
ESP - like on rails
 What we commonly refer to as ESP or Stability Program is actually an extensive ABS system. The more components it has, the more tasks can be assigned to it.
What we commonly refer to as ESP or Stability Program is actually an extensive ABS system. The more components it has, the more tasks can be assigned to it.
What we commonly refer to as ESP or Stability Program is actually an extensive ABS system. The more components it has, the more tasks can be assigned to it.
ESP is a registered trademark of Daimler AG. In 1995, this manufacturer was the first to introduce a stabilization system into mass production, installing it on a Mercedes-Benz S class car. The followers were forced to adopt their nomenclature, so we have VSA in Honda, VSC in Toyota and Lexus. , VDC for Alfa Romeo and Subaru, PSM for Porsche, MSD for Maserati, CST for Ferrari, DSC for BMW, DSTC for Volvo, etc.
Common are not only the general principles of work, but also the addressees of the facilitating system.  keeping the car on the road in conditions of skidding. First of all, these are drivers with little experience and low driving skills who do not know how to correctly and quickly pull the car out of a skid. However, even experienced riders should not shy away from ESP. Belief in one's own strength is often deceptive, especially when the situation becomes an emergency.
keeping the car on the road in conditions of skidding. First of all, these are drivers with little experience and low driving skills who do not know how to correctly and quickly pull the car out of a skid. However, even experienced riders should not shy away from ESP. Belief in one's own strength is often deceptive, especially when the situation becomes an emergency.
The operation of ESP is based on the braking of the corresponding wheel or wheels, which allows you to create a correctly directed torque, opposite to the moment when the car is trying to turn, caused by driver error. A car that exceeds the speed limit on the curve, determined by the car's design and traction, will begin to rotate around the vertical axis. However, rotation can take different directions depending on whether there is understeer or oversteer.
In understeer, when a skidding vehicle tries to pull out of a corner, the left, inner rear wheel must be braked first. With oversteer, when the car is slipping, tighten the corner (throws back) of the right outer front wheel. Subsequent braking depends on the further movement of the car and the reaction of the driver.
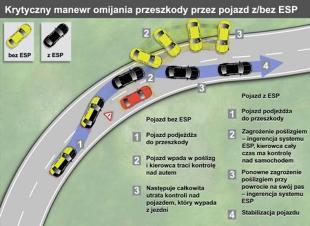
Since the coefficient of friction of the surface and the tire cannot be influenced, the braking process is used to increase grip. The braked wheel becomes heavier and puts more pressure on the road, which improves its grip on the road. Applying that force in the right place creates a torque in the right direction, which helps the car to regain the previously chosen direction of travel.
Of course, the maximum speed on the arc can be exceeded so much that the system cannot cope with an emergency. However, thanks to the actions of ESP, the car will always be closer to the correct path, and this can significantly minimize the consequences of a possible accident. For example, the probability that a collision with an obstacle after exiting a turn will be greater will be the front of the car, and therefore in the most favorable way for drivers (full deployment of the pressure zone, airbags, seat belts).
The condition for the correct functioning of the ESP is not only the perfect performance of the sensors and control system, but also the efficiency of the shock absorbers. The system can fail if there is a loss of traction due to faulty shock absorbers. Especially on uneven surfaces, which often create problems for the ABS system.
ESP yesterday, today, tomorrow...
It started with the Mercedes S-Class in 1995. Then came the serially installed stabilization system in its original form. However, after a few years, the system stopped braking individual wheels. Designers, improving solutions, have introduced a number of new functions, thanks to which modern ESPs have much greater capabilities.
For example, it can run on two or three wheels at the same time. When understeer is detected, both front wheels are braked, and if the effect is unsatisfactory, both begin to brake on the inside of the turn. Even more advanced ESP systems work in tandem with the steering to point it in the right direction.
This automatic "skid control" extends the range of track stabilization, improves handling, and also reduces braking distances in conditions of varying grip. This is not the end. It is on the basis of ESP that a number of functions have been developed to help the driver in various ways.
These include the Emergency Brake Assist System (BAS, also known as Brake Assist), Engine Brake Control (MSR, works the opposite of ASR, i.e. accelerates when needed), keeping the car uphill before the driver starts uphill (Hill Holder), hill descent brake (HDC), dynamic brake force distribution to maximize the use of heavy-duty wheel traction (CDC), rollover protection (ROM , RSE), smooth braking applied in vehicles with distance control to the vehicle in front (EDC) as well as trailer track stabilization (TSC) to dampen vehicle sway caused by trailer sway .
But this is not the last word of the ESP experts. In the near future, it can be expected that more and more stabilization systems will work with both front and rear wheel steering systems. Such solutions have already been tried and tested and are based on the classic active steering system on the front axle and hydraulic or electro-hydraulic wishbones on the rear axle. They were used, for example, in the latest Renault Laguna.
Popular cars on the Polish market with ESP
Model | Existence of ESP |
Skoda Fabia | Not available in Start and Junior versions Option with 1.6 engine - as standard In other versions – additional PLN 2500 |
Toyota Yaris | Available for Luna A / C and Sol versions - surcharge PLN 2900. |
Skoda Octavia | Not available in Mint version Cross 4 × 4 standard In other versions – additional PLN 2700 |
Ford Focus | Standard for all versions |
Toyota Auris | Standard on Prestige and X versions Other versions not available |
Fiat Panda | Available in the Dynamic version - for an additional fee of PLN 2600. In the 100 hp version. – as standard |
Opel Astra | In the Essentia, Enjoy, Cosmo versions - PLN 3250 surcharge. Standard on Sport and OPC versions |
Fiat Grande Punto | In Sport versions – standard In other versions – additional PLN 2600 |
Opel Corsa | Standard in OPC and GSi versions In other versions – additional PLN 2000 |