
How to test a transformer with a multimeter
Content
From large units on power lines to smaller units in devices like phone chargers, transformers come in all shapes and sizes.
However, they perform the same function, ensuring that your devices and appliances are supplied with exact amount of voltage they should work correctly.
However, like any other electronic device, transformers develop shortcomings.
Replacing them might be an option you don't want to use, so how do you diagnose a transformer and determine the appropriate solution it needs?
This article gives answers to this, because we give information about how the transformer works, and about the various methods for checking it for faults.
Without further ado, let's get started.
What is a transformer
A transformer is a device that converts an alternating current (AC) signal from high voltage to low voltage or vice versa.
The transformer that converts to a low potential difference is called a step down transformer and is the more common of the two that serve us daily.
Step-down transformers on power lines step down thousands of voltages to low voltage 240V for home use.
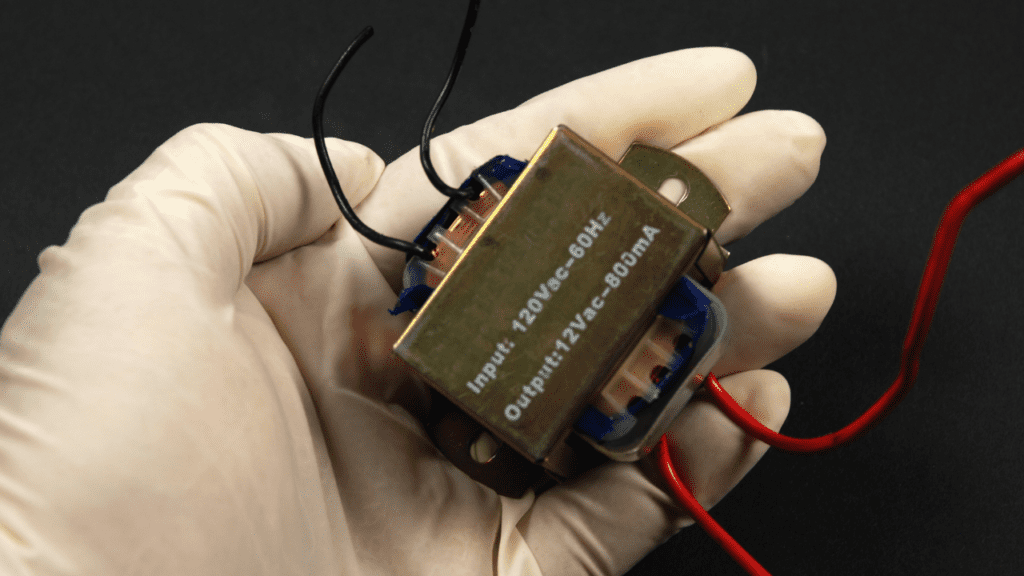
Our various devices such as laptop connectors, phone chargers and even doorbells use their own transformers.
They reduce the voltage to just 2V to keep the device working.
An alternative to these is called a step-up transformer and is commonly used in central power plants to increase power for distribution.
However, we are more interested in step-down transformers, since this is what we usually deal with. But how do they work?
How Step Down Transformers Work
Step-down transformers use two coils, also known as windings. These are the primary coil and the secondary coil.
The primary coil is the input coil receiving current from an AC voltage source such as a power line.
The secondary coil is the output coil that sends low potential signals to appliances in your home.
Each coil is wound on a core and when current passes through the primary coil, a magnetic field is created which induces current in the secondary coil.
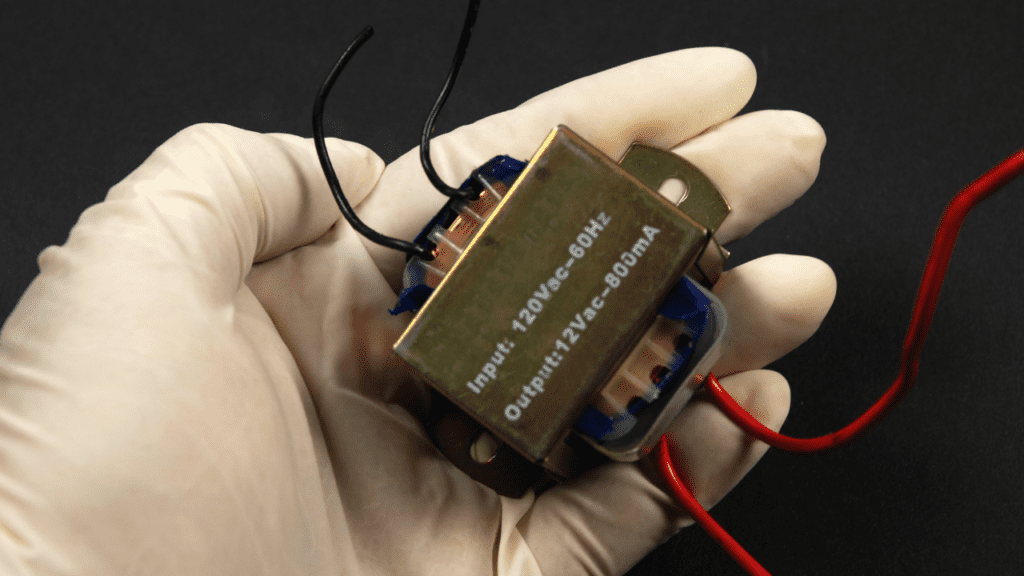
In step down transformers, the primary winding has more turns than the secondary winding. Without going into details, the number of windings is directly proportional to the voltage of the electromagnetic force (EMF) generated by the coil.
