic design.


Whether or not to buy a car with TSI depends on the car owner's willingness to pay for decent dynamics with minimal gas consumption. First of all, he needs to be ready for expensive maintenance (which is inaccessible for most areas due to the lack of qualified specialists).
To avoid serious problems, you need to follow three simple rules:
- Undergo scheduled maintenance on time;
- Change the oil regularly, using the option recommended by the manufacturer;
- Refuel the car at approved gas stations, and do not use low-octane gasoline.
Conclusion
So, if we talk about the first generation TSI motors, then they had many flaws, despite the amazing indicators of economy and performance. In the second generation, some shortcomings were eliminated, and with the release of the third generation of power units, it became cheaper to service them. As engineers create new systems, there is a chance that the problem of high oil consumption and key unit malfunctions will be eliminated.
Questions and answers:
What does TSI sign mean? TSI - Turbo Statified Injection. This is a turbocharged engine in which fuel is sprayed directly into the cylinders. This unit is a modification of the related FSI (there is no turbocharging in it).
В is the difference between TSI and TFSI? Previously, such abbreviations were used to designate engines with direct injection, only the TFSI was a forced modification of the first. Today, engines with a twin turbocharger can be denoted.
What's wrong with the TSI motor? The weak link of such a motor is the timing mechanism drive. The manufacturer solved this problem by installing a toothed belt instead of a chain, but such a motor still consumes a lot of oil.
Which engine is better than TSI or TFSI? It depends on the requests of the motorist. If he needs a productive motor, but no frills, then TSI is enough, and if there is a need for a forced unit, TFSI is required.

