How the ignition coil works
How it works
Your car's ignition system has a special element that provides a spark to ignite the fuel mixture in the cylinders of the power plant. This happens in the ignition coil, which converts the low-voltage on-board voltage into a high-voltage pulse, reaching tens of thousands of volts.
Устройство
Thank you for the diagram site automn.ru
The generation of a high-voltage pulse is the main purpose of this part, since the on-board electronics are completely incapable of delivering such voltages. Ready pulse is applied to the spark plugs.
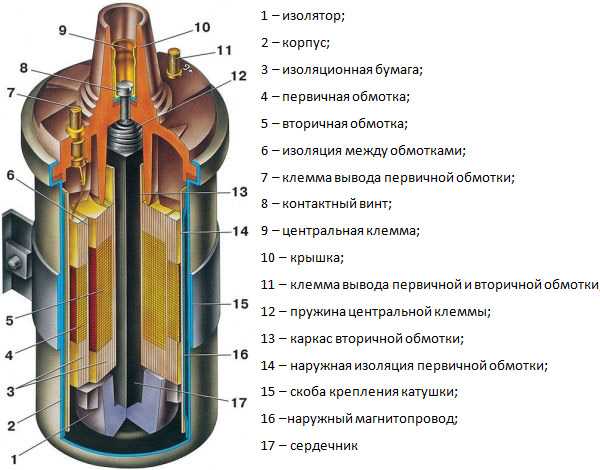
The generation of a pulse of such high power is achieved due to the design itself. According to its design, it is a transformer in an insulated case, inside which there are two windings, primary and secondary with a steel core.
One of the windings - low-voltage - is used to receive voltage from a generator or battery. This winding consists of coils of copper wire with a large cross section. The wide cross section does not allow applying a sufficiently high number of turns, and there are no more than 150 of them in the primary winding. To prevent potential voltage surges and the occurrence of a short circuit, a protective insulating layer is applied to the wire. The ends of the primary winding are displayed on the cover of the coil, where wiring with a voltage of 12 volts is connected to them.
The secondary winding is most often located inside the primary. It is a wire with a small cross section, due to which a large number of turns is provided - from 15 to 30 thousand. One end of the secondary winding is connected to the "minus" of the primary winding, and the second output is "plus" connected to the central output. It is here that high voltage is created, which is fed directly to the spark plugs.
How it works
The power supply applies low voltage to the turns in the primary winding, which creates a magnetic field. This field affects the secondary winding. As the breaker periodically "cuts off" this voltage, the magnetic field is reduced and converted into an electromotive force (EMF) in the turns of the ignition coil. If you recall the school physics course, the EMF value that is formed in the coil will be the higher the more turns of the winding. Since the secondary winding contains a large number of turns (recall, there are up to 30 thousand of them), the impulse formed in it will reach a voltage of tens of thousands of volts. The impulse is fed through special high-voltage wires straight to the spark plug. This pulse is capable of causing a spark between the electrodes of the spark plug. The combustible mixture comes out and ignites.
The core located inside further enhances the magnetic field, due to which the output voltage reaches its maximum value. And the housing is filled with transformer oil to cool the windings from high current heating. The coil itself is sealed and cannot be repaired if it breaks.
In older car models, a high-voltage impulse was applied immediately to all candles through the ignition distributor. But this principle of operation did not justify itself and now the ignition coils (It happens that they are called candles) are installed on each candle separately.
Types of ignition coils
They are individual and double-ended.
Two-terminal are used in systems with direct supply to the candle. In their design, they differ from those described above (general) only in the presence of two high-voltage terminals, which can supply a spark to two candles at once. Although in practice this does not happen. The compression stroke can occur simultaneously in only one of the cylinders, and therefore the second spark passes “idle”. This principle of operation eliminates the need for a special spark distributor, however, the spark will be supplied only to two of the four cylinders. Therefore, four-pin coils are used in such cars: these are just two two-pin coils closed in a single block.
Individual ones are used in systems with electronic ignition. Compared to a two-terminal coil, here the primary winding is located inside the secondary. Such coils are connected directly to the candles, and the impulse passes with virtually no power loss.
Operating Tips
- Do not leave the ignition on for a long time without starting the internal combustion engine. This reduces the running time
- We recommend periodically cleaning the coils and preventing water from getting on its surface. Check wire fastenings, especially high-voltage ones.
- Never disconnect coil wires with the ignition on.

