How does an electric car work?
Content
- Recharging
- Converter
- Battery
- Transmission of infection
- Regenerative braking
- Breaking
- A small lesson in mechanics on an electric car
- Charging: where it all starts
- The important role of the converter in a plug-in vehicle
- Two types of electric car engine
- Battery, electric vehicle power supply
- How to change the look of your electric car without a gearbox?
- What to remember about a lithium-ion battery?
- Amazing Electric Vehicle Braking Feature
- How do you recharge these new green cars?
- Can electrical models fail?
- How much does it cost to charge an electric vehicle?
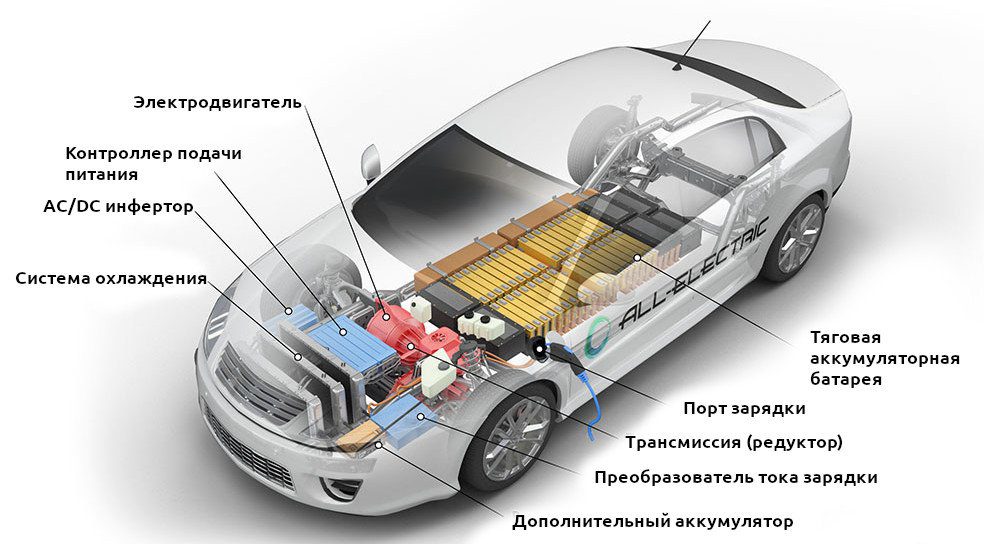
Forget pistons, gearboxes and belts: an electric car doesn't have them. These cars run much easier than a diesel or gasoline powered car. Automobile-Propre explains their mechanics in detail.
In appearance, an electric car is similar to any other vehicle. You have to look under the hood, but also under the floor, to see the differences. In place of an internal combustion engine using heat as energy, it uses electricity. To understand step by step how an electric car works, we will trace the path of electricity from the public grid to the wheel.
Recharging
It all starts with recharging. To refuel, the vehicle must be plugged into an outlet, wall box or charging station. The connection is made with a cable with suitable connectors. There are several of them, corresponding to the desired charging mode. For charging at home, work, or small public terminals, you usually use your own Type 2 cable. A cable is attached to the quick-detachable terminals that meets two standards: the European "Combo CCS" and "Chademo". Japanese. It may seem daunting at first, but in reality, as you get used to it, it will get easier. There is no risk of error: the connectors have different shapes and therefore cannot be inserted into the wrong slot.
Once connected, the alternating electrical current (AC) that circulates in the distribution network flows through the cable that is connected to the vehicle. He performs a series of checks through his on-board computer. In particular, it ensures that the current is of good quality, is correctly set and that the ground phase is sufficient to guarantee safe recharging. If everything is in order, the car passes electricity through the first on-board element: a converter, also called an “on-board charger”.
Renault Zoé Combo CCS standard charging port.
Converter
This body converts the alternating current of the mains into direct current (DC). Indeed, batteries store energy only in the form of direct current. To avoid this step and speed up recharging, some terminals themselves convert electricity to supply DC power directly to the battery. These are so-called "fast" and "ultra-fast" DC charging stations, similar to those found at motorway stations. These very expensive and cumbersome terminals are not designed to be installed in a private home.
Battery
In a battery, the current is distributed within its constituent elements. They come in the form of small piles or pockets gathered together. The amount of energy stored by the battery is expressed in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is equivalent to a “liter” of the fuel tank. Electricity flow or power is expressed in kilowatts "kW". Manufacturers may report "usable" capacity and / or "nominal" capacity. It's pretty simple: usable capacity is the amount of energy actually used by the vehicle. The difference between useful and nominal gives the headroom to extend battery life.
An example to understand: A 50 kWh battery that charges with 10 kW can be recharged in about 5 hours. Why "around"? Since it is above 80%, the batteries will automatically slow down the charging speed. Like a bottle of water that you fill from a tap, you must reduce the flow to avoid splashing.
