How to diagnose a fuel pump. Diagnostics of the fuel pump in the car
The fuel pump, as the name implies, is designed to pump fuel in the engine power supply system. In order for the injectors to be able to inject a sufficient amount of gasoline into the cylinders of the internal combustion engine, a certain pressure must be maintained in the fuel system. This is exactly what the fuel pump does. If the fuel pump starts to act up, this immediately affects the operation of the internal combustion engine. In many cases, the diagnosis and troubleshooting of a fuel pump is quite affordable for motorists to do on their own.
In the old days, gasoline pumps were often mechanical, but such devices have long been a history, although they can still be found on old cars with carburetor ICEs. All modern cars are equipped with an electric pump. It is activated when the corresponding relay is activated. And the relay is activated when the ignition is turned on. It is better to wait a couple of seconds with the starter cranking, during which time the pump will create sufficient pressure in the fuel system for the normal start of the internal combustion engine. When the engine is turned off, the relay that starts the fuel pump is de-energized, and the pumping of fuel into the system stops.
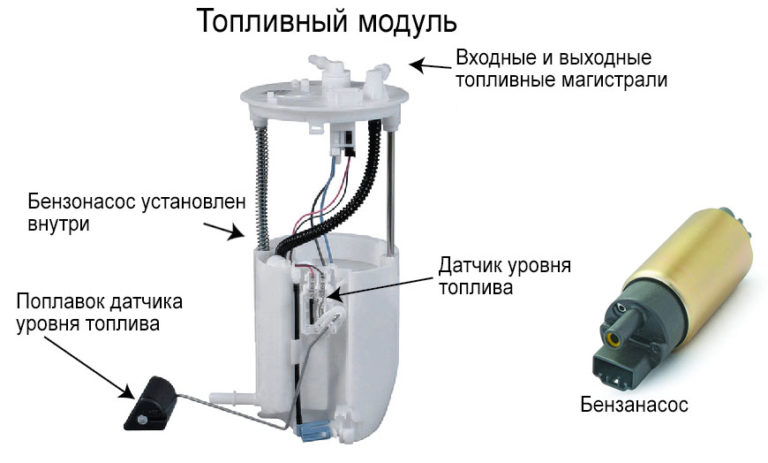
As a rule, the gasoline pump is located inside the fuel tank (submersible type device). This arrangement solves the problem of cooling and lubricating the pump, which occur due to washing with fuel. In the same place, in the gas tank, there is usually a fuel level sensor equipped with a float and a bypass valve with a calibrated spring that regulates the pressure in the system. In addition, at the pump inlet there is a coarse filtration mesh that does not allow relatively large debris to pass through. Together, all these devices make up a single fuel module.
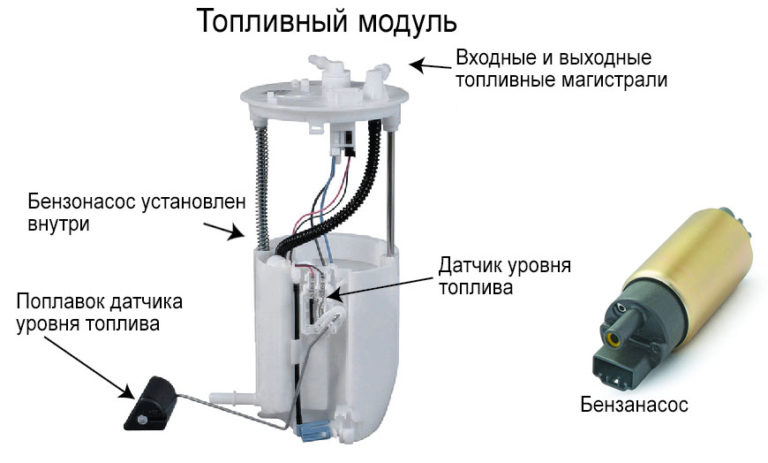
The electrical part of the pump is a direct current electric internal combustion engine, powered by an on-board network with a voltage of 12 V.
