How does a brake master cylinder work?
Content
The hydraulic system of a car's brake drive begins with a device that must convert the mechanical force on the pedals into working fluid pressure. This role is played by a hydraulic cylinder, named after the place it occupies as the “main”. At the same time, all others are not secondary, they are called workers or executive.
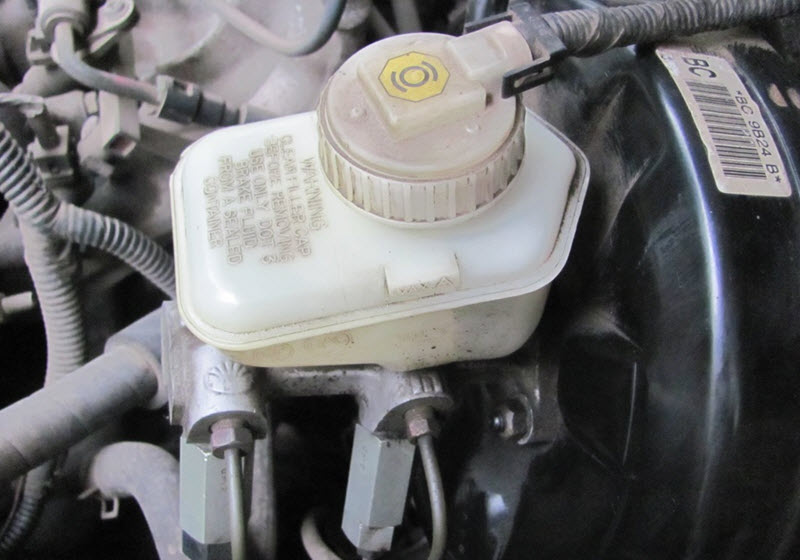

The purpose of the GTZ in the car
Braking starts with pressing the pedal. For now, you can not consider all sorts of smart driver assistance systems that do an excellent job without his participation.
The maximum that will support the leg of a person who wishes to slow down the car is a vacuum brake booster (VUT), located between the pedal assembly and the first hydraulic device in the chain ending with the brake pads.
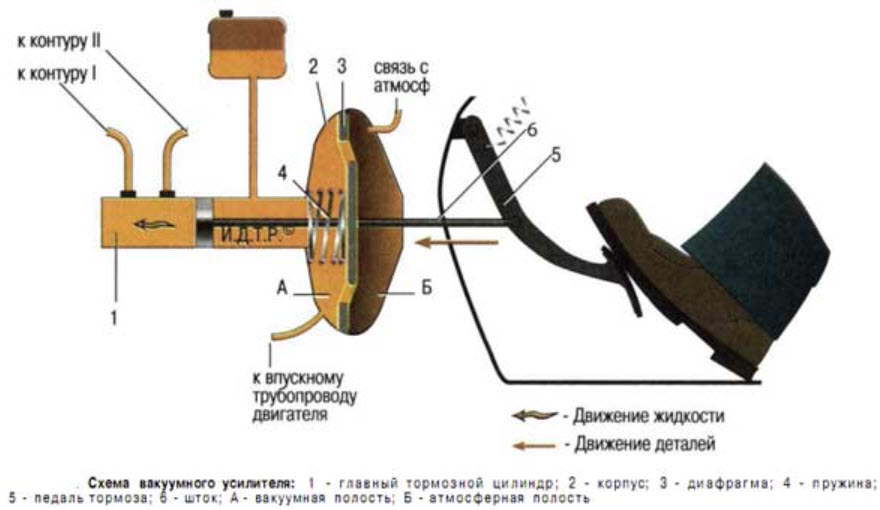
The joint action of muscle force and the atmosphere through the WUT membrane should increase the pressure in the entire hydraulic system. If the ABS valves and pumps do not intervene, then this pressure is the same at any point.
Liquids are incompressible, which is why they are used in the brakes of cars. Prior to this, no less incompressible solids were used in the form of rods and cables for driving the pads of the first machines.
Direct pressure is created precisely by the piston of the main brake cylinder (GTZ). Due to incompressibility, it grows very quickly, each driver felt how the pedal hardens under the foot after choosing its free play.