The current accumulated in the battery is then sent to one or more electric motors. Rotation is carried out by the rotor of the motor under the influence of a magnetic field created in the stator (static coil of the motor). Before reaching the wheels, the movement usually passes through a gearbox with a fixed gear ratio to optimize the rotational speed.


Transmission of infection
Thus, an electric vehicle does not have a gearbox. This is not necessary, because the electric motor can operate without problems at speeds up to several tens of thousands of revolutions per minute. It rotates directly, as opposed to a heat engine, which must convert the linear motion of the pistons into circular motion through the crankshaft. It makes sense that an electric car has far fewer moving parts than a diesel locomotive. It does not require engine oil, does not have a timing belt and therefore requires much less maintenance.
Regenerative braking
Another advantage of battery-powered vehicles is that they can generate electricity. This is called "regenerative braking" or "B mode". Indeed, when an electric motor rotates "in a vacuum" without supplying current, it produces it. This happens every time you take your foot off the accelerator or brake pedal. In this way, the recovered energy is directly injected into the battery.
The most recent EV models even offer modes for selecting the power of this regenerative brake. In maximum mode, it strongly brakes the car without loading the discs and pads, and at the same time saves several kilometers of power reserve. In diesel locomotives, this energy is simply wasted and accelerates the wear of the braking system.
An electric vehicle's dashboard often has a meter showing the power of the regenerative braking.
Breaking
Therefore, technical breakdowns of electric vehicles are less common. However, it can happen that you run out of energy after waiting poorly for the driver, like in a gasoline or diesel car. In this case, the vehicle will warn in advance about a low battery level, usually 5 to 10% remaining. One or more messages are displayed on the dashboard or center screen and alert the user.
Depending on the model, you can drive several tens of additional kilometers to the charging point. Engine power is sometimes limited in order to reduce consumption and therefore widen the range. In addition, the "turtle mode" is automatically activated: the car gradually slows down to a complete stop. Signals on the dashboard urge the driver to find a place to stop while waiting for a tow truck.
A small lesson in mechanics on an electric car
To make things easier, tell yourself that instead of a heat engine, your car has an electric motor. This energy source is in the battery.
You may have noticed that the electric vehicle does not have a clutch. In addition, the driver only has to press the accelerator pedal to obtain a constant current. Direct current is converted into alternating current due to the action of the converter. It is also what generates the electromagnetic field through your motor's moving copper coil.
Your motor contains one or more fixed magnets. They oppose their magnetic field to the field of the coil, which sets them in motion and makes the motor run.
Informed drivers might have noticed that there was no gearbox either. In an electric vehicle, this is the engine axle, which, without an intermediary, includes the axles of the driving wheels. Therefore, the car does not need pistons.
Finally, so that all these "devices" are perfectly synchronized with each other, the on-board computer checks and modulates the developed power. Therefore, depending on the situation, the engine of your car adjusts its power in accordance with the ratio of revolutions per minute. This is often less than on combustion vehicles.
Charging: where it all starts
In order for your car to be able to drive your car, you need to plug it into a power outlet or charging station. This can be done using a cable with suitable connectors. There are different models to suit different charging modes. If you want to find your new car at home, work, or public charging stations, you will need a Type 2 connector. Use a “Combo CCS” or “Chedemo” cable to use the quick terminals.
During charging, an alternating electric current flows through the cable. Your car goes through several checks:
- You need a high-quality and well-tuned current;
- Grounding must provide safe charging.
After checking these two points, the car gives permission for electricity to flow through the converter.
The important role of the converter in a plug-in vehicle
The converter "converts" the alternating current flowing through the terminal into direct current. This step is necessary because EV batteries can only store DC current. However, keep in mind that you can find terminals that directly convert AC to DC. They send their "product" directly to your vehicle's battery. These charging stations provide fast or super fast charging, depending on the model. On the other hand, if you were to equip yourself with these terminals to charge your new electric car, know that they are very expensive and impressive, and therefore they are installed, in any case, at the moment only in public places (for example, for example, recreation areas on highways).
Two types of electric car engine
An electric vehicle can be equipped with two types of motors: a synchronous motor or an asynchronous motor.
An asynchronous motor generates a magnetic field when it rotates. To do this, he relies on the stator, which receives electricity. In this case, the rotor is constantly rotating. The asynchronous motor is mainly installed in vehicles that make long journeys and move at high speeds.
In an induction motor, the rotor itself takes over the role of an electromagnet. Therefore, it actively creates a magnetic field. The rotor speed depends on the frequency of the current received by the motor. It is the ideal engine type for city driving, frequent stops and slow starts.
Battery, electric vehicle power supply
The battery does not contain a few liters of gasoline, but kilowatt-hours (kWh). The consumption that the battery can provide is expressed in kilowatts (kW).
The battery of all electric vehicles consists of thousands of cells. When current passes through them, it is distributed among these thousands of components. To give you a more concrete idea of these cells, think of them as piles or pockets connected to each other.