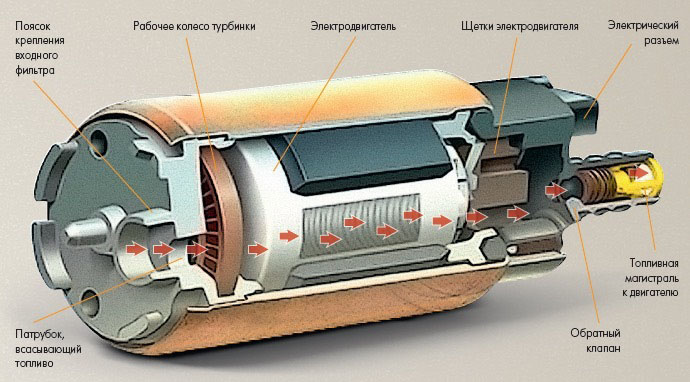
The most widely used gasoline pumps are centrifugal (turbine) type. In them, an impeller (turbine) is mounted on the axis of the electric internal combustion engine, the blades of which inject fuel into the system.
Less common are pumps with a mechanical part of the gear and roller type. Usually these are remote-type devices that are mounted in a break in the fuel line.
In the first case, two gears are located on the axis of the electric internal combustion engine, one inside the other. The inner one rotates on an eccentric rotor, as a result of which areas with rarefaction and increased pressure alternately form in the working chamber. Due to the pressure difference, the fuel is pumped.
In the second case, instead of gears, the pressure difference in the supercharger creates a rotor with rollers located around the perimeter.
Since gear and rotary roller pumps are installed outside the fuel tank, overheating becomes their main problem. It is for this reason that such devices are almost never used in vehicles.
The fuel pump is a fairly reliable device. Under normal operating conditions, he lives an average of about 200 thousand kilometers. But certain factors can significantly affect its lifespan.
The main enemy of the fuel pump is dirt in the system. Because of it, the pump has to work in a more intense mode. Excessive current in the winding of the electric motor contributes to its overheating and increases the risk of a wire break. Sand, metal filings and other deposits on the blades destroy the impeller and can cause it to jam.
Foreign particles in most cases enter the fuel system along with gasoline, which is often not clean at filling stations. To clean the fuel in the car, there are special filters - the already mentioned coarse filtration mesh and a fine fuel filter.
The fuel filter is a consumable item that must be replaced periodically. If it is not replaced in time, the fuel pump will tear, with difficulty pumping fuel through a clogged filter element.
The coarse mesh also becomes clogged, but unlike the filter, it can be washed and reused.
It happens that dirt accumulates at the bottom of the fuel tank, which can lead to quick clogging of the filters. In this case, the tank must be flushed.
Shortens the life of the fuel pump and the habit of some drivers to drive on the remnants of fuel until the warning light comes on. Indeed, in this case, the pump is outside the gasoline and is deprived of cooling.
In addition, the fuel pump can malfunction due to electrical problems - damaged wiring, oxidized contacts in the connector, a blown fuse, a failed start relay.
Rare causes that cause the fuel pump to malfunction include incorrect installation and deformation of the tank, for example, as a result of an impact, due to which the fuel module and the pump located in it may become defective.
If the pump is faulty, this will primarily affect the pressure in the fuel supply system to the internal combustion engine. At low pressure, the optimal composition of the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chambers will not be ensured, which means that problems will arise in the operation of the internal combustion engine.
External manifestations may be different.
·
The sound of the internal combustion engine may be slightly different from the usual, especially during warm-up. This symptom is typical for the early stage of the fuel pump disease.
Noticeable loss of power. At first, it affects mainly at high speeds and while driving uphill. But as the condition of the pump worsens, twitches and periodic slowdowns can also occur in normal modes on flat sections of the road.
Tripping, floating turns are signs of a further aggravation of the situation.
Increased noise or a loud hum coming from the fuel tank indicates the need for urgent intervention. Either the pump itself is on its last legs, or it cannot handle the load due to contamination in the system. It is possible that a simple cleaning of the coarse filter screen will save the fuel pump from death. A fuel filter that performs fine cleaning can also create a problem if it is defective or has not been changed for a long time.