Releasing pressure after releasing the pedal and replenishing the lines with liquid when necessary are also functions of the GTZ.
Principle of operation
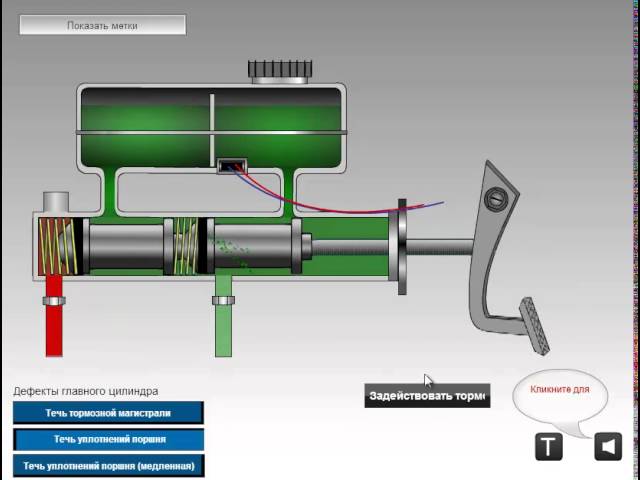
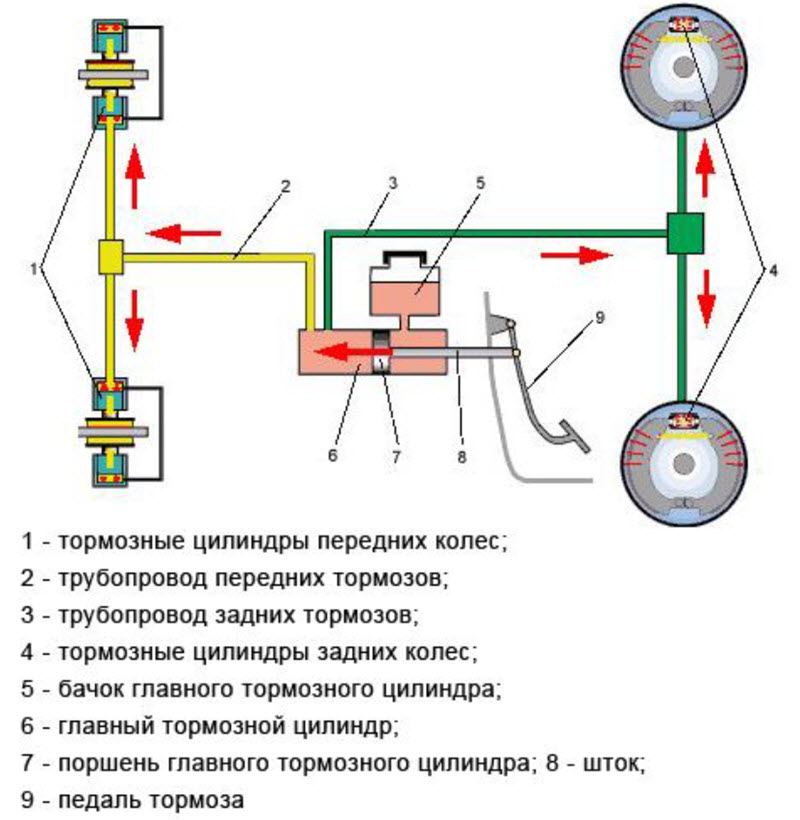
Single-circuit GTZ, where there was only one piston, are no longer found in cars, so it is worth considering only a double-circuit one. It is distinguished by the presence of two pistons, each of which is responsible for the pressure in its branch of the system.
Thus, the brakes are duplicated, which is required for safety. If a fluid leak occurs, then the branch remaining in good condition will allow you to stop the car without applying the parking brake and other emergency techniques.