Once the current passes through the batteries in the battery, it is sent to your car's electric motor (s). At this stage, the stator sees the generated magnetic field. It is the latter that drives the rotor of the engine. Unlike a heat engine, it prints its motion on wheels. Depending on the car model, it can transmit its motion to the wheels through a gearbox. It only has one report, which increases its rotation speed. It is he who finds the best ratio between torque and rotational speed. Good to know: the rotor speed directly depends on the frequency of the current flowing through the motor.
For information, be aware that new rechargeable batteries use lithium. The power reserve of an electric vehicle ranges on average from 150 to 200 km. New batteries (lithium-air, lithium-sulfur, etc.) will significantly increase the battery capacity of these vehicles over the next few years.
How to change the look of your electric car without a gearbox?
This type of vehicle has an engine that can rotate several tens of thousands of revolutions per minute! Thus, you do not need a gearbox to change the cruising speed.
An all-electric vehicle's engine transmits rotation directly to the wheels.
What to remember about a lithium-ion battery?
If you are seriously considering buying an electric vehicle, here is some important information about lithium-ion batteries.
One of the advantages of this battery is its low self-discharge rate. Concretely, this means that if you do not use your car for a year, it will lose less than 10% of its carrying capacity.
Another significant advantage: this type of battery requires virtually no maintenance. On the other hand, it must be systematically equipped with a protection and regulation circuit, BMS.
Battery charging times may vary depending on the model and manufacturer of your vehicle. So, to find out how long your car will stay plugged in, refer to its battery density and the charging mode you choose. The charge will last approximately 10 hours. Plan ahead and expect!
If you don’t want to, or don’t have time to plan ahead, connect your car to a charging station or wall box: charging time will be cut in half!
Another alternative for those in a hurry: opt for a "quick charge" over a full charge: your car will be charged up to 80% in just 30 minutes!
Good to know: In most cases, car batteries are located under the floor. Their power ranges from 15 to 100 kWh.
Amazing Electric Vehicle Braking Feature
You may not know it yet, but driving an electric car allows you to generate electricity! Car manufacturers have endowed their electric vehicles with "superpower": when your engine runs out of electricity (for example, when your foot is lifted off the accelerator pedal or when you brake), it does it! This energy goes straight to your battery.
All modern electric vehicles have several modes that allow their drivers to select one or another power of regenerative braking.
How do you recharge these new green cars?
Do you live in a small house? In this case, you can charge the car right at home.
Charge your car at home
To charge your car at home, take the cable that was sold with your car and plug it into a standard power outlet. The one from which you are used to charging your smartphone will do! However, be aware of the potential risk of overheating. The amperage is often limited to 8 or 10A to avoid any accidents. Plus, if you need a full charge to keep your small EV running, it's best to schedule it to turn on at night. This is because lower current results in longer charging times.
Another solution is to install a wall box. It costs between € 500 and € 1200, but you can request a 30% tax credit. You will get faster charging and higher current (approximately 16A).
Charge your car at the public terminal
If you live in an apartment, cannot connect your car at home, or are traveling, you can connect your car to a public charging station. You will find it all in specialized applications or on the Internet. Know ahead of time: You may need a kiosk-access card issued by the brand or community that installed the kiosk in question.
The transmitted power and therefore the charging time also differ depending on the different devices.
Can electrical models fail?
These greener vehicles also have the advantage of less breakage. It is logical, since they have fewer components!
However, these vehicles may experience power outages. Indeed, as far as gasoline or diesel vehicles are concerned, if you don't expect enough "fuel" in your "tank", your car will not be able to move forward!
Your all-electric vehicle will send you a warning message when the battery level becomes particularly low. Know that you have 5 to 10% of your energy left! Warnings appear on the dashboard or center screen.
Rest assured, you will (not necessarily) be on the edge of a deserted road. These clean vehicles can carry you anywhere from 20 to 50 km - it's time to get to the charging point.
After this distance, your car reduces engine power and you should feel a gradual deceleration. If you keep driving, you will see other warnings. Then the Turtle mode is activated when your car is really out of breath. Your top speed will not exceed ten kilometers, and if you (really) don't want to be on the edge of a lonely road, you will definitely have to park or charge your battery.
How much does it cost to charge an electric vehicle?
The top-up cost depends on several factors. Please note that charging your car at home will cost you less than charging at a public terminal. Take Renault Zoé for example. Charging in Europe will cost around 3,71 euros, or just 4 cents per kilometer!
With a public terminal, expect around € 6 to cover 100 km.
You will also find 22kW terminals free of charge for a period of time before they become paid.
The most expensive are undoubtedly the “fast charging” stations. This is due to the fact that they require a lot of power and this requires a certain infrastructure. If we continue with our Renault Zoé example, 100 km of autonomy will cost you € 10,15.
Finally, know that in general, an electric car will cost you less than a diesel locomotive. On average, it costs 10 euros to travel 100 km.