Launch problems. Things are really bad, even if the warmed-up internal combustion engine starts with difficulty. the need for a long cranking of the starter means that the pump cannot create enough pressure in the system to start the internal combustion engine.
ICE stalls when you press the gas pedal. As they say, "arrived" ...
The absence of the usual sound from the gas tank indicates that the fuel pump is not working. Before putting an end to the pump, you need to diagnose the starting relay, fuse, wire integrity and the quality of the contacts in the connector.
It must be borne in mind that some of these symptoms may indicate not only the fuel pump, but also a number of other parts - a mass air flow sensor, a throttle position sensor, a damper actuator, an idle speed controller, a clogged air filter, unadjusted valve clearances.
If there are doubts about the health of the pump, it is worth carrying out additional diagnostics, in particular, measuring the pressure in the system.
During any manipulations related to the fuel supply system, one should be aware of the risk of gasoline ignition, which can spill when disconnecting the fuel lines, replacing the fuel filter, connecting a pressure gauge, etc.
The pressure is measured using a fuel pressure gauge. In addition, you may need an adapter or tee to connect. It happens that they come with the device, otherwise you will have to purchase them separately. You can use an air (tire) pressure gauge, but such a device is designed for a much higher pressure, and at the beginning of the scale will give a significant error.
First of all, you need to relieve the pressure in the system. To do this, de-energize the fuel pump by removing the relay that starts it or the corresponding fuse. Where the relay and fuse are located can be found in the service documentation of the car. then you need to start the internal combustion engine with a de-energized pump. Since there will be no fuel pumping, the internal combustion engine will stall after a set of seconds, having exhausted the remaining gasoline in the ramp.
Next, you need to find a special fitting on the fuel rail and connect a pressure gauge. If there is no place on the ramp for connecting a pressure gauge, the device can be connected through a tee to the outlet fitting of the fuel module.
Reinstall the start relay (fuse) and start the engine.
For gasoline internal combustion engines, the starting pressure should be approximately 3 ... 3,7 bar (atmosphere), at idle - about 2,5 ... 2,8 bar, with a pinched drain pipe (return) - 6 ... 7 bar.
If the pressure gauge has a scale graduation in MegaPascals, the ratio of units of measurement is as follows: 1 MPa = 10 bar.
The indicated values are averaged and may differ depending on the parameters of a particular internal combustion engine.
A slow increase in pressure at start-up indicates a heavily contaminated fuel filter. Another reason could be that there is not enough fuel in the tank, in which case the pump may be sucking in air, which is known to compress easily.
The fluctuation of the pressure gauge needle at idle speed of the internal combustion engine indicates incorrect operation of the fuel pressure regulator. Or the coarse mesh is simply clogged. By the way, in some cases, the fuel module bulb may have an additional grid, which should also be diagnosed and washed if necessary.
Turn off the engine and follow the pressure gauge readings. The pressure should drop relatively quickly to approximately 0,7…1,2 bar and remain at this level for some time, then it will slowly decrease over 2…4 hours.
A rapid decrease in the instrument readings to zero after the engine stops may indicate a malfunction of the fuel pressure regulator.
To roughly estimate the performance of the fuel pump, no instruments are required. To do this, you need to disconnect the return line from the ramp, and instead connect the hose and direct it into a separate container with a measuring scale. In 1 minute, a working pump should normally pump about one and a half liters of fuel. This value may vary slightly depending on the pump model and fuel system parameters. Reduced performance indicates problems with the pump itself or contamination of the fuel line, injectors, filter, mesh, etc.
Turning the ignition key supplies 12 volts to the relay that starts the fuel pump. Within a few seconds, the rumble of a running pump is clearly audible from the fuel tank, creating the necessary pressure in the system. further, if the internal combustion engine is not started, it stops, and you can usually hear the click of the relay. If this does not happen, you need to find out the cause of the problem. And you should start by checking the power supply.