From ~ V
Let's call the input winding of the coil W1, the output winding of the coil W2, the input voltage E1 and the output voltage E2. Step-down transformers have more turns on the input coil than the output coil.
P1 > P2
This means that the voltage of the output (secondary) coil is lower than the voltage of the input coil.
E2 < E1
So the high AC voltage is converted to low. In addition, a higher current is passed through the secondary coil to balance the capacitance of both windings.
Transformers aren't everything, but it's the basic knowledge you'll need before testing your transformer.
If you suspect that your transformer is not working well, you just need a multimeter to diagnose it.
How to test a transformer with a multimeter
To test a transformer, you use a multimeter to test the AC voltage readings at the input source and output terminals while the transformer is connected. You also use a multimeter to test the continuity of a transformer when it is not connected to any power source. .
They will be explained next.
Input and output tests
Typically, this test is only carried out at the output terminals of the transformer.
However, to ensure accurate readings from the output terminals, you must be sure that the voltage applied to them is also accurate. That's why you are testing your input source.
For household appliances, the input signal sources are usually sockets in the walls. You want to check that they provide the exact amount of voltage.
To do this, follow these steps
- Set the multimeter to 200 VAC.
- Place the multimeter leads on the power supply leads. For wall outlets, you simply insert the wires into the outlet holes.
You expect to see a value between 120V and 240V, but it depends.
If the readings are inaccurate, your power supply may be causing problems. If the readings are correct, proceed to check the output terminals of the transformer. Do it,
- Connect the transformer to the power supply
- Reduce the voltage range on the multimeter
- Place the multimeter leads on the output terminals of your transformer.
- Check readings
By looking at the readings on the multimeter, you check whether the result is correct. Here you are looking at the recommended output characteristics of the transformer to draw a conclusion.
Transformer integrity check
A transformer integrity check is carried out in order to make sure that there is no open or short circuit in the coils. You run this test when the transformer is disconnected from the power supply. What are you doing?
- Set the multimeter scale to Ohm or Resistance. This is usually denoted by the symbol (Ω).
- Place the leads of a multimeter on each of the input terminals on your transformer.
Where the transformer has a short circuit, the multimeter will give very high or infinite readings. Infinite Reading is represented by "OL" which stands for "Open Loop".
If the input terminals look normal, you repeat this process for the output terminals.
In the event that any of these terminals gives a high or infinite value, the transformer must be replaced. Here is a video showing this procedure.
Conclusion
Transformer diagnostics is a procedure that needs to be handled with care, especially when checking the input and output terminals.
However, you should note that transformers usually have a long lifespan. A problem with them signals a malfunction somewhere else in the electrical circuit.
In this regard, it is recommended to monitor newly installed transformers for bad sounds, as well as to check that other parts of the circuit, such as fuses, are in good condition.
F.A.Q.
How to know if the transformer is faulty?
If the transformer is faulty, you may experience that the device does not work, the circuit breaker constantly turns off, or you hear the transformer buzzing. The meter will also help you make further checks on the coils and their voltage readings.
What are you going to do to test the continuity of the transformer?
To check the integrity of the transformer, disconnect it and place the meter probes on the input terminals. If the terminals output a high or infinite "OL" value, then there is no continuity. The same is true for the output terminals.
What happens when a transformer fails?
When the transformer fails, the device may not work, or you may hear humming or humming sounds coming from the transformer.
What is the resistance of the transformer?
The resistance of a transformer depends on the device it is intended to power. You must check the characteristics of the transformer to draw a conclusion.