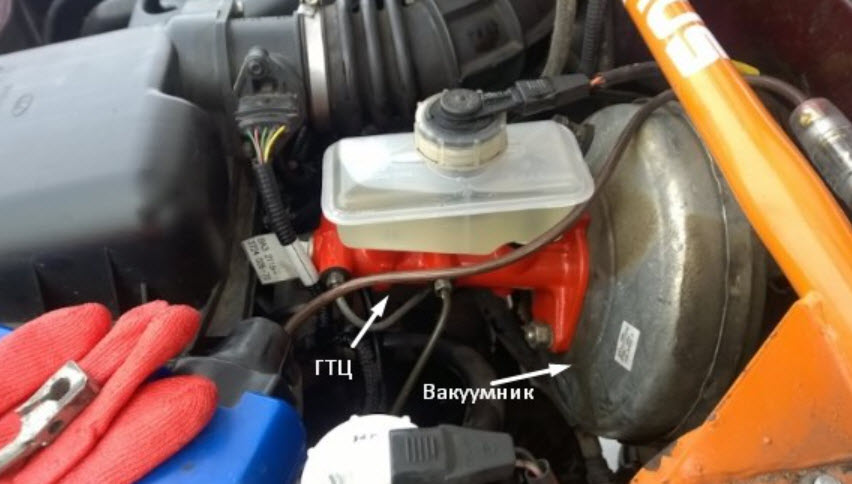

The first piston is directly connected to the pedal stem. Starting to move forward, it closes the bypass and compensation holes, after which the force through the liquid volume will be immediately transferred to the pads of the primary circuit. They will press against the discs or drums, and deceleration will begin with the help of friction forces.
Interaction with the second piston is made through a short rod with a return spring and the primary circuit fluid. That is, the pistons are connected in series, hence such GTZs are called tandem. The piston of the second circuit works similarly to its branch of the system.
Typically, the working wheel cylinders work diagonally, that is, one front and one rear wheel is connected to each circuit. This is done with the aim of in any case to use the front, more efficient brakes, at least partially.
But there are cars in which, for structural reasons, one circuit works only on the front wheels, and the second on all four, for which additional sets of wheel cylinders are used.
Устройство
The GTC includes:
- housing with fittings supplying liquid from the supply tank and draining to the lines of the working cylinders;
- pistons of the first and second circuits;
- sealing rubber cuffs located in the grooves of the pistons;
- return springs that compress when the pistons move;
- anther covering the place of entry of the rod from the VUT or the pedal into the recess of the back side of the first piston;
- a screw plug that closes the cylinder from the end, by unscrewing which you can assemble or disassemble the cylinder.
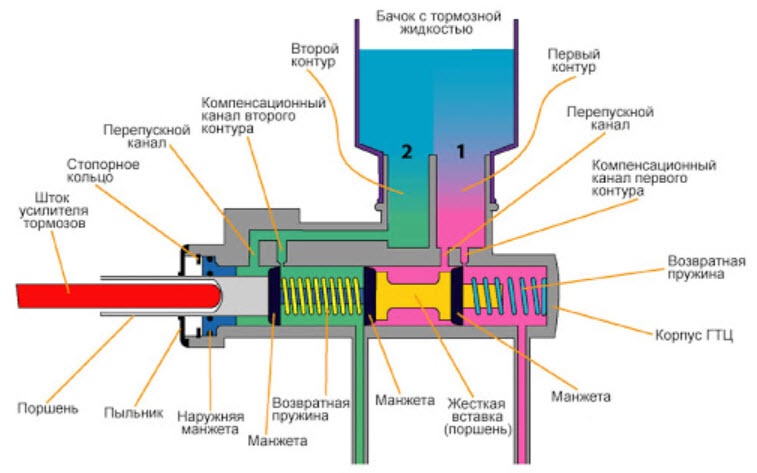
Compensation holes are located in the upper part of the cylinder body, they can overlap when the pistons move, separating the high pressure cavity and the supply tank with a supply of fluid.
The tank itself is usually attached directly to the cylinder through sealing cuffs, although it can be moved to another place in the engine compartment, and the connection is made through low pressure hoses.