1. First of all, we find and check the integrity of the fuse through which the fuel pump is powered. can be diagnosed visually or with an ohmmeter. We replace the blown fuse with a similar one of the same rating (calculated for the same current). If everything worked, we are glad that we got off lightly. But it is likely that the new fuse will also blow. This will mean that there is a short circuit in its circuit. Further attempts to change the fuse are meaningless until the short circuit is eliminated.
Wires can short - both to the case and to each other. You can determine by calling with an ohmmeter.
An interturn short circuit can also be in the winding of an electric internal combustion engine - it is difficult to confidently diagnose it with a dial tone, since the resistance of the winding of a serviceable internal combustion engine is usually only 1 ... 2 Ohm.
Exceeding the allowable current can also be caused by mechanical jamming of the electric internal combustion engine. To diagnose this, you will have to remove the fuel module and dismantle the fuel pump.
2. If the pump does not start, the start relay may be faulty.
Lightly tap on it, for example, with the handle of a screwdriver. Perhaps the contacts are just stuck.
Try taking it out and putting it back in. This may work if the terminals are oxidized.
Ring the relay coil to make sure it is not open.
Finally, you can simply replace the relay with a spare one.
There is another situation - the pump starts, but does not turn off due to the fact that the relay contacts did not open. Sticking in most cases can be eliminated by tapping. If this fails, then the relay must be replaced.
3. If the fuse and relay are OK, but the pump does not start, diagnose if 12V is getting to the connector on the fuel module.
Connect the multimeter probes to the connector terminals in the DC voltage measurement mode at the limit of 20 ... 30 V. If there is no multimeter, you can connect a 12 Volt light bulb. Turn on the ignition and diagnose the readings of the device or the light bulb. If there is no voltage, diagnose the integrity of the wiring and the presence of a contact in the connector itself.
4. If power is applied to the fuel module connector, but our patient still does not show signs of life, we need to remove it into the light of day and scroll by hand to make sure there is no (or presence) of mechanical jamming.
Next, you should diagnose the winding with an ohmmeter. If it is broken, then you can finally declare the death of the fuel pump and order a new one from a trustworthy seller. Don't waste your time resuscitating. This is a hopeless matter.
If the winding rings, you can diagnose the device by applying voltage to it directly from the battery. It works - return it to its place and proceed to the next check point. No - buy and install a new fuel pump.
It is possible to start the fuel pump removed from the tank only for a short time, since normally it is cooled and lubricated with gasoline.
5. Since the fuel module has been dismantled, it's time to diagnose and flush the coarse filtration mesh. Use a brush and gasoline, but do not overdo it so as not to tear the mesh.
6. Diagnose the fuel pressure regulator.
The regulator may be suspicious if the pressure in the system quickly drops to zero after the engine is turned off. Normally, it should decrease slowly over several hours. Also, due to its breakdown, the pressure in the system can be significantly lower than normal when the pump is running, since part of the gasoline will constantly return to the tank through the open check valve.
In some cases, a stuck valve can be returned to the correct position. To do this, clamp the return hose and start the fuel pump (turn on the ignition). When the pressure in the system reaches a maximum, you need to abruptly release the hose.
If the situation cannot be corrected in this way, the fuel pressure regulator will have to be replaced.
7. Wash the injection nozzles. They can also become clogged and complicate the operation of the fuel pump, causing its increased noise. Clogging of the fuel lines and ramps is less common, but this cannot be completely ruled out.
8. If everything is checked and washed, the fuel filter is replaced, and the gas pump still makes a loud noise and pumps fuel poorly, there is only one thing left - to buy a new device, and send the old one to a well-deserved rest. In this case, it is not necessary to buy a complete fuel module, it is enough to purchase only the ICE itself.
Since the lion's share of foreign particles enters the fuel system during refueling, we can say that the purity of the fuel is the key to the health of the fuel pump.
Try to refuel with high-quality fuel at proven gas stations.
Do not use old metal canisters for storing gasoline, which may have corrosion of the inner walls.
Change / clean filter elements in time.
Avoid completely emptying the tank, it should always have at least 5 ... 10 liters of fuel. Ideally, it should always be at least a quarter full.
These simple measures will keep the fuel pump in good condition for a long time and avoid unpleasant situations associated with its failure.