Major faults
Breakdowns in the master brake cylinder are practically excluded, and all malfunctions are associated with the passage of fluid through the seals:
- wear and aging of the sealing collars on the rod side, the liquid goes into the cavity of the vacuum booster or, in its absence, into the passenger compartment, to the driver's feet;
- similar violations of the cuffs on the pistons, the cylinder starts to bypass one of the circuits, the pedal fails, braking worsens;
- wedging of the pistons due to corrosion of themselves and the cylinder mirror, as well as loss of elasticity of the return springs;
- an increase in stroke and a decrease in pedal stiffness during braking due to air in the brake line.
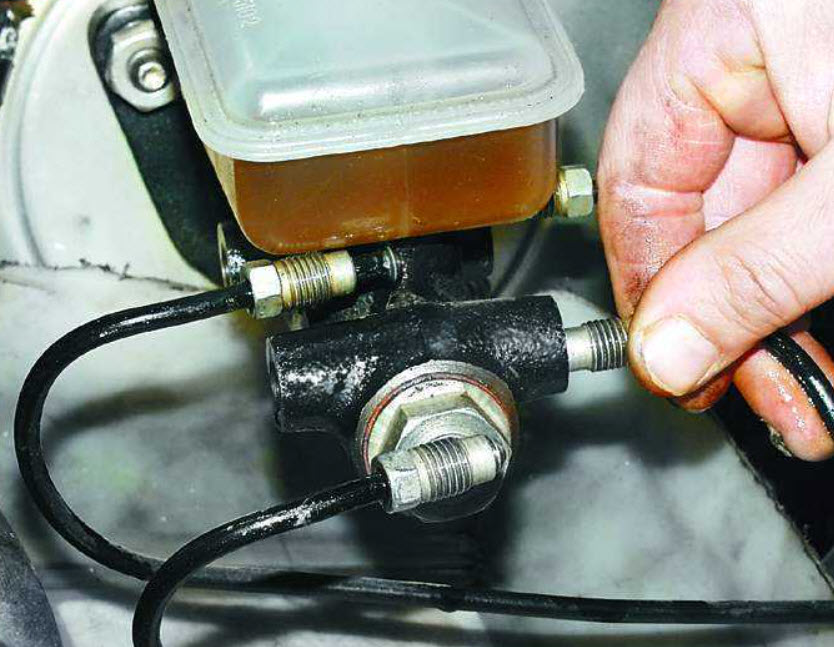

For some cars, repair kits with pistons and cuffs are still preserved in the spare parts catalogs. As well as recommendations for removing cylinder surface defects with sandpaper.
In practice, this occupation does not make much sense, it is unlikely that it will be possible to significantly extend the resource of the GTZ that has worked out, and driving with an unreliable brake hydraulic cylinder, which is not in vain called the main one, is unpleasant and dangerous. Therefore, in the vast majority of cases, the cylinder is replaced with a new assembly.
How to check and bleed the master brake cylinder
The GTZ is checked for symptoms of a problem with the brakes. Usually this is a failing or soft pedal with increased travel. If the check of all working cylinders and hoses does not show signs of a malfunction, then it is concluded in the main one, which should be replaced.
You can roughly estimate the performance by loosening the brake pipe fittings from the GTZ in turn and observing the intensity of leaks when you press the pedal. But there is no particular need for this, the GTZ that has worked is replaced at the slightest suspicion, safety is more expensive.
When replacing the cylinder, it is filled with fresh liquid, and excess air goes into the tank through the bypass holes, so there is no special need for a separate pumping. It is enough to repeatedly press the pedal with a general pumping of the system through the valves of the working mechanisms.
If, for some reason, it is also necessary to pump the GTZ, then for this, working together, the output fittings are successively blocked, except for one. Air escapes through it by opening it before pressing the pedal and closing it before releasing it.
There is no need to even disconnect the tubes, it is enough to “undermine” them by slightly loosening the union nut. In this case, it is necessary to monitor a sufficient amount of liquid in the tank.
The safety of the cylinder and ensuring its long service life is ensured by the timely scheduled replacement of the brake fluid with flushing the system. Over time, water gets there, taken by a hygroscopic composition from the air.
As a result, not only does the boiling point drop, which is dangerous, but corrosion of the surfaces of pistons and cylinders begins, and the cuffs lose their elasticity. The procedure is recommended to be carried out every two years.
